BIOCELL is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on molecular and cellular biosciences. The journal welcomes high quality original research articles, review papers, communications, perspectives, commentaries, etc. Topics of interests include but are not limited to: Cellular Biochemistry, Structural & Molecular Biology, Cellular/Molecular Biology, Immunology, Pathology & Neurobiology, Cell Signaling, Regenerative Biology & Stem Cells, Cancer Biology, RNA Biology, Genomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics & Metabolomics, Plant Molecular & Cellular Biology.
Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE): 2024 Impact Factor 1.0; Journal Citation Report/Science Edition (JCR); Scopus; Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 2.0; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.256; Sociedad Argentina de Investigaciones en Bioquímica y Biología Molecular (SAIB); Portico, etc.
 Open Access
Open Access
SHORT COMMUNICATION
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.071798 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Cell Signaling Pathways in Health and Disease)
Abstract RING protein 213 (RNF213), the susceptibility gene for Moyamoya disease (MMD), possesses two active AAA+ ATPase (ATPases Associated with diverse cellular Activities) modules, a RING, and RNF213-ZNFX1 finger (RZ finger) domains. Several RNF213 variants have been reported in MMD patients, including the p.R4810K variant (rs112735431), which is a founder polymorphism associated with MMD in East Asia. To elucidate the function of RNF213 and its variant, we investigated the localization of RNF213 and the R4810K variant in this study. RNF213 induced circular hole structures near the nucleus, similar to lipid droplets (LDs), in U-2 OS cells. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072273 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cellular Senescence in Health and Disease)
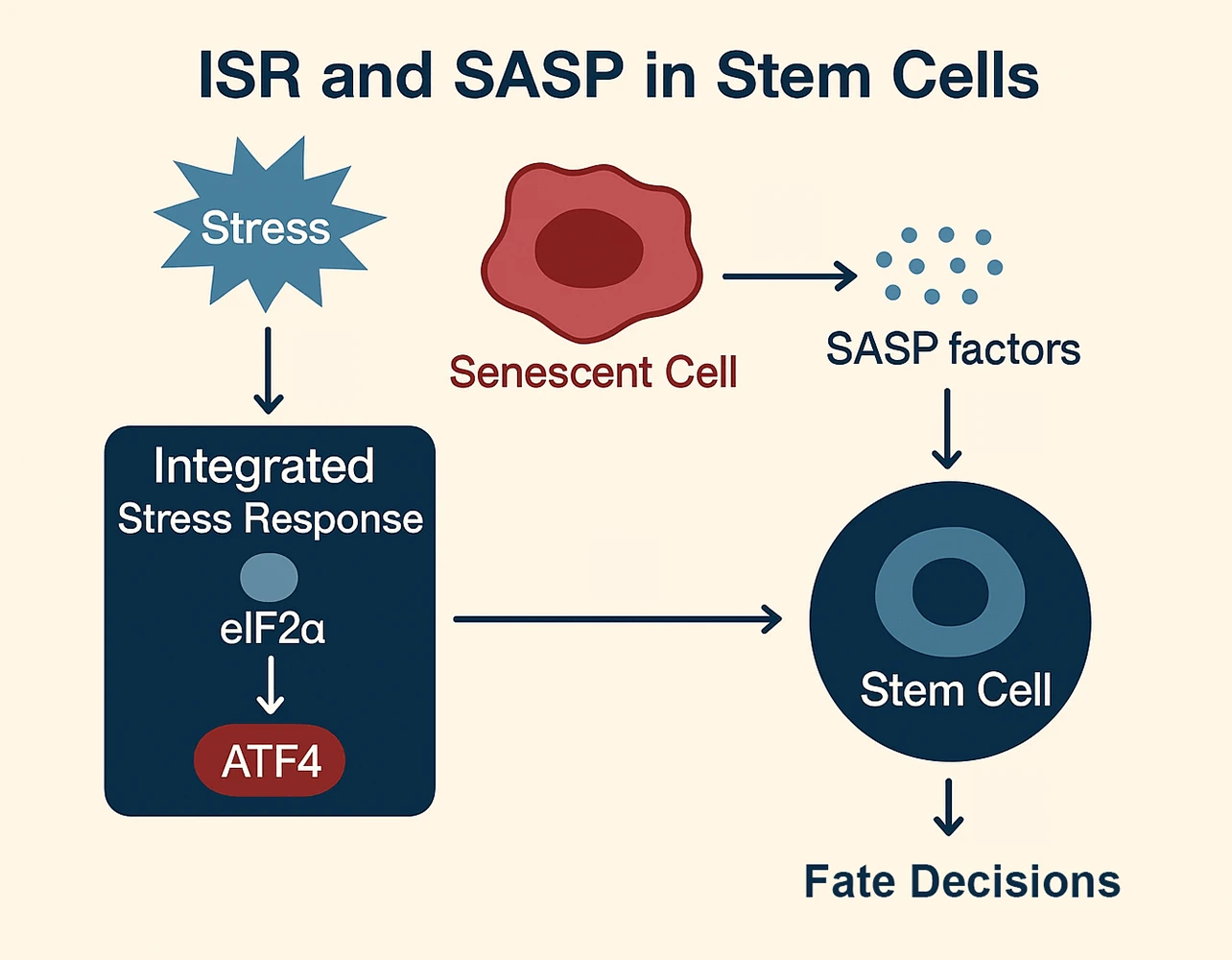
Abstract Stem cell fate decisions are increasingly understood through the dynamic interplay of two fundamental stress-adaptive programs: the integrated stress response (ISR) and the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). These pathways act as a Yin–Yang system, balancing beneficial and detrimental outcomes across development, tissue homeostasis, and disease. On the yin (protective) side, transient ISR activation and acute SASP signaling foster adaptation, embryonic patterning, wound healing, and regeneration. On the yang (maladaptive) side, chronic ISR signaling and unresolved SASP output drive stem cell exhaustion, fibrosis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. This duality highlights their roles as both guardians and disruptors More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.068245 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Melatonin and Mitochondria: Exploring New Frontiers)
Abstract Aerobic glycolysis, also known as the Warburg effect, and the accumulation of lactate that it causes, are increasingly recognized outside the field of oncology as triggers of chronic non-neoplastic disorders. This review integrates preclinical and clinical evidence to evaluate the ability of melatonin to reverse Warburg-effect-like metabolic reprogramming. Literature on neurodegeneration, age-related sarcopenia, type 2 diabetes, chronic kidney disease, heart failure and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) has been reviewed and synthesised. In all of these conditions, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) inhibit the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. This diverts pyruvate away… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072557 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Melatonin and Mitochondria: Exploring New Frontiers)
Abstract Ischemic stroke is one of the major causes of long-term disability and mortality worldwide. It results from an interruption in the cerebral blood flow, triggering a cascade of detrimental events like oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroinflammation, excitotoxicity, and apoptosis, causing neuronal injury and cellular death. Melatonin, a pleiotropic indoleamine produced by the pineal gland, has multifaceted neuroprotective effects on stroke pathophysiology. Interestingly, the serum melatonin levels are associated with peroxidation and antioxidant status, along with mortality score in patients with severe middle cerebral artery infarction. Melatonin exhibits strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic properties and preserves More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072337 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: NETs: A Decade of Pathological Insights and Future Therapeutic Horizons)
Abstract Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) have emerged as key mediators of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), linking innate immune activation to vascular injury, thrombosis, and maladaptive remodeling. This review synthesizes recent insights into the molecular and cellular pathways driving NET formation, including post-translational modifications, metabolic reprogramming, inflammasome signaling, and autophagy. It highlights the role of NETs in atherosclerosis, thrombosis, myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, and hypertension, emphasizing common control points such as peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PAD4)-dependent histone citrullination and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidases 2 (NOX2)-mediated oxidative stress. Mechanistic interpretation of circulating biomarkers, including myeloperoxidase (MPO)-DNA complexes, citrullinated histone H3,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073781 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: NETs: A Decade of Pathological Insights and Future Therapeutic Horizons)
Abstract Neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation or NETosis is a specialized innate immune process in which neutrophils release chromatin fibers decorated with histones and antimicrobial proteins. Although pivotal for pathogen clearance, aberrant NETosis has emerged as a critical modulator of acute and chronic respiratory pathologies, including acute respiratory distress syndrome, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Dysregulated NET release exacerbates airway inflammation by inducing epithelial injury, mucus hypersecretion, and the recruitment of inflammatory leukocytes, thereby accelerating tissue remodeling and functional decline. Mechanistically, NETosis is governed by peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PADI4)-mediated histone citrullination, NADPH oxidase-dependent reactive More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072368 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Mechanisms Driving COPD, Atherosclerosis, and Cardiovascular Disease: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Innovations)
Abstract Peripheral artery disease (PAD) remains a significant global health issue, with current treatments primarily focused on relieving symptoms and addressing macrovascular issues. However, critical immunoinflammatory mechanisms are often overlooked. Recent evidence suggests that monocyte phenotypic plasticity plays a central role in PAD development, affecting atherogenesis, plaque progression, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and chronic ischemic remodeling. This narrative review aims to summarize the latest advances (2023–2025) in understanding monocyte diversity, functional states, and their changes throughout different stages of PAD. We discuss both established and emerging biomarkers, such as circulating monocyte subset proportions, functional assays, immune checkpoint expression, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.071635 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Melatonin and Mitochondria: Exploring New Frontiers)
Abstract Objectives: Oxidative stress (OS) plays a pivotal role in chronic and neurodegenerative diseases, which has sparked interest in molecules that modulate redox-regulating enzymes. Melatonin and its metabolites exhibit antioxidant properties; however, their molecular mechanisms of enzymatic and transcriptional modulation remain unclear. This study aimed to investigate, through an exploratory in silico approach, the interactions of melatonin and related compounds with OS-related enzymes to generate hypotheses about their role in cellular redox control. Methods: A rational selection of antioxidant, pro-oxidant, and transcriptional targets was performed. Ligands were optimized at the DFT level (M05-2X/6-311+G(d,p)) and docked to OS… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073085 - 23 January 2026
Abstract Objective: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks among the most prevalent malignant tumors globally. Metabolically associated fatty liver disease is a significant risk factor for HCC. Adiponectin, a key regulatory protein in glucolipid metabolism, presents potential as an anti-tumor target in HCC cells. The study focused on evaluating the anti-HCC properties of AdipoRon, an agonist of the adiponectin receptor. Method: Cell viability and proliferation were assessed using the cell counting kit-8 and colony formation assays, respectively. AdipoRon’s effect on HCC cell damage was evaluated via flow cytometry, apoptosis, and (lactate dehydrogenase) LDH assays. Mitochondrial function was evaluated… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.068322 - 23 January 2026
Abstract Objectives: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality, with limited understanding of lncRNA-driven mechanisms in tumor progression. This study aimed to identify differentially expressed lncRNAs in NSCLC tissues and elucidate the functional role of the significantly upregulated RP3-340N1.2 in promoting malignancy. Methods: RNA sequencing was used to screen dysregulated lncRNAs. RP3-340N1.2 was functionally characterized via gain/loss-of-function assays in NSCLC cells, assessing proliferation, migration, and macrophage polarization. Mechanisms of interleukin 6 (IL-6) regulation were explored using cytokine profiling, Actinomycin D assays, and RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays to study RP3-340N1.2 interactions with… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072736 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Natural Compounds in Metabolic Health: Mechanisms and Applications)
Abstract Objectives: Postmenopausal osteoporosis is the most common form of osteoporosis in clinical practice, affecting millions of postmenopausal women worldwide. Postmenopausal osteoporosis demands safe and effective therapies. This study aimed to evaluate the potential of hederagenin (Hed) for treating osteoporosis and to elucidate its underlying mechanisms of action. Methods: The anti-osteoporotic potential of Hed was assessed by investigating its effects on ovariectomy (OVX)-induced bone loss in mice and on receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells. Network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking were employed to identify key targets, which were subsequently validated experimentally. Results:… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073401 - 23 January 2026
Abstract Objective: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein 1 (Lrg1) could regulate diverse cells in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Our study seeks to uncover Lrg1’s impact on endothelial cell heterogeneity via differentiation pathways and transcription factors. Method: The CSOmap model measured cell-to-brain-center distances using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data in middle cerebral artery occlusion reperfusion (MCAO/R). Monocle2 mapped endothelial differentiation paths. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) analyzed endothelial subcluster variations. Database searches revealed a zinc finger MIZ-type containing 1 protein-frizzled 3 (Zmiz1-Fzd3) promoter interaction. Endothelial cells were transfected with a Fzd3 promoter-luciferase plasmid. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and western blotting assessed… More >