 Open Access
Open Access
PROCEEDINGS
Full-Field Deformation Measurement Systems with Advanced Region-Based Image Alignment
School of Energy and Power Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, 102206, China
* Corresponding Author: Qinghua Wang. Email:
The International Conference on Computational & Experimental Engineering and Sciences 2025, 34(1), 1-2. https://doi.org/10.32604/icces.2025.012693
Abstract
This study presents a robust and automated image registration framework designed to enhance the precision and efficiency of full-field deformation measurement in experimental mechanics applications. Traditional optical techniques, such as the sampling moiré method, rely on manual alignment processes that introduce significant errors and inefficiencies, particularly when analyzing large datasets or operating under dynamic experimental conditions. Addressing these limitations, the proposed method integrates the Maximally Stable Extremal Regions (MSER) algorithm to automate the alignment of grating images with sub-pixel accuracy. The technique is specifically tailored to handle challenges arising from high-noise environments and complex deformation scenarios, such as those encountered during in-situ mechanical testing under microscopes.The core innovation lies in the adaptation of the MSER algorithm for grating image analysis (See Fig.1). Unlike traditional corner detection methods, which struggle with the repetitive and dense patterns of grating points, MSER excels at identifying stable extremal regions through iterative thresholding and watershed-inspired segmentation. By analyzing grayscale variations across incremental thresholds, the algorithm isolates regions exhibiting minimal area variation within user-defined regions of interest (ROI). The iterative adjustment process optimizes the threshold parameters and pixel count parameters to ensure reliable identification of microscale stains, serving as a reference point for registration.
The validation experiment was conducted in two different scenarios: low-noise images of aluminum samples and high-noise images of titanium alloy samples. For translational testing, images were displaced by 5-50 pixels in 5-pixel increments, while tensile simulations applied 0-30% stretching (0-10% for low-noise cases due to field-of-view constraints). Results demonstrated exceptional alignment accuracy, with centroid coordinate errors consistently below ±0.1 pixels in both translation and stretching modes (As shown in Fig.2). Theoretical and empirical analyses confirmed the linear relationship between applied displacements and detected feature shifts, validating the method's accuracy. It is worth noting that even under high noise conditions, the performance of this algorithm remains stable, as traditional methods often fail due to background interference.
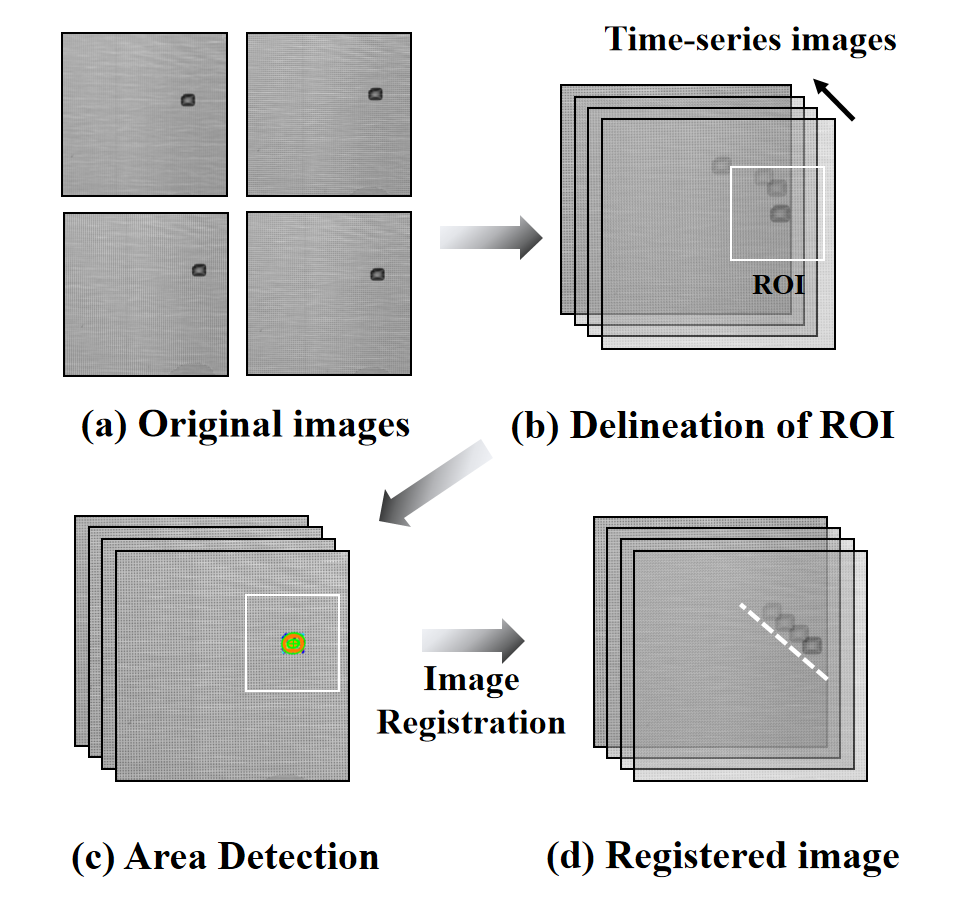
Figure 1: Time-series image registration process
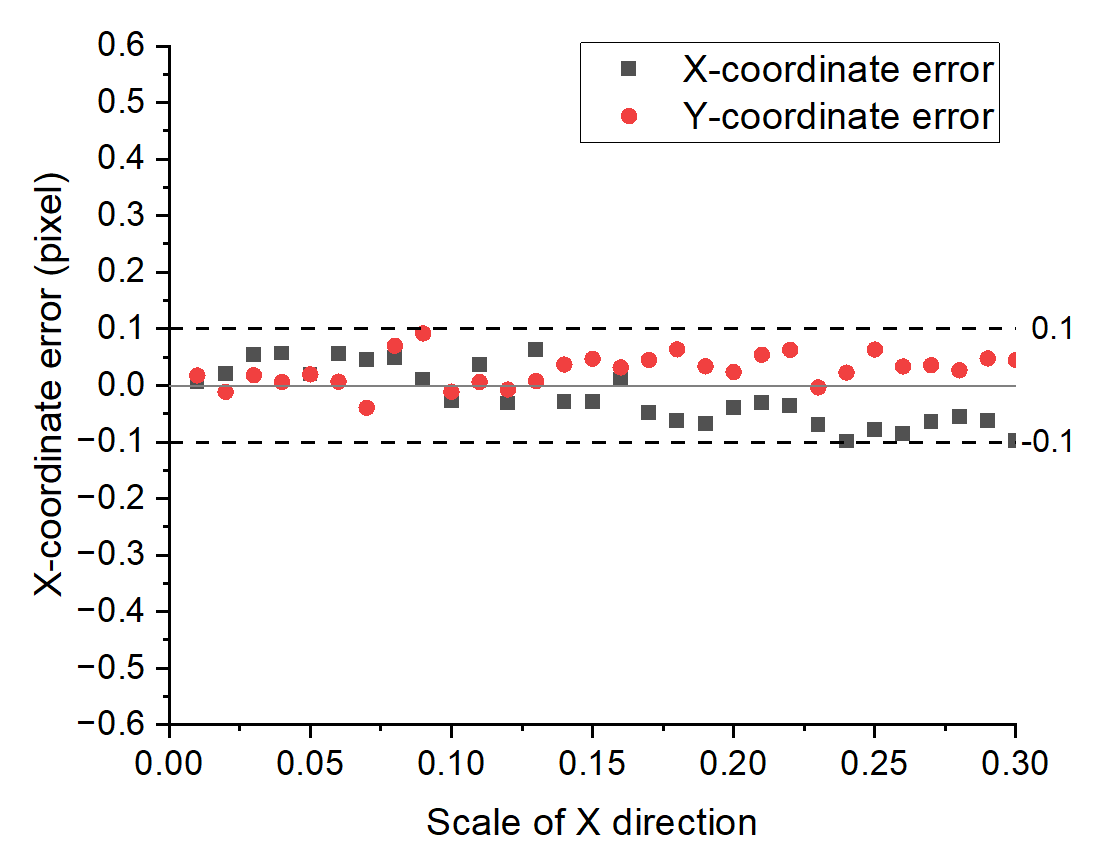
Figure 2: Registration error of high-noise stretched images
Practical implementation was further evaluated through tensile testing of notched single-crystal nickel alloy specimens. Grating patterns fabricated via UV lithography were subjected to incremental loads while monitored using a laser scanning microscope. In order to keep the gap area within the field of view, manual adjustment of the stage is required, but the stretching of the specimen still introduces displacement that cannot be completely corrected manually. The analysis after registration shows that the error area caused by dislocations is significantly reduced (See Fig.3). In conclusion, this registration strategy enables full automation of deformation measurements through the sampling moiré technique while expanding analyzable zones around critical defect areas like crack [1].

Figure 3: Comparison of strain fields in tensile process of single crystal nickel alloy before and after registration
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools