
This journal publishes original research papers of reasonable permanent intellectual value, in the areas of computer modeling in engineering & Sciences, including, but not limited to computational mechanics, computational materials, computational mathematics, computational physics, computational chemistry, and computational biology, pertinent to solids, fluids, gases, biomaterials, and other continua spanning from various spatial length scales (quantum, nano, micro, meso, and macro), and various time scales (picoseconds to hours) are of interest. Papers which deal with multi-physics problems, as well as those which deal with the interfaces of mechanics, chemistry, and biology, are particularly encouraged. Novel computational approaches and state-of-the-art computation algorithms, such as soft computing, artificial intelligence-based machine learning methods, and computational statistical methods are welcome.
Science Citation Index (Web of Science): 2024 Impact Factor 2.5; Current Contents: Engineering, Computing & Technology; Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 4.4; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.693; RG Journal Impact (average over last three years); Engineering Index (Compendex); Applied Mechanics Reviews; Cambridge Scientific Abstracts: Aerospace and High Technology, Materials Sciences & Engineering, and Computer & Information Systems Abstracts Database; CompuMath Citation Index; INSPEC Databases; Mathematical Reviews; MathSci Net; Mechanics; Science Alert; Science Navigator; Zentralblatt fur Mathematik; Portico, etc...
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074388 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Enhanced Computational Methods in Engineering and Physical Science)
Abstract Inverse design of advanced materials represents a pivotal challenge in materials science. Leveraging the latent space of Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) for material optimization has emerged as a significant advancement in the field of material inverse design. However, VAEs are inherently prone to generating blurred images, posing challenges for precise inverse design and microstructure manufacturing. While increasing the dimensionality of the VAE latent space can mitigate reconstruction blurriness to some extent, it simultaneously imposes a substantial burden on target optimization due to an excessively high search space. To address these limitations, this study adopts a Variational… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.071052 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Deep Learning for Energy Systems)
Abstract Predicting the behavior of renewable energy systems requires models capable of generating accurate forecasts from limited historical data, a challenge that becomes especially pronounced when commissioning new facilities where operational records are scarce. This review aims to synthesize recent progress in data-efficient deep learning approaches for addressing such “cold-start” forecasting problems. It primarily covers three interrelated domains—solar photovoltaic (PV), wind power, and electrical load forecasting—where data scarcity and operational variability are most critical, while also including representative studies on hydropower and carbon emission prediction to provide a broader systems perspective. To this end, we examined… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074768 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Emerging Artificial Intelligence Technologies and Applications-II)
Abstract The integration of machine learning (ML) into geohazard assessment has successfully instigated a paradigm shift, leading to the production of models that possess a level of predictive accuracy previously considered unattainable. However, the black-box nature of these systems presents a significant barrier, hindering their operational adoption, regulatory approval, and full scientific validation. This paper provides a systematic review and synthesis of the emerging field of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) as applied to geohazard science (GeoXAI), a domain that aims to resolve the long-standing trade-off between model performance and interpretability. A rigorous synthesis of 87 foundational… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074902 - 29 January 2026
Abstract Network-on-Chip (NoC) systems are progressively deployed in connecting massively parallel megacore systems in the new computing architecture. As a result, application mapping has become an important aspect of performance and scalability, as current trends require the distribution of computation across network nodes/points. In this paper, we survey a large number of mapping and scheduling techniques designed for NoC architectures. This time, we concentrated on 3D systems. We take a systematic literature review approach to analyze existing methods across static, dynamic, hybrid, and machine-learning-based approaches, alongside preliminary AI-based dynamic models in recent works. We classify them… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.075741 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: The Collection of the Latest Reviews on Advances and Challenges in AI)
Abstract Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), as a deep learning framework specifically designed for graph-structured data, have achieved deep representation learning of graph data through message passing mechanisms and have become a core technology in the field of graph analysis. However, current reviews on GNN models are mainly focused on smaller domains, and there is a lack of systematic reviews on the classification and applications of GNN models. This review systematically synthesizes the three canonical branches of GNN, Graph Convolutional Network (GCN), Graph Attention Network (GAT), and Graph Sampling Aggregation Network (GraphSAGE), and analyzes their integration pathways More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.073789 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Engineering Applications of Discrete Optimization and Scheduling Algorithms)
Abstract Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) have become foundational in numerous real-world applications, ranging from environmental monitoring and industrial automation to healthcare systems and smart city development. As these networks continue to grow in scale and complexity, the need for energy-efficient, scalable, and robust communication protocols becomes more critical than ever. Metaheuristic algorithms have shown significant promise in addressing these challenges, offering flexible and effective solutions for optimizing WSN performance. Among them, the Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) algorithm has attracted growing attention due to its simplicity, fast convergence, and strong global search capabilities. Accordingly, this survey provides… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075980 - 29 January 2026
Abstract Peridynamics (PD) demonstrates unique advantages in addressing fracture problems, however, its nonlocality and meshfree discretization result in high computational and storage costs. Moreover, in its engineering applications, the computational scale of classical GPU parallel schemes is often limited by the finite graphics memory of GPU devices. In the present study, we develop an efficient particle information management strategy based on the cell-linked list method and on this basis propose a subdomain-based GPU parallel scheme, which exhibits outstanding acceleration performance in specific compute kernels while significantly reducing graphics memory usage. Compared to the classical parallel scheme,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074898 - 29 January 2026
Abstract In this work, a computational modelling and analysis framework is developed to investigate the thermal buckling behavior of doubly-curved composite shells reinforced with graphene-origami (G-Ori) auxetic metamaterials. A semi-analytical formulation based on the First-Order Shear Deformation Theory (FSDT) and the principle of virtual displacements is established, and closed-form solutions are derived via Navier’s method for simply supported boundary conditions. The G-Ori metamaterial reinforcements are treated as programmable constructs whose effective thermo-mechanical properties are obtained via micromechanical homogenization and incorporated into the shell model. A comprehensive parametric study examines the influence of folding geometry, dispersion arrangement, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.073757 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning Based Computational Mechanics)
Abstract Patient-specific finite element analysis (FEA) is a promising tool for noninvasive quantification of cardiac and vascular structural mechanics in vivo. However, inverse material property identification using FEA, which requires iteratively solving nonlinear hyperelasticity problems, is computationally expensive which limits the ability to provide timely patient-specific insights to clinicians. In this study, we present an inverse material parameter identification strategy that integrates deep neural networks (DNNs) with FEA, namely inverse DNN-FEA. In this framework, a DNN encodes the spatial distribution of material parameters and effectively regularizes the inverse solution, which aims to reduce susceptibility to local optima… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075706 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Structural Reliability and Computational Solid Mechanics: Modeling, Simulation, and Uncertainty Quantification)
Abstract In this work, the Hierarchical Quadrature Element Method (HQEM) formulation of geometrically exact shells is proposed and applied for geometrically nonlinear analyses of both isotropic and laminated shells. The stress resultant formulation is developed within the HQEM framework, consequently significantly simplifying the computations of residual force and stiffness matrix. The present formulation inherently avoids shear and membrane locking, benefiting from its high-order approximation property. Furthermore, HQEM’s independent nodal distribution capability conveniently supports local p-refinement and flexibly facilitates mesh generation in various structural configurations through the combination of quadrilateral and triangular elements. Remarkably, in lateral buckling… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.075351 - 29 January 2026
Abstract Concrete-filled steel tubes (CFST) are widely utilized in civil engineering due to their superior load-bearing capacity, ductility, and seismic resistance. However, existing design codes, such as AISC and Eurocode 4, tend to be excessively conservative as they fail to account for the composite action between the steel tube and the concrete core. To address this limitation, this study proposes a hybrid model that integrates XGBoost with the Pied Kingfisher Optimizer (PKO), a nature-inspired algorithm, to enhance the accuracy of shear strength prediction for CFST columns. Additionally, quantile regression is employed to construct prediction intervals for… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074029 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Modeling and Simulation of Explosive Effects on Structural Elements and Materials)
Abstract Unbonded post-tensioned (PT) concrete systems are widely used in safety-critical structures, yet modeling practices for prestress implementation and tendon-concrete interaction remain inconsistent. This study investigates the effects of sheath (duct) implementation and confinement assumptions through nonlinear finite element analysis. Four modeling cases were defined, consisting of an explicit sheath without tendon-concrete confinement (S) and three no-sheath variants with different confinement levels (X, N, A). One-way beams and two-way panels were analyzed, and panel blast responses were validated against experimental results. In both beams and panels, average initial stress levels were similar across models, through local More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074787 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Modeling and Simulation for Sustainable Construction Materials and Structures)
Abstract Conventional low-carbon concrete design approaches have often overlooked carbonation durability and the progressive loss of cover caused by surface scaling, both of which can increase the long-term risk of reinforcement corrosion. To address these limitations, this study proposes an improved design framework for low-carbon slag concrete that simultaneously incorporates carbonation durability and cover scaling effects into the mix proportioning process. Based on experimental data, a linear predictive model was developed to estimate the 28-day compressive strength of slag concrete, achieving a correlation coefficient of R = 0.87711 and a root mean square error (RMSE) of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.069691 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Meta-heuristic Algorithms in Materials Science and Engineering)
Abstract Optimization is the key to obtaining efficient utilization of resources in structural design. Due to the complex nature of truss systems, this study presents a method based on metaheuristic modelling that minimises structural weight under stress and frequency constraints. Two new algorithms, the Red Kite Optimization Algorithm (ROA) and Secretary Bird Optimization Algorithm (SBOA), are utilized on five benchmark trusses with 10, 18, 37, 72, and 200-bar trusses. Both algorithms are evaluated against benchmarks in the literature. The results indicate that SBOA always reaches a lighter optimal. Designs with reducing structural weight ranging from 0.02%… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.073555 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Swarm and Metaheuristic Optimization for Applied Engineering Application)
Abstract Accurate prediction of concrete compressive strength is fundamental for optimizing mix designs, improving material utilization, and ensuring structural safety in modern construction. Traditional empirical methods often fail to capture the non-linear relationships among concrete constituents, especially with the growing use of supplementary cementitious materials and recycled aggregates. This study presents an integrated machine learning framework for concrete strength prediction, combining advanced regression models—namely CatBoost—with metaheuristic optimization algorithms, with a particular focus on the Somersaulting Spider Optimizer (SSO). A comprehensive dataset encompassing diverse mix proportions and material types was used to evaluate baseline machine learning models,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075792 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Enhanced Computational Mechanics and Structural Optimization Methods)
Abstract Optimization problems are prevalent in various fields of science and engineering, with several real-world applications characterized by high dimensionality and complex search landscapes. Starfish optimization algorithm (SFOA) is a recently optimizer inspired by swarm intelligence, which is effective for numerical optimization, but it may encounter premature and local convergence for complex optimization problems. To address these challenges, this paper proposes the multi-strategy enhanced crested porcupine-starfish optimization algorithm (MCPSFOA). The core innovation of MCPSFOA lies in employing a hybrid strategy to improve SFOA, which integrates the exploratory mechanisms of SFOA with the diverse search capacity of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
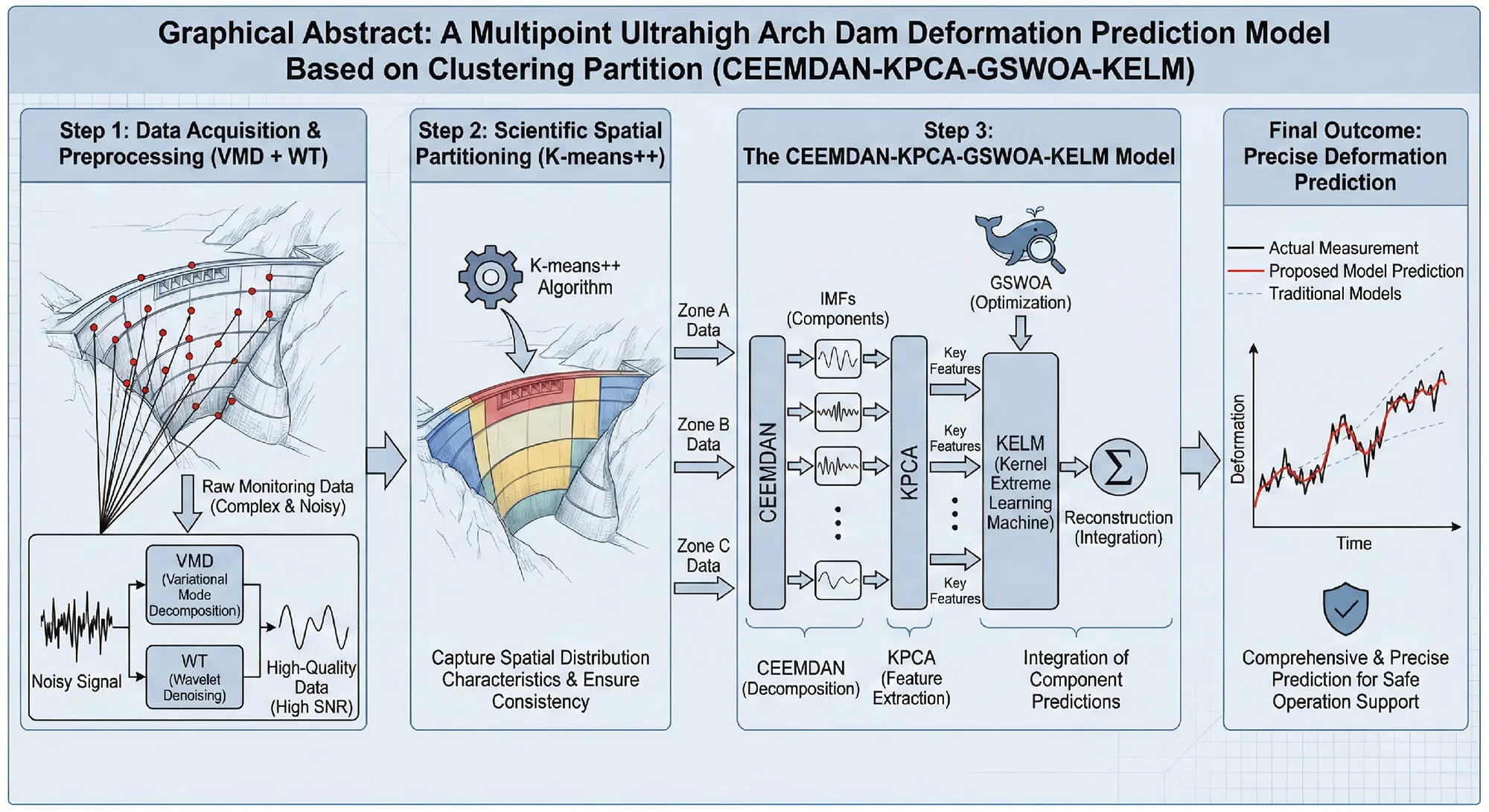
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.074757 - 29 January 2026
Abstract Deformation prediction for extra-high arch dams is highly important for ensuring their safe operation. To address the challenges of complex monitoring data, the uneven spatial distribution of deformation, and the construction and optimization of a prediction model for deformation prediction, a multipoint ultrahigh arch dam deformation prediction model, namely, the CEEMDAN-KPCA-GSWOA-KELM, which is based on a clustering partition, is proposed. First, the monitoring data are preprocessed via variational mode decomposition (VMD) and wavelet denoising (WT), which effectively filters out noise and improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the data, providing high-quality input data for subsequent prediction… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.069854 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Meshless Methods and Its Applications in Porous Media Problems)
Abstract A hybrid model combining Fully Non-Linear Potential Flow Theory (FNPT) based on the Finite Element Method (FEM) and the Unified Navier-Stokes equation, using the 3D Improved Meshless Local Petrov Galerkin method with Rankine Source (IMLPG_R), is developed to study wave interactions with a porous layer. In previous studies, the above formulations are applied to wave interaction with fixed cylindrical structures. The present study extends this framework by integrating a unified governing equation within the hybrid modeling approach to capture the dynamics of wave interaction with porous media. The porous layers are employed to replicate the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.070435 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Applications of Modelling and Simulation in Nanofluids)
Abstract The present investigation inspects the unsteady, incompressible MHD-induced flow of a ternary hybrid nanofluid made of
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074680 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Intelligent Systems for Solving Complex Engineering Problems: Principles and Applications-III)
Abstract Fluid dynamic research on rectangular and trapezoidal fins is aimed at increasing heat transfer by means of large surfaces. The trapezoidal cavity form is compared with its thermal and flow performance, and it is revealed that trapezoidal fins tend to be more efficient, particularly when material optimization is critical. Motivated by the increasing need for sustainable energy management, this work analyses the thermal performance of inclined trapezoidal and rectangular porous fins utilising a unique hybrid nanofluid. The effectiveness of nanoparticles in a working fluid is primarily determined by their thermophysical properties; hence, optimising these properties… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.071817 - 29 January 2026
Abstract The composite material layering process has attracted considerable attention due to its production advantages, including high scalability and compatibility with a wide range of raw materials. However, changes in process conditions can lead to degradation in layer quality and non-uniformity, highlighting the need for real-time monitoring to improve overall quality and efficiency. In this study, an AI-based monitoring system was developed to evaluate layer width and assess quality in real time. Three deep learning models Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (R-CNN), You Only Look Once version 8 (YOLOv8), and Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) were… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074066 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Incomplete Data Test, Analysis and Fusion Under Complex Environments)
Abstract In data communication, limited communication resources often lead to measurement bias, which adversely affects subsequent system estimation if not effectively handled. This paper proposes a novel bias calibration algorithm under communication constraints to achieve accurate system states of the interested system. An output-based event-triggered scheme is first employed to alleviate transmission burden. Accounting for the limited-communication-induced measurement bias, a novel bias calibration algorithm following the Kalman filtering line is developed to restrain the effect of the measurement bias on system estimation, thereby achieving accurate system state estimates. Subsequently, the Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) implementation More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074679 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Monitoring of Rotating Machinery: Diagnostic and Prognostic Paradigms)
Abstract Motor imbalance is a critical failure mode in rotating machinery, potentially causing severe equipment damage if undetected. Traditional vibration-based diagnostic methods rely on direct sensor contact, leading to installation challenges and measurement artifacts that can compromise accuracy. This study presents a novel radar-based framework for non-contact motor imbalance detection using 24 GHz continuous-wave radar. A dataset of 1802 experimental trials was sourced, covering four imbalance levels (0, 10, 20, 30 g) across varying motor speeds (500–1500 rpm) and load torques (0–3 Nm). Dual-channel in-phase and quadrature radar signals were captured at 10,000 samples per second… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.073808 - 29 January 2026
Abstract Optimization algorithms are crucial for solving NP-hard problems in engineering and computational sciences. Metaheuristic algorithms, in particular, have proven highly effective in complex optimization scenarios characterized by high dimensionality and intricate variable relationships. The Mountain Gazelle Optimizer (MGO) is notably effective but struggles to balance local search refinement and global space exploration, often leading to premature convergence and entrapment in local optima. This paper presents the Improved MGO (IMGO), which integrates three synergistic enhancements: dynamic chaos mapping using piecewise chaotic sequences to boost exploration diversity; Opposition-Based Learning (OBL) with adaptive, diversity-driven activation to speed up… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.069733 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Deep Learning for Energy Systems)
Abstract Accurate wind speed prediction is crucial for stabilizing power grids with high wind energy penetration. This study presents a novel machine learning model that integrates clustering, deep learning, and transfer learning to mitigate accuracy degradation in 24-h forecasting. Initially, an optimized DB-SCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise) algorithm clusters wind fields based on wind direction, probability density, and spectral features, enhancing physical interpretability and reducing training complexity. Subsequently, a ResNet (Residual Network) extracts multi-scale patterns from decomposed wind signals, while transfer learning adapts the backbone network across clusters, cutting training time by over… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.073533 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Methods Applied to Energy Systems)
Abstract Sustainable energy systems will entail a change in the carbon intensity projections, which should be carried out in a proper manner to facilitate the smooth running of the grid and reduce greenhouse emissions. The present article outlines the TransCarbonNet, a novel hybrid deep learning framework with self-attention characteristics added to the bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM) network to forecast the carbon intensity of the grid several days. The proposed temporal fusion model not only learns the local temporal interactions but also the long-term patterns of the carbon emission data; hence, it is able to give… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.073985 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Methods Applied to Energy Systems)
Abstract This study proposes a novel forecasting framework that simultaneously captures the strong periodicity and irregular meteorological fluctuations inherent in solar radiation time series. Existing approaches typically define inter-regional correlations using either simple correlation coefficients or distance-based measures when applying spatio-temporal graph neural networks (STGNNs). However, such definitions are prone to generating spurious correlations due to the dominance of periodic structures. To address this limitation, we adopt the Elastic-Band Transform (EBT) to decompose solar radiation into periodic and amplitude-modulated components, which are then modeled independently with separate graph neural networks. The periodic component, characterized by strong More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074815 - 29 January 2026
Abstract We present a computer-modeling framework for photovoltaic (PV) source emulation that preserves the exact single-diode physics while enabling iteration-free, real-time evaluation. We derive two closed-form explicit solvers based on the Lambert W function: a voltage-driven V-Lambert solver for high-fidelity I–V computation and a resistance-driven R-Lambert solver designed for seamless integration in a closed-loop PV emulator. Unlike Taylor-linearized explicit models, our proposed formulation retains the exponential nonlinearity of the PV equations. It employs a numerically stable analytical evaluation that eliminates the need for lookup tables and root-finding, all while maintaining limited computational costs and a small… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.073945 - 29 January 2026
Abstract Environmental problems are intensifying due to the rapid growth of the population, industry, and urban infrastructure. This expansion has resulted in increased air and water pollution, intensified urban heat island effects, and greater runoff from parks and other green spaces. Addressing these challenges requires prioritizing green infrastructure and other sustainable urban development strategies. This study introduces a novel Integrated Decision Support System that combines Pythagorean Fuzzy Sets with the Advanced Alternative Ranking Order Method allowing for Two-Step Normalization (AAROM-TN), enhanced by a dual weighting strategy. The weighting approach integrates the Criteria Importance Through Intercriteria Correlation… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074160 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovative Applications of Fractional Modeling and AI for Real-World Problems)
Abstract Lassa Fever (LF) is a viral hemorrhagic illness transmitted via rodents and is endemic in West Africa, causing thousands of deaths annually. This study develops a dynamic model of Lassa virus transmission, capturing the progression of the disease through susceptible, exposed, infected, and recovered populations. The focus is on simulating this model using the fractional Caputo derivative, allowing both qualitative and quantitative analyses of boundedness, positivity, and solution uniqueness. Fixed-point theory and Lipschitz conditions are employed to confirm the existence and uniqueness of solutions, while Lyapunov functions establish the global stability of both disease-free and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.070268 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Developments on Computational Biology-II)
Abstract Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) infection and heavy alcohol consumption are the two primary pathogenic causes of liver cirrhosis. In this paper, we proposed a deterministic mathematical model and a logistic equation to investigate the dynamics of liver cirrhosis progression as well as to explain the implications of variations in alcohol consumption on chronic hepatitis B patients, respectively. The intricate interactions between liver cirrhosis, recovery, and treatment dynamics are captured by the model. This study aims to show that alcohol consumption by Hepatitis B-infected individuals accelerates liver cirrhosis progression while treatment of acutely infected individuals reduces… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.071837 - 29 January 2026
Abstract Mobile service robots (MSRs) in hospital environments require precise and robust trajectory tracking to ensure reliable operation under dynamic conditions, including model uncertainties and external disturbances. This study presents a cognitive control strategy that integrates a Numerical Feedforward Inverse Dynamic Controller (NFIDC) with a Feedback Radial Basis Function Neural Network (FRBFNN). The robot’s mechanical structure was designed in SolidWorks 2022 SP2.0 and validated under operational loads using finite element analysis in ANSYS 2022 R1. The NFIDC-FRBFNN framework merges proactive inverse dynamic compensation with adaptive neural learning to achieve smooth torque responses and accurate motion control.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.075442 - 29 January 2026
Abstract It remains difficult to automate the creation and validation of Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagrams due to unstructured requirements, limited automated pipelines, and the lack of reliable evaluation methods. This study introduces a cohesive architecture that amalgamates requirement development, UML synthesis, and multimodal validation. First, LLaMA-3.2-1B-Instruct was utilized to generate user-focused requirements. Then, DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B applies its reasoning skills to transform these requirements into PlantUML code. Using this dual-LLM pipeline, we constructed a synthetic dataset of 11,997 UML diagrams spanning six major diagram families. Rendering analysis showed that 89.5% of the generated diagrams compile correctly, while… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074938 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Emerging Artificial Intelligence Technologies and Applications-II)
Abstract Soft-tissue motion introduces significant challenges in robotic teleoperation, especially in medical scenarios where precise target tracking is critical. Latency across sensing, computation, and actuation chains leads to degraded tracking performance, particularly around high-acceleration segments and trajectory inflection points. This study investigates machine learning-based predictive compensation for latency mitigation in soft-tissue tracking. Three models—autoregressive (AR), long short-term memory (LSTM), and temporal convolutional network (TCN)—were implemented and evaluated on both synthetic and real datasets. By aligning the prediction horizon with the end-to-end system delay, we demonstrate that prediction-based compensation significantly reduces tracking errors. Among the models, TCN More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.076439 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Signal Processing and Computer Vision)
Abstract Scalable simulation leveraging real-world data plays an essential role in advancing autonomous driving, owing to its efficiency and applicability in both training and evaluating algorithms. Consequently, there has been increasing attention on generating highly realistic and consistent driving videos, particularly those involving viewpoint changes guided by the control commands or trajectories of ego vehicles. However, current reconstruction approaches, such as Neural Radiance Fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting, frequently suffer from limited generalization and depend on substantial input data. Meanwhile, 2D generative models, though capable of producing unknown scenes, still have room for improvement in terms… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074292 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Image Segmentation and Object Detection: Innovations, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract Salient object detection (SOD) models struggle to simultaneously preserve global structure, maintain sharp object boundaries, and sustain computational efficiency in complex scenes. In this study, we propose SPSALNet, a task-driven two-stage (macro–micro) architecture that restructures the SOD process around superpixel representations. In the proposed approach, a “split-and-enhance” principle, introduced to our knowledge for the first time in the SOD literature, hierarchically classifies superpixels and then applies targeted refinement only to ambiguous or error-prone regions. At the macro stage, the image is partitioned into content-adaptive superpixel regions, and each superpixel is represented by a high-dimensional region-level… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074467 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Image Segmentation and Object Detection: Innovations, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS), which relies only on image-level labels, has attracted significant attention for its cost-effectiveness and scalability. Existing methods mainly enhance inter-class distinctions and employ data augmentation to mitigate semantic ambiguity and reduce spurious activations. However, they often neglect the complex contextual dependencies among image patches, resulting in incomplete local representations and limited segmentation accuracy. To address these issues, we propose the Context Patch Fusion with Class Token Enhancement (CPF-CTE) framework, which exploits contextual relations among patches to enrich feature representations and improve segmentation. At its core, the Contextual-Fusion Bidirectional Long Short-Term More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.075834 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Image Segmentation and Object Detection: Innovations, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract Breast cancer screening programs rely heavily on mammography for early detection; however, diagnostic performance is strongly affected by inter-reader variability, breast density, and the limitations of conventional computer-aided detection systems. Recent advances in deep learning have enabled more robust and scalable solutions for large-scale screening, yet a systematic comparison of modern object detection architectures on nationally representative datasets remains limited. This study presents a comprehensive quantitative comparison of prominent deep learning–based object detection architectures for Artificial Intelligence-assisted mammography analysis using the MammosighTR dataset, developed within the Turkish National Breast Cancer Screening Program. The dataset comprises… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074410 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Pattern Recognition)
Abstract Multivariate anomaly detection plays a critical role in maintaining the stable operation of information systems. However, in existing research, multivariate data are often influenced by various factors during the data collection process, resulting in temporal misalignment or displacement. Due to these factors, the node representations carry substantial noise, which reduces the adaptability of the multivariate coupled network structure and subsequently degrades anomaly detection performance. Accordingly, this study proposes a novel multivariate anomaly detection model grounded in graph structure learning. Firstly, a recommendation strategy is employed to identify strongly coupled variable pairs, which are then used More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.075909 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Pattern Recognition)
Abstract Reliable detection of traffic signs and lights (TSLs) at long range and under varying illumination is essential for improving the perception and safety of autonomous driving systems (ADS). Traditional object detection models often exhibit significant performance degradation in real-world environments characterized by high dynamic range and complex lighting conditions. To overcome these limitations, this research presents FED-YOLOv10s, an improved and lightweight object detection framework based on You Only look Once v10 (YOLOv10). The proposed model integrates a C2f-Faster block derived from FasterNet to reduce parameters and floating-point operations, an Efficient Multiscale Attention (EMA) mechanism to More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074627 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Models in Healthcare: Challenges, Methods, and Applications)
Abstract Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing healthcare by helping with diagnosis. However, for doctors to trust AI tools, they need to be both accurate and easy to understand. In this study, we created a new machine learning system for the early detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in children. Our main goal was to build a model that is not only good at predicting ASD but also clear in its reasoning. For this, we combined several different models, including Random Forest, XGBoost, and Neural Networks, into a single, more powerful framework. We used two different types More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.075064 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Models in Healthcare: Challenges, Methods, and Applications)
Abstract The global population is rapidly expanding, driving an increasing demand for intelligent healthcare systems. Artificial intelligence (AI) applications in remote patient monitoring and diagnosis have achieved remarkable progress and are emerging as a major development trend. Among these applications, mouth motion tracking and mouth-state detection represent an important direction, providing valuable support for diagnosing neuromuscular disorders such as dysphagia, Bell’s palsy, and Parkinson’s disease. In this study, we focus on developing a real-time system capable of monitoring and detecting mouth state that can be efficiently deployed on edge devices. The proposed system integrates the Facial… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2026.074395 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Pattern Recognition)
Abstract Spam emails remain one of the most persistent threats to digital communication, necessitating effective detection solutions that safeguard both individuals and organisations. We propose a spam email classification framework that uses Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) for contextual feature extraction and a multiple-window Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for classification. To identify semantic nuances in email content, BERT embeddings are used, and CNN filters extract discriminative n-gram patterns at various levels of detail, enabling accurate spam identification. The proposed model outperformed Word2Vec-based baselines on a sample of 5728 labelled emails, achieving an accuracy of 98.69%, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.075119 - 29 January 2026
Abstract Mental-health risk detection seeks early signs of distress from social media posts and clinical transcripts to enable timely intervention before crises. When such risks go undetected, consequences can escalate to self-harm, long-term disability, reduced productivity, and significant societal and economic burden. Despite recent advances, detecting risk from online text remains challenging due to heterogeneous language, evolving semantics, and the sequential emergence of new datasets. Effective solutions must encode clinically meaningful cues, reason about causal relations, and adapt to new domains without forgetting prior knowledge. To address these challenges, this paper presents a Continual Neuro-Symbolic Graph… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, Vol.146, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/cmes.2025.074799 - 29 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Next-Generation Intelligent Networks and Systems: Advances in IoT, Edge Computing, and Secure Cyber-Physical Applications)
Abstract The rapid proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in critical healthcare infrastructure has introduced significant security and privacy challenges that demand innovative, distributed architectural solutions. This paper proposes FE-ACS (Fog-Edge Adaptive Cybersecurity System), a novel hierarchical security framework that intelligently distributes AI-powered anomaly detection algorithms across edge, fog, and cloud layers to optimize security efficacy, latency, and privacy. Our comprehensive evaluation demonstrates that FE-ACS achieves superior detection performance with an AUC-ROC of 0.985 and an F1-score of 0.923, while maintaining significantly lower end-to-end latency (18.7 ms) compared to cloud-centric (152.3 ms) and fog-only (34.5… More >