Structural Durability & Health Monitoring (SDHM) is an interdisciplinary journal that serves as a platform for publishing high-quality research on the performance, safety, durability, and sustainability of structural systems across their full lifecycle. While continuing to emphasize structural durability, fatigue, damage mechanics, and health monitoring techniques, the journal also welcomes original studies in the broader fields of structural engineering.
This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 2.5; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.604; RG Journal Impact (average over last three years); Engineering Index (Compendex); Applied Mechanics Reviews; Cambridge Scientific Abstracts: Aerospace and High Technology, Materials Sciences & Engineering, and Computer & Information Systems Abstracts Database; INSPEC Databases; Mechanics; Science Navigator; Portico, etc...
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.072361 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Health Monitoring of Transportation Infrastructure Structure)
Abstract Vehicle-induced response separation is a crucial issue in structural health monitoring (SHM). This paper proposes a block-wise sliding recursive wavelet transform algorithm to meet the real-time processing requirements of monitoring data. To extend the separation target from a fixed dataset to a continuously updating data stream, a block-wise sliding framework is first developed. This framework is further optimized considering the characteristics of real-time data streams, and its advantage in computational efficiency is theoretically demonstrated. During the decomposition and reconstruction processes, information from neighboring data blocks is fully utilized to reduce algorithmic complexity. In addition, a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.070194 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sustainable and Durable Construction Materials)
Abstract Concrete production often relies on natural aggregates, which can lead to resource depletion and environmental harm. In addition, improper disposal of thermoplastic waste exacerbates ecological problems. Although significant attention has recently been given to recycling various waste materials into concrete, studies specifically addressing thermoplastic recycled aggregates are still trending. This underscores the need to comprehensively review existing literature, identify research trends, and recognize gaps in understanding the mechanical performance of thermoplastic-based recycled aggregate concrete. Accordingly, this review summarizes recent investigations focused on the mechanical properties of thermoplastic-based recycled aggregate concrete, emphasizing aspects such as compressive… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.071317 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-driven Monitoring, Condition Assessment, and Data Analytics for Enhancing Infrastructure Resilience)
Abstract Crack detection accuracy in computer vision is often constrained by limited annotated datasets. Although Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have been applied for data augmentation, they frequently introduce blurs and artifacts. To address this challenge, this study leverages Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPMs) to generate high-quality synthetic crack images, enriching the training set with diverse and structurally consistent samples that enhance the crack segmentation. The proposed framework involves a two-stage pipeline: first, DDPMs are used to synthesize high-fidelity crack images that capture fine structural details. Second, these generated samples are combined with real data to train… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.071007 - 08 January 2026
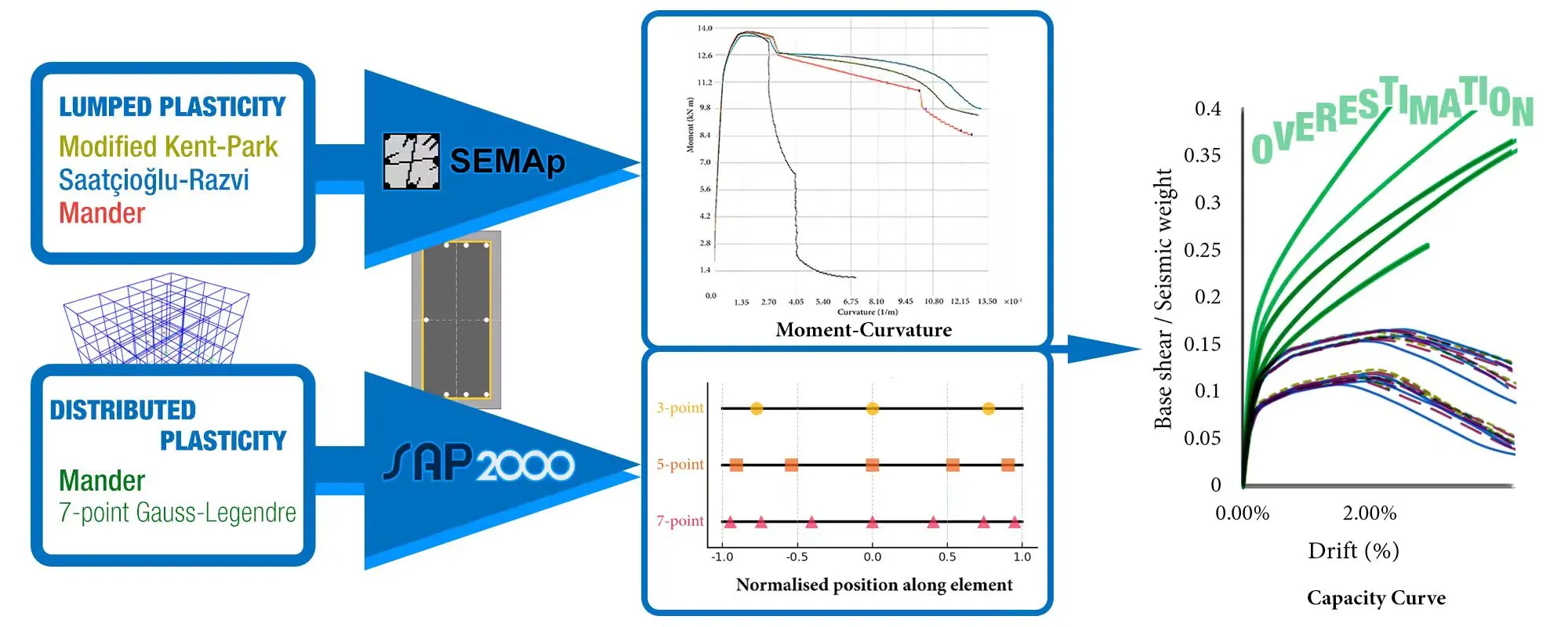
Abstract Nonlinear static procedures are widely adopted in structural engineering practice for seismic performance assessment due to their simplicity and computational efficiency. However, their reliability depends heavily on how the nonlinear behaviour of structural components is represented. The recent earthquakes in Albania (2019) and Türkiye (2023) have underscored the need for accurate assessment techniques, particularly for older reinforced concrete buildings with poor detailing. This study quantifies the discrepancies between default and user-defined component modelling in pushover analysis of pre-modern reinforced concrete structures, analysing two representative low- and mid-rise reinforced concrete frame buildings. The lumped plasticity approach… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.070185 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Applications for Bridge Structures)
