 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Outcomes of Self-Expanding Transcatheter Pulmonary Valves: Extended Follow-Up of a Prospective Trial
1 Department of Structural Heart Disease, National Center for Cardiovascular Disease, China & Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
2 Department of Structural Heart Disease, Central China Fuwai Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
3 Yunnan Fuwai Cardiovascular Hospital, Kunming, China
4 Department of Radiology, National Center for Cardiovascular Disease, China & Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
* Corresponding Author: Gejun Zhang. Email:
Congenital Heart Disease 2023, 18(2), 219-234. https://doi.org/10.32604/chd.2023.027562
Received 07 November 2022; Accepted 09 January 2023; Issue published 15 March 2023
Abstract
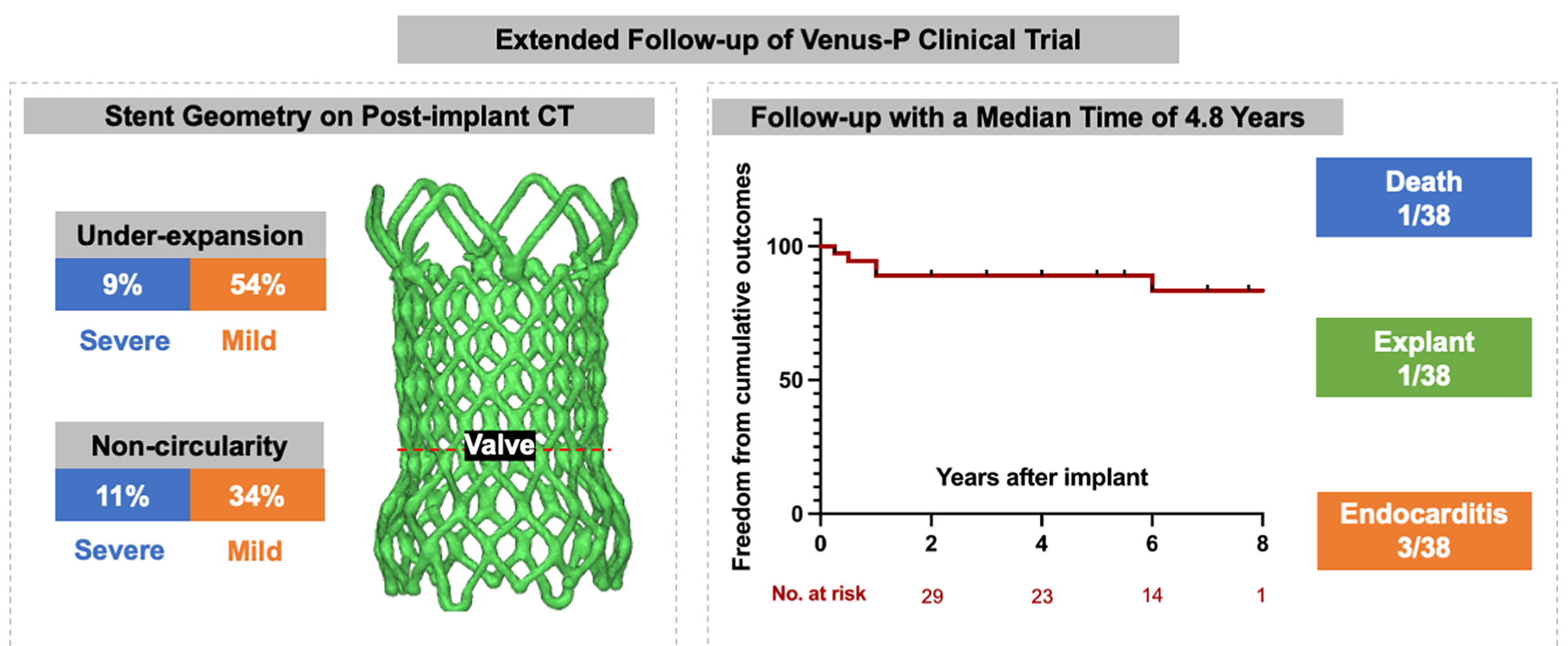
Background: The Venus-P valve was the first self-expanding valve used world-wide for transcatheter pulmonary valve replacement (TPVR) in patients with severe pulmonary regurgitation (PR). We intended to report the extended follow-up results from the prospective trial (No. NCT02590679). Methods: A total of 38 patients with severe PR (mean age 24.2 ± 13.2) were included. Follow-up data were obtained after implanted at 1, 6, and 12 months and yearly after. The frame geometry was assessed on post-implant computer tomography (CT) scanning by calculating the non-circularity [circularity ratio (minimum diameter/maximum diameter) < 0.9] and under-expansion [expansion ratio (derived external valve area/nominal external valve area) < 0.9). Adverse events (all-cause mortality, reintervention, valve dysfunction, stent fracture and endocarditis) were recorded. Results: All valves were implanted successfully with normal function at discharge. Geometric CT analysis showed under-expanded valve was detected in 22 patients (63%) and non-circular valve was seen in 16 patients (46%). During a median follow-up of 4.8 years (range 0.3–8.1), there were 1 death and 1 surgical explant, both resulting from endocarditis. Five-year freedom from valve dysfunction and stent fracture were 84.8% (95%CI 74.8–94.7) and 83.5% (95%CI 73.8–93.2). Endocarditis occurred in 3 patients at a median time of 7 months. Stent fracture was more common in patients with non-circularity stents. Conclusion: TPVR using Venus-P valve is associated with favorable outcomes at 5 years. Non-circular shapes in the valve level may have a higher risk of stent fracture.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools