 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Deployable and Accurate Time Series Prediction Model for Earth-Retaining Wall Deformation Monitoring
1 Department of Geotechnical Engineering Research, Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology, Goyang-si, 10223, Republic of Korea
2 Department of Industrial Engineering, Yonsei University, Seoul, 03722, Republic of Korea
* Corresponding Author: Seunghwan Seo. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 144(3), 2893-2922. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.069668
Received 27 June 2025; Accepted 19 August 2025; Issue published 30 September 2025
Abstract
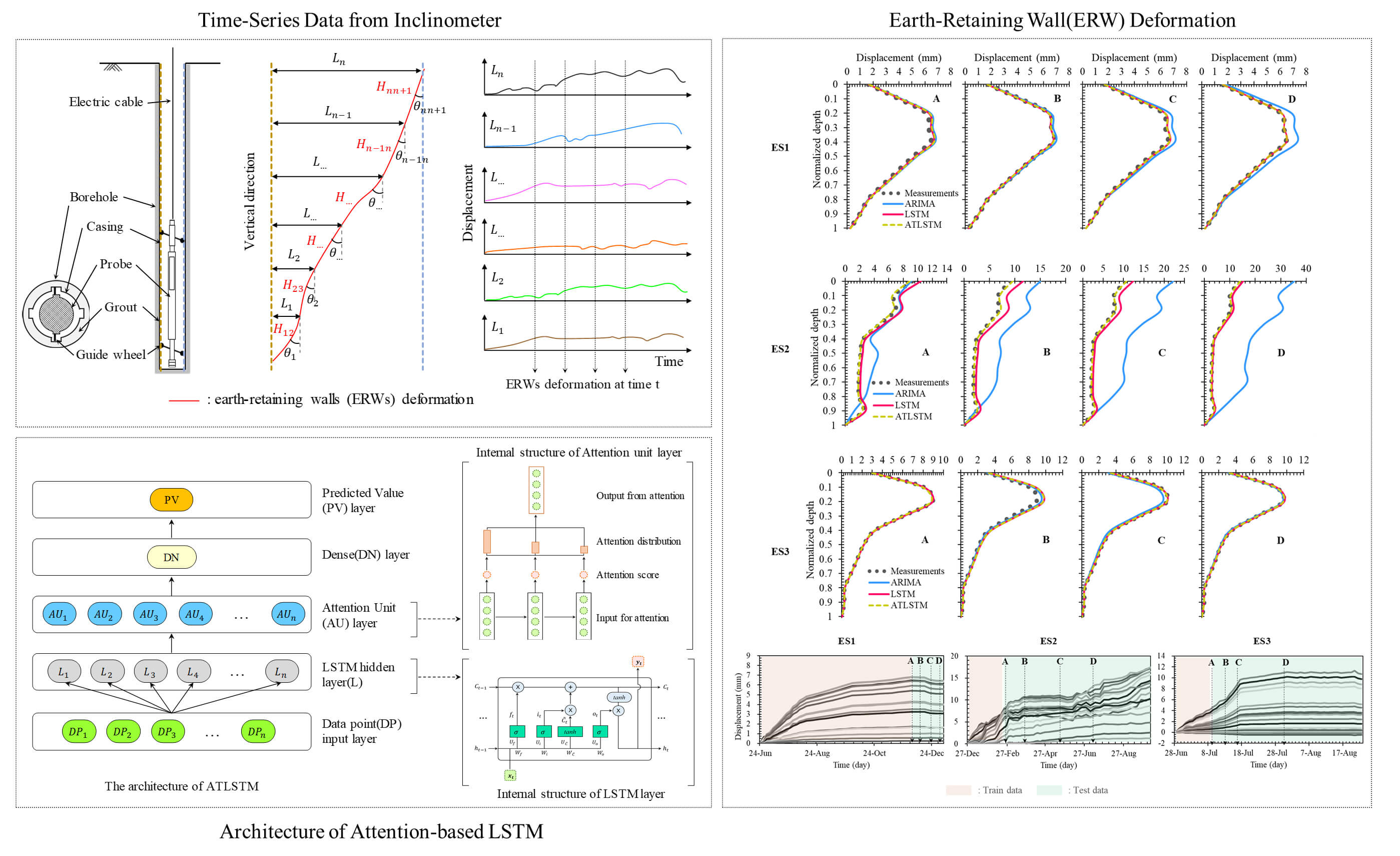
Excavation-induced deformations of earth-retaining walls (ERWs) can critically affect the safety of surrounding structures, highlighting the need for reliable prediction models to support timely decision-making during construction. This study utilizes traditional statistical ARIMA (Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average) and deep learning-based LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) models to predict earth-retaining walls deformation using inclinometer data from excavation sites and compares the predictive performance of both models. The ARIMA model demonstrates strengths in analyzing linear patterns in time-series data as it progresses over time, whereas LSTM exhibits superior capabilities in capturing complex non-linear patterns and long-term dependencies within the time series data. This research includes preprocessing of measurement data for inclinometer, performance evaluation based on various time series data lengths and input variable conditions, and demonstrates that the LSTM model offers statistically significant improvements in predictive performance over the ARIMA model. In addition, by combining LSTM with attention mechanism, attention-based LSTM (ATLSTM) is proposed to improve the short- and long-term prediction performance and solve the problem of excavation site domain change. This study presents the advantages and disadvantages of major time series analysis models for the stability evaluation of mud walls using geotechnical inclinometer data from excavation sites, and suggests that time series analysis models can be used effectively through comparative experiments.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools