 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Identification of Cardiac Risk Factors from ECG Signals Using Residual Neural Networks
Department of Electronics Engineering, Madras Institute of Technology, Anna University, Chennai, 600044, India
* Corresponding Author: Vignesh Ochathevan. Email:
Congenital Heart Disease 2025, 20(4), 477-501. https://doi.org/10.32604/chd.2025.070372
Received 15 July 2025; Accepted 05 September 2025; Issue published 18 September 2025
Abstract
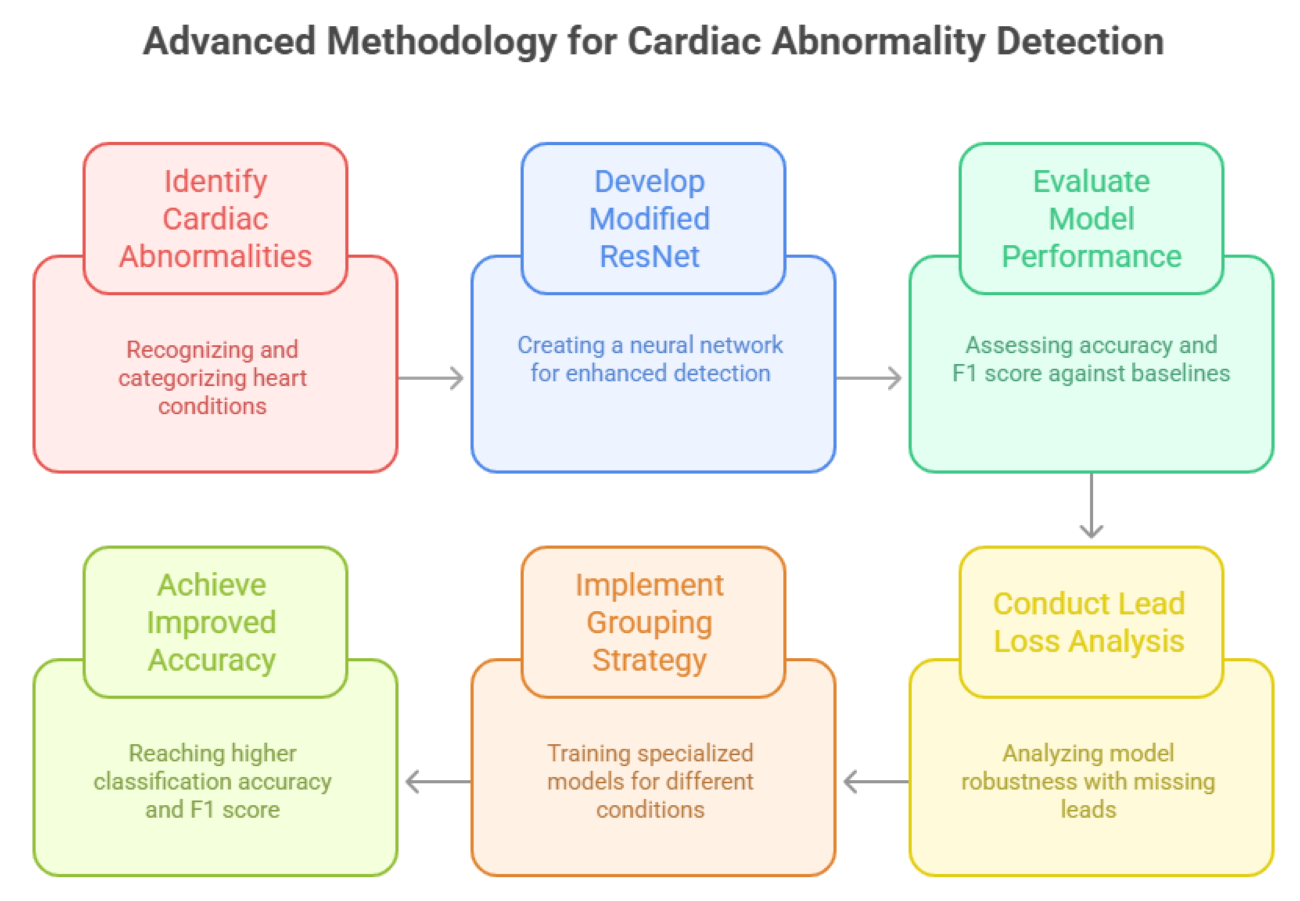
Background: The accurate identification of cardiac abnormalities is essential for proper diagnosis and effective treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Method: This work introduces an advanced methodology for detecting cardiac abnormalities and estimating electrocardiographic age (ECG Age) using sophisticated signal processing and deep learning techniques. This study looks at six main heart conditions found in 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) data. It addresses important issues like class imbalances, missing lead scenarios, and model generalizations. A modified residual neural network (ResNet) architecture was developed to enhance the detection of cardiac abnormalities. Results: The proposed ResNet demonst rated superior performance when compared with two linear models and an alternative ResNet architectures, achieving an overall classification accuracy of 91.25% and an F1 score of 93.9%, surpassing baseline models. A comprehensive lead loss analysis was conducted, evaluating model performance across 4096 combinations of missing leads. The results revealed that pulse rate-based factors remained robust with up to 75% lead loss, while block-based factors experienced significant performance declines beyond the loss of four leads. Conclusion: This analysis highlighted the importance of addressing lead loss impacts to maintain a robust model. To optimize performance, targeted training approaches were developed for different conditions. Based on these insights, a grouping strategy was implemented to train specialized models for pulse rate-based and block-based conditions. This approach resulted in notable improvements, achieving an overall classification accuracy of 95.12% and an F1 score of 95.79%.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools