 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Significant Advancements in UAV Technology for Reliable Oil and Gas Pipeline Monitoring
1 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Seri Iskandar, Perak, 32610, Malaysia
2 Interdisciplinary Research Centre for Aviation and Space Exploration (IRC-ASE), King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM), Dhahran, 31261, Saudi Arabia
3 Department of Computer Engineering, University of Ilorin, Ilorin, 240003, Nigeria
* Corresponding Author: Ghulam E Mustafa Abro. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 142(2), 1155-1197. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.058598
Received 16 September 2024; Accepted 25 November 2024; Issue published 27 January 2025
Abstract
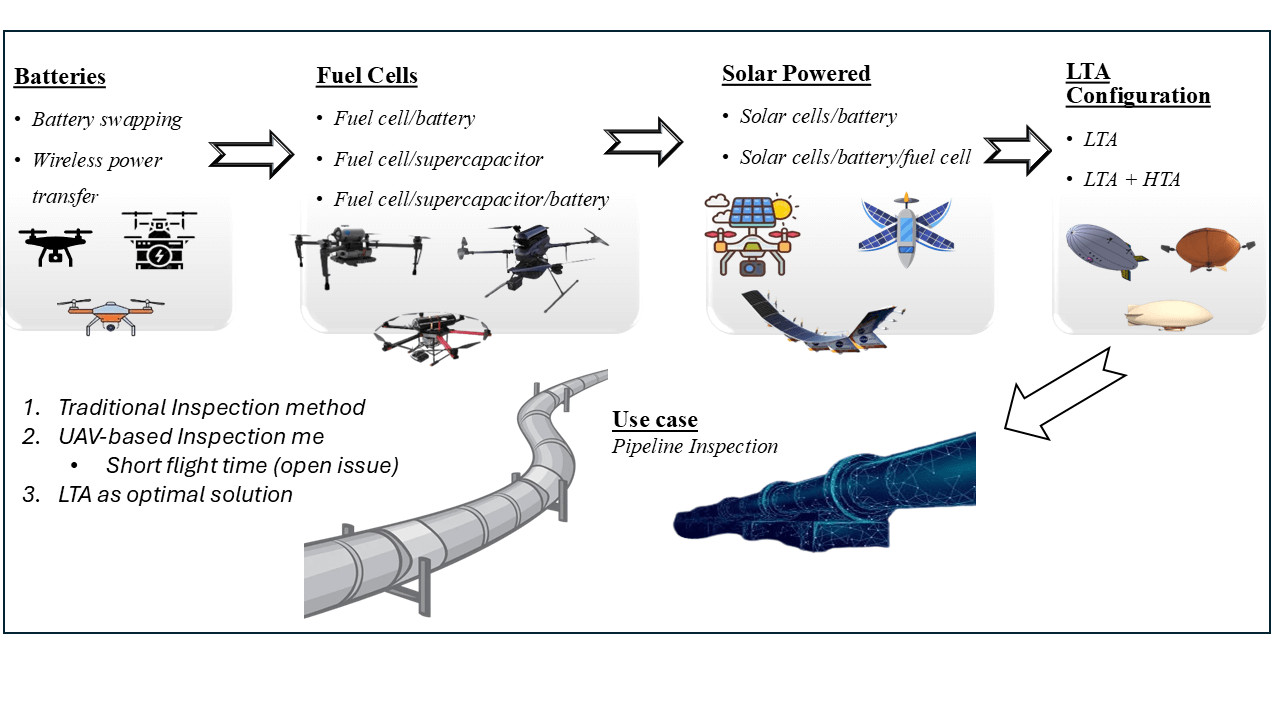
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) technology is rapidly advancing, offering innovative solutions for various industries, including the critical task of oil and gas pipeline surveillance. However, the limited flight time of conventional UAVs presents a significant challenge to comprehensive and continuous monitoring, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of pipeline infrastructure. This review paper evaluates methods for extending UAV flight endurance, focusing on their potential application in pipeline inspection. Through an extensive literature review, this study identifies the latest advancements in UAV technology, evaluates their effectiveness, and highlights the existing gaps in achieving prolonged flight operations. Advanced techniques, including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL), are reviewed for their roles in pipeline monitoring. Notably, DL algorithms like You Only Look Once (YOLO) are explored for autonomous flight in UAV-based inspections, real-time defect detection, such as cracks, corrosion, and leaks, enhancing reliability and accuracy. A vital aspect of this research is the proposed deployment of a hybrid drone design combining lighter-than-air (LTA) and heavier-than-air (HTA) principles, achieving a balance of endurance and maneuverability. LTA vehicles utilize buoyancy to reduce energy consumption, thereby extending flight durations. The paper details the methodology for designing LTA vehicles, presenting an analysis of design parameters that align with the requirements for effective pipeline surveillance. The ongoing work is currently at Technology Readiness Level (TRL) 4, where key components have been validated in laboratory conditions, with fabrication and flight testing planned for the next phase. Initial design analysis indicates that LTA configurations could offer significant advantages in flight endurance compared to traditional UAV designs. These findings lay the groundwork for future fabrication and testing phases, which will be critical in validating and assessing the proposed approach’s real-world applicability. By outlining the technical complexities and proposing specialized techniques tailored for pipeline monitoring, this paper provides a foundational framework for advancing UAV capabilities in the oil and gas sector. Researchers and industry practitioners can use this roadmap to further develop UAV-enabled surveillance solutions, aiming to improve the reliability, efficiency, and safety of pipeline monitoring.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools