Fluid Dynamics and Materials Processing is an essential reading for all those concerned with complex fluids, multiphase flows and the intersection of fluid dynamics with materials processing and/or with the more general field of engineering optimization. It features original theoretical, computational, and experimental investigations. All subjects where a material, at a certain stage of its “life”, is in a fluid state, behaves as a fluid (e.g. many types of granular media) or interacts with a fluid should be considered relevant to FDMP. Relevant examples include (but are not limited to) the most modern and advanced processes for the production of inorganic (semiconductors, metal alloys, foams, plastics, polymers, ceramic materials, cement, asphalt and resins of various kinds), organic (protein crystals, drugs and medicines) materials and "living" (in vitro) biological tissues. We are especially interested in those studies where emphasis is put on the fluid-dynamic conditions under which a material is operated. However, FDMP also welcomes manuscripts dealing with more fundamental aspects such as the rheological behavior of multiphase systems or the convective currents that are produced in a fluid as a result of the thermal, chemical and/or mechanical stimuli typically applied in various processing or manufacturing methods (e.g. thermal gradients, shaking, mixing, etc). Some attention is devoted as well to all those problems of “structure/fluid” interaction that have extensive background applications in important fields such as marine, chemical, aeronautical and aerospace engineering and the oil sector, i.e. all those cases where fluid-dynamic analysis is instrumental in guiding the design/optimization of the considered systems (or related components) and the selection of the required “materials”.
Emerging Source Citation Index (Web of Science): 0.7; Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 1.5; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.350; Engineering Index (Compendex); EBSCO; Google Scholar; Proquest; Portico, etc...
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.076681 - 06 February 2026
Abstract Predicting the precise impacts of climate change on extreme winds remains challenging, yet strong storms are widely expected to occur more frequently in a warming climate. Wind barriers are commonly used on bridges to reduce aerodynamic loads on trains through blocking effects. This study develops a novel wind barrier based on Tesla valves, which not only blocks incoming flow but also dissipates mechanical energy through fluid collision. To demonstrate this energy-dissipation capability, a Tesla plate is placed in a circular duct to examine its influence on pressure drop. Experimental tests and numerical simulations comparing a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.076238 - 06 February 2026
Abstract For hypersonic air-breathing vehicles, the V-shaped leading edges (VSLEs) of supersonic combustion ramjet (scramjet) inlets experience complex shock interactions and intense aerodynamic loads. This paper provides a comprehensive review of flow characteristics at the crotch of VSLEs, with particular focus on the transition of shock interaction types and the variation of wall heat flux under different freestream Mach numbers and geometric configurations. The mechanisms governing shock transition, unsteady oscillations, hysteresis, and three-dimensional effects in VSLE flows are first examined. Subsequently, thermal protection strategies aimed at mitigating extreme heating loads are reviewed, emphasizing their relevance to More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.075865 - 06 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Fluid and Thermal Dynamics in the Development of Unconventional Resources III)
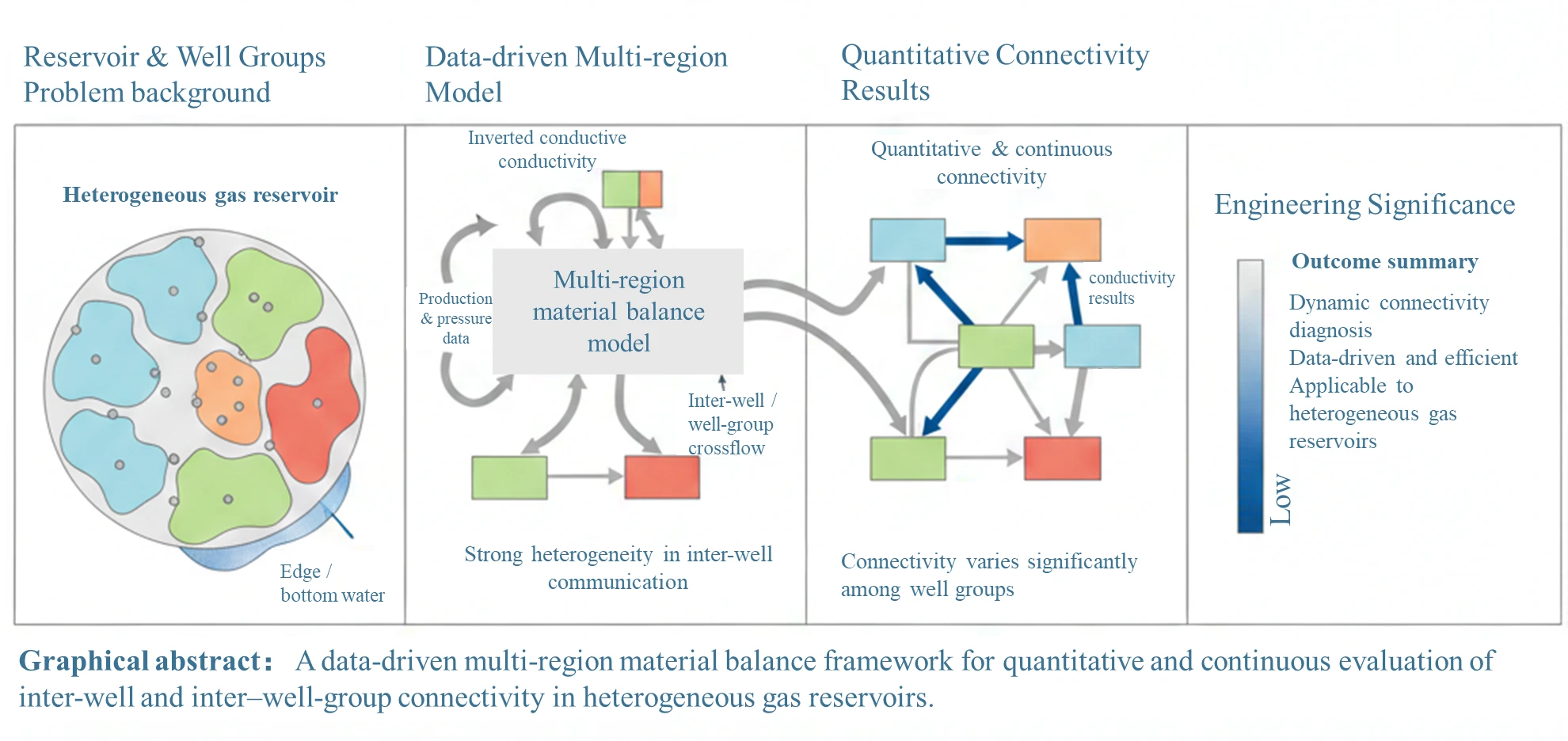
Abstract Carbonate gas reservoirs are often characterized by strong heterogeneity, complex inter-well connectivity, extensive edge or bottom water, and unbalanced production, challenges that are also common in many heterogeneous gas reservoirs with intricate storage and flow behavior. To address these issues within a unified, data-driven framework, this study develops a multi-block material balance model that accounts for inter-block flow and aquifer influx, and is applicable to a wide range of reservoir types. The model incorporates inter-well and well-group conductive connectivity together with pseudo–steady-state aquifer support. The governing equations are solved using a Newton–Raphson scheme, while particle More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.075227 - 06 February 2026
Abstract The low-pressure and low-density conditions encountered at high altitudes significantly reduce the operating Reynolds number of micro radial-flow turbines, frequently bringing it below the self-similarity critical threshold of 3.5 × 104. This departure undermines the applicability of conventional similarity-based design approaches. In this study, micro radial-flow turbines with rotor diameters below 50 mm are investigated through a combined approach integrating high-fidelity numerical simulations with experimental validation, aiming to elucidate the mechanisms by which low Reynolds numbers influence aerodynamic and thermodynamic performance. The results demonstrate that decreasing Reynolds number leads to boundary-layer thickening on blade surfaces, enhanced More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.074335 - 06 February 2026
Abstract As a controllable power generation method requiring no energy storage, Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) technology demonstrates characteristics of abundant reserves, low pollution, and round-the-clock stable operation. The free-standing cold-water pipe (CWP) in the system withstands various complex loads during operation, posing potential failure risks. To reveal the deformation and stress mechanisms of OTEC CWPs, this study first analyzes wave particle velocity and acceleration to determine wave loads at different water depths. Based on the Euler-Bernoulli beam model, a quasi-static load calculation model for OTEC CWPs was established. The governing equations were discretized using the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.074990 - 06 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Subsurface Fluid Flow Dynamics and Applications in Carbon Reduction Technologies)
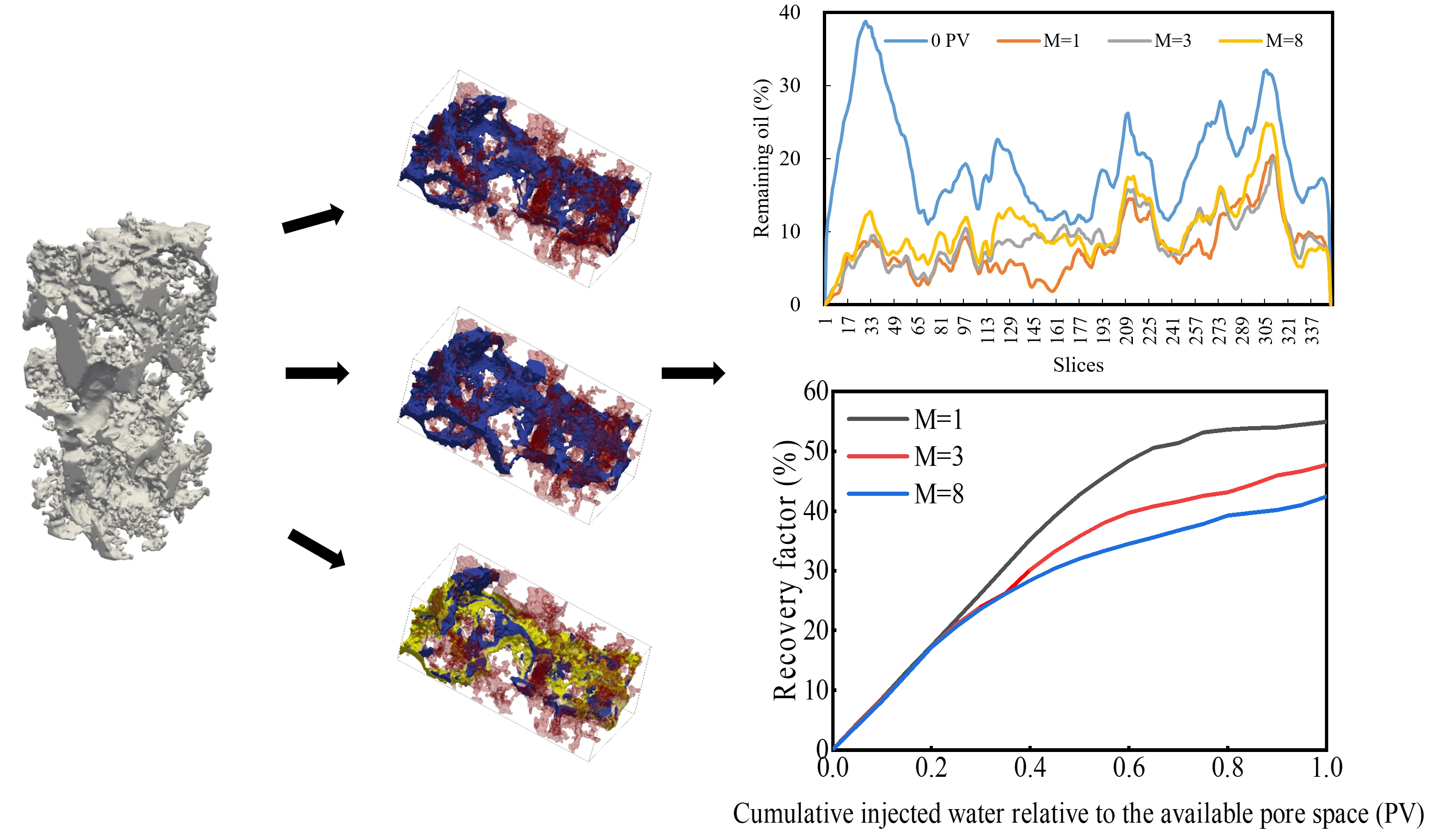
Abstract Weak water-drive offshore reservoirs with complex pore architecture and strong permeability heterogeneity present major challenges, including rapid depletion of formation energy, low waterflood efficiency, and significant lateral and vertical variability in crude oil properties, all of which contribute to limited recovery. To support more effective field development, alternative strategies and a deeper understanding of pore-scale flow behavior are urgently needed. In this work, CT imaging and digital image processing were used to construct a digital rock model representative of the target reservoir. A pore-scale flow model was then developed, and the Volume of Fluid (VOF)… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.073294 - 06 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Subsurface Fluid Flow Dynamics and Applications in Carbon Reduction Technologies)
Abstract Identifying geohazards such as landslides and methane leakage is crucial during gas extraction from natural gas hydrate (NGH) reservoirs, and understanding reservoir settlement behavior is central to this assessment. Horizontal wells can enlarge the pressure relief zone within the formation, improving single-well productivity, and are therefore considered a promising approach for NGH development. This study examines the settlement response of hydrate-bearing sediments during depressurization using horizontal wells. A fully coupled thermal, hydraulic, mechanical, and chemical (THMC) model with representative reservoir properties (Shenhu region in the South China Sea) is presented accordingly. The simulations show that More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.075388 - 06 February 2026
Abstract Self-suspended proppants, which enable clear-water fracturing, represent a promising new class of materials for reservoir stimulation. Given the economic limitations associated with their exclusive use, this study investigates proppant transport behavior in hybrid systems combining self-suspended proppants with conventional 40/70 mesh quartz sand at various mixing ratios. A dedicated experimental apparatus was developed to replicate field-relevant complex fracture networks, consisting of a main fracture and two branching fractures with different deflection angles. Using this system, sand bank formation and proppant distribution were examined for both conventional quartz sand fracturing and fracturing augmented with self-suspended proppants.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.074345 - 06 February 2026
Abstract In this study, a Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) surrogate model coupled with a Bayesian optimization algorithm was employed for the single-objective design optimization of fan-shaped film cooling holes on a concave wall. Fan-shaped holes, commonly used in gas turbines and aerospace applications, flare toward the exit to form a protective cooling film over hot surfaces, enhancing thermal protection compared to cylindrical holes. An initial hole configuration was used to improve adiabatic cooling efficiency. Design variables included the hole injection angle, forward expansion angle, lateral expansion angle, and aperture ratio, while the objective function was the More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing, Vol.22, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/fdmp.2026.075630 - 06 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Multiphase Fluid Flow Behaviors in Oil, Gas, Water, and Solid Systems during CCUS Processes in Hydrocarbon Reservoirs)
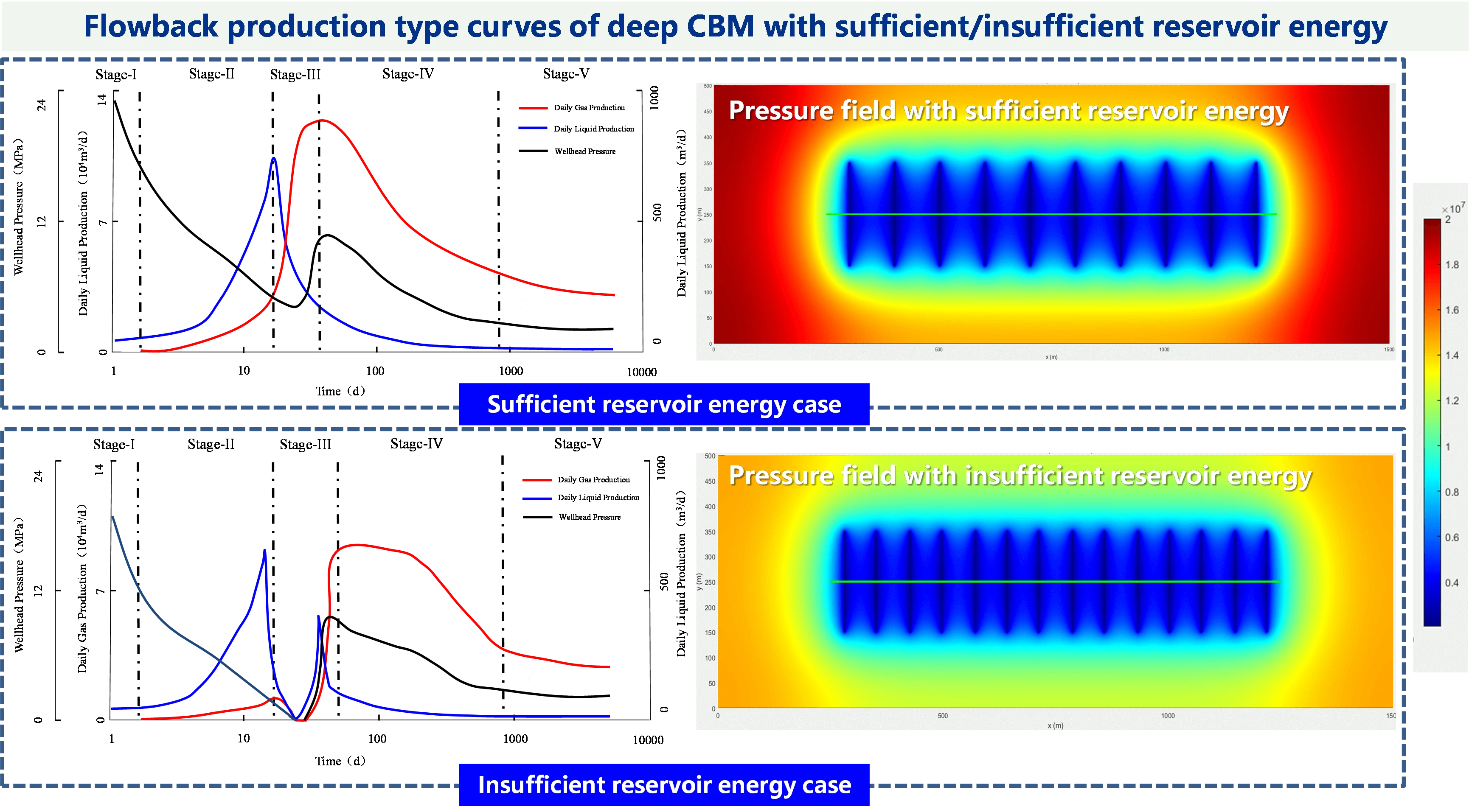
Abstract Significant differences exist between deep and medium-shallow coalbed methane (CBM) reservoirs. The unclear understanding of flowback and production behavior severely constrains the development of deep CBM resources. To address this challenge, guided by the gas-liquid two-phase flow theory in ultra-low permeability reservoirs, and integrating theoretical analysis, numerical simulation, and insights from production practices, this study classifies the flowback and production stages of deep CBM well considering the Daning-Jixian Block, Eastern Ordos Basin as a representative case. We summarize the flowback characteristics for each stage and establish a standard flowback production type curve, aiming to guide… More >
Graphic Abstract