Abstract This study explores theoretical insights and experimental results on monitoring load-carrying capacity degradation in bridge spans through frequency analysis. Experiments were conducted on real bridge structures, including the Binh Thuan Bridge, focusing on analyzing the power spectral density (PSD) of vibration signals under random traffic loads. Detailed digital models of various bridge spans with different structural designs and construction periods were developed to ensure diversity. The study utilized PSD to analyze the vibration signals from the bridge spans under various loading conditions, identifying the vibration frequencies and the corresponding response regions. The research correlated the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.068987 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Enhanced Low-Altitude Technology Applications in Structural Integrity Evaluation and Safety Management of Transportation Infrastructure Systems)
Abstract With the rapid development of transportation infrastructure, ensuring road safety through timely and accurate highway inspection has become increasingly critical. Traditional manual inspection methods are not only time-consuming and labor-intensive, but they also struggle to provide consistent, high-precision detection and real-time monitoring of pavement surface defects. To overcome these limitations, we propose an Automatic Recognition of Pavement Defect (ARPD) algorithm, which leverages unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based aerial imagery to automate the inspection process. The ARPD framework incorporates a backbone network based on the Selective State Space Model (S3M), which is designed to capture long-range temporal dependencies.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.072237 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Health Monitoring of Transportation Infrastructure Structure)
Abstract Quantitative detection of sleeve grouting compactness is a technical challenge in civil engineering testing. This study explores a novel quantitative detection method based on ultrasonic time-frequency dual-domain analysis. It establishes a mapping relationship between sleeve grouting compactness and characteristic parameters. First, this study made samples with gradient defects for two types of grouting sleeves, G18 and G20. These included four cases: 2D, 4D, 6D defects (where D is the diameter of the grouting sleeve), and no-defect. Then, an ultrasonic input/output data acquisition system was established. Three-dimensional sound field distribution data were obtained through an orthogonal… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.063718 - 08 January 2026
Abstract To investigate the impact of temporary structures on the mechanical behavior of shaped bridge towers during the construction process, the Dianbu River Special Bridge was selected as the engineering background. A finite element model of the middle tower column during the construction stage was established using ABAQUS to analyze the effects of key parameters, including the angle and pretension of temporary cables, as well as the wall thickness and diameter of temporary diagonal braces. The study examines how these parameters influence the stresses at the tower-girder consolidation. The results indicate that the angle of temporary More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.066408 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Fault Diagnosis and Health Monitoring for Pipelines)
Abstract Maintaining the structural integrity of parallel natural gas pipelines during leakage-induced jet fires remains a critical engineering challenge. Existing methods often fail to account for the complex interactions among heat transfer, material behavior, and pipeline geometry, which can lead to overly simplified and potentially unsafe assessments. To address these limitations, this study develops a multiphysics approach that integrates small-orifice leakage theory with detailed thermo-fluid-structural simulations. The proposed framework contributes to a more accurate failure analysis through three main components: (1) coupled modeling that tracks transient heat flow and stress development as fire conditions evolve; (2)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.071300 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Health Monitoring of Transportation Infrastructure Structure)
Abstract Roadbed disease detection is essential for maintaining road functionality. Ground penetrating radar (GPR) enables non-destructive detection without drilling. However, current identification often relies on manual inspection, which requires extensive experience, suffers from low efficiency, and is highly subjective. As the results are presented as radar images, image processing methods can be applied for fast and objective identification. Deep learning-based approaches now offer a robust solution for automated roadbed disease detection. This study proposes an enhanced Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNN) framework integrating ResNet-50 as the backbone and two-dimensional discrete Fourier spectrum transformation (2D-DFT) for… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.071664 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Strategies for Structural and Non-Structural Seismic Protection and Damage Prediction in Reinforced Concrete Structures)
Abstract This study investigates the thermo–mechanical behavior of C40 concrete and reinforced concrete subjected to elevated temperatures up to 700°C by integrating experimental testing and advanced numerical modeling. A temperature-indexed Concrete Damage Plasticity (CDP) framework incorporating bond–slip effects was developed in Abaqus to capture both global stress–strain responses and localized damage evolution. Uniaxial compression tests on thermally exposed cylinders provided residual strength data and failure observations for model calibration and validation. Results demonstrated a distinct two-stage degradation regime: moderate stiffness and strength reduction up to ~400°C, followed by sharp deterioration beyond 500°C–600°C, with residual capacity at… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.071189 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: High Resolution Ultrasonic Non-Destructive Testing of Complex Structures)
Abstract In ultrasonic non-destructive testing of high-temperature industrial equipment, sound velocity drift induced by non-uniform temperature fields can severely compromise defect localization accuracy. Conventional approaches that rely on room-temperature sound velocities introduce systematic errors, potentially leading to misjudgment of safety-critical components. Two primary challenges hinder current methods: first, it is difficult to monitor real-time changes in sound velocity distribution within a thermal gradient; second, traditional uniform-temperature correction models fail to capture the nonlinear dependence of material properties on temperature and their effect on ultrasonic velocity fields. Here, we propose a defect localization correction method based on… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.066572 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Assessment, Monitoring and Optimization of Steel and Composite Structures against Seismic Events and Extreme Actions)
Abstract To address the neglect of seismic performance in conventional double-girder bridge crane optimization, this paper introduces a time-history analysis-based seismic optimization methodology for crane structures. Using a 25-t nuclear power crane as a case study, a bridge frame finite element model is established and validated through static analysis, confirming its accurate representation of the physical entity’s mechanical behavior. Furthermore, with bridge mass reduction as the objective and structural strength, stiffness, stability, and seismic mechanical performance as constraints, an optimization model is developed employing the Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA). More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.070589 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence and Data Mining Applications in Fault Diagnosis and Damage Identification of Infrastructure)
Abstract In industrial manufacturing, efficient surface defect detection is crucial for ensuring product quality and production safety. Traditional inspection methods are often slow, subjective, and prone to errors, while classical machine vision techniques struggle with complex backgrounds and small defects. To address these challenges, this study proposes an improved YOLOv11 model for detecting defects on hot-rolled steel strips using the NEU-DET dataset. Three key improvements are introduced in the proposed model. First, a lightweight Guided Attention Feature Module (GAFM) is incorporated to enhance multi-scale feature fusion, allowing the model to better capture and integrate semantic and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.070873 - 08 January 2026
Abstract The existing 2D settlement monitoring systems for utility tunnels are heavily reliant on manual interpretation of deformation data and empirical prediction models. Consequently, early anomalies (e.g., minor cracks) are often misjudged, and warnings lag by about 24 h without automated spatial localization. This study establishes a technical framework for requirements analysis, architectural design, and data-integration protocols. Revit parametric modelling is used to build a 3D tunnel model with structural elements, pipelines and 18 monitoring points (for displacement and joint width). Custom Revit API code integrated real-time sensor data into the BIM platform via an automated… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.071278 - 08 January 2026
Abstract In dry-coupled ultrasonic thickness measurement, thick rubber layers introduce high-amplitude parasitic echoes that obscure defect signals and degrade thickness accuracy. Existing methods struggle to resolve overlap-ping echoes under variable coupling conditions and non-stationary noise. This study proposes a novel dual-criterion framework integrating energy contribution and statistical impulsivity metrics to isolate specimen re-flections from coupling-layer interference. By decomposing A-scan signals into Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs), the framework employs energy contribution thresholds (>85%) and kurtosis indices (>3) to autonomously select IMFs containing valid specimen echoes. Hybrid time-frequency thresholding further suppresses interference through amplitude filtering and spectral focusing. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.070137 - 08 January 2026
Abstract To examine stress redistribution phenomena in bridges subjected to varying operational conditions, this study conducts a comprehensive analysis of three years of monitoring data from a 153-m double-deck road–rail steel arch bridge. An initial statistical comparison of sensor data distributions reveals clear temporal variations in stress redistribution patterns. XGBoost (eXtreme Gradient Boosting), a gradient-boosting machine learning (ML) algorithm, was employed not only for predictive modeling but also to uncover the underlying mechanisms of stress evolution. Unlike traditional numerical models that rely on extensive assumptions and idealizations, XGBoost effectively captures nonlinear and time-varying relationships between stress… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, Vol.20, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.070531 - 08 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Strategies for Structural and Non-Structural Seismic Protection and Damage Prediction in Reinforced Concrete Structures)
Abstract This study employed tri-component continuous monitoring data from 10 measurement points on both sides of a base isolation layer in the basement of a large-span high-rise building in Beijing, as well as from a free-field station and roof frame, during a Mw 5.5 magnitude earthquake in Pingyuan, Shandong, in 2023. The H/V spectral ratio method was used to evaluate the structural dynamic response characteristics of the building and analyze the regulatory effect of the base-isolation layer on seismic waves. The results indicate that during the earthquake, the peak frequency of the free-field and the measurement points… More >