 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Forecasting Performance Indicators of a Single-Channel Solar Chimney Using Artificial Neural Networks
1 División Académica de Ingeniería y Arquitectura, Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco, Tabasco, 86690, México
2 Facultad de Contaduría, Administración e Informática, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos, Morelos, 62209, México
3 Department of Engineering, Instituto de Matemática de Bahía Blanca (INMABB), Universidad Nacional del Sur-CONICET, Bahía Blanca, B8000CPB, Argentina
4 Facultad de Ingeniería, Universidad de la República, Montevideo, 11300, Uruguay
5 Departamento de Ingeniería Agrