 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Video-Based Human Activity Recognition Using Hybrid Deep Learning Model
1 School of Computer Science and Engineering, The University of Aizu, Aizuwakamatsu, 965-8580, Japan
2 Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Rajshahi University of Engineering & Technology, Rajshahi, 6204, Bangladesh
3 Statistics Discipline, Khulna University, Khulna, 9208, Bangladesh
4 Department of Computer Science, College of Computer and Information Sciences, King Saud University, Riyadh, 11543, Saudi Arabia
* Corresponding Author: Jungpil Shin. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Pattern Recognition)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 143(3), 3615-3638. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.064588
Received 19 February 2025; Accepted 23 May 2025; Issue published 30 June 2025
Abstract
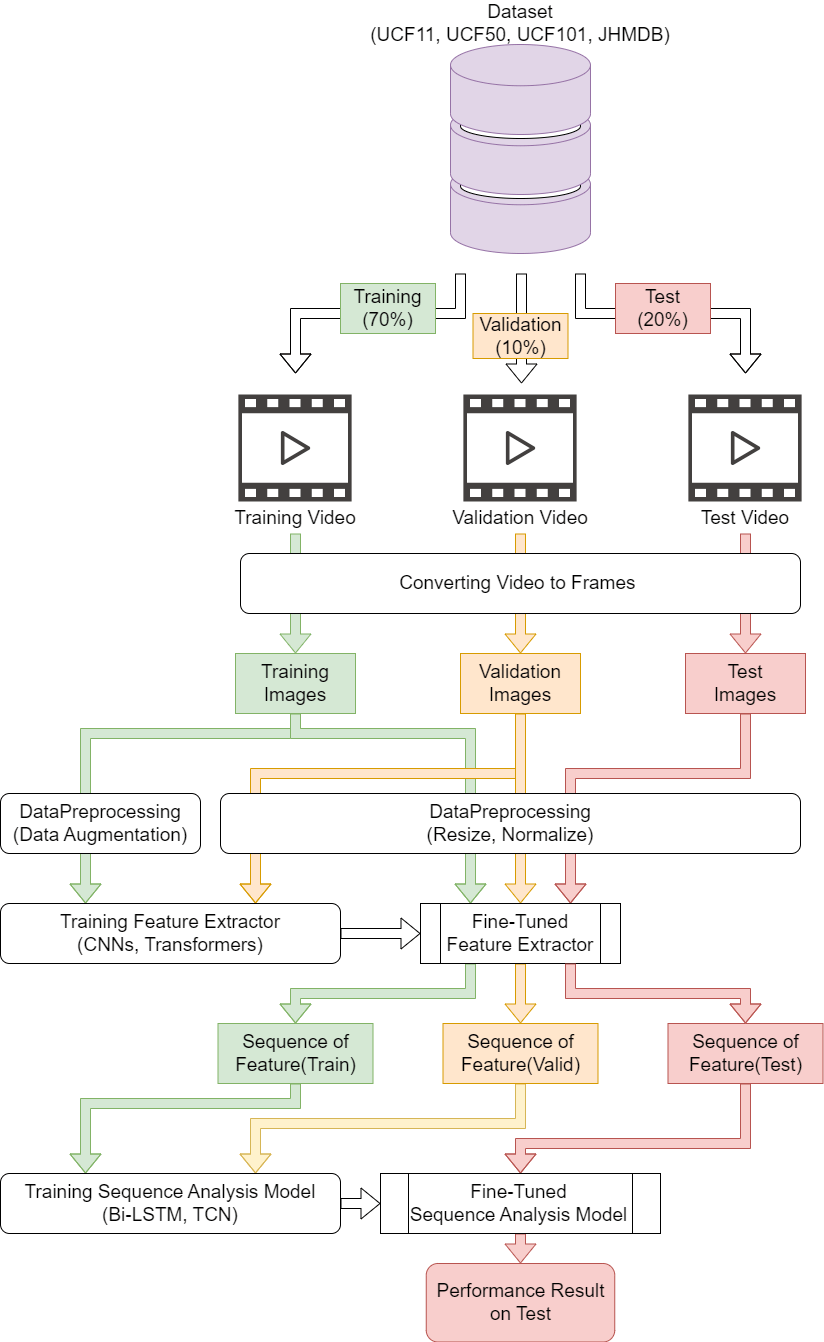
Activity recognition is a challenging topic in the field of computer vision that has various applications, including surveillance systems, industrial automation, and human-computer interaction. Today, the demand for automation has greatly increased across industries worldwide. Real-time detection requires edge devices with limited computational time. This study proposes a novel hybrid deep learning system for human activity recognition (HAR), aiming to enhance the recognition accuracy and reduce the computational time. The proposed system combines a pre-trained image classification model with a sequence analysis model. First, the dataset was divided into a training set (70%), validation set (10%), and test set (20%). Second, all the videos were converted into frames and deep-based features were extracted from each frame using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with a vision transformer. Following that, bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM)- and temporal convolutional network (TCN)-based models were trained using the training set, and their performances were evaluated using the validation set and test set. Four benchmark datasets (UCF11, UCF50, UCF101, and JHMDB) were used to evaluate the performance of the proposed HAR-based system. The experimental results showed that the combination of ConvNeXt and the TCN-based model achieved a recognition accuracy of 97.73% for UCF11, 98.81% for UCF50, 98.46% for UCF101, and 83.38% for JHMDB, respectively. This represents improvements in the recognition accuracy of 4%, 2.67%, 3.67%, and 7.08% for the UCF11, UCF50, UCF101, and JHMDB datasets, respectively, over existing models. Moreover, the proposed HAR-based system obtained superior recognition accuracy, shorter computational times, and minimal memory usage compared to the existing models.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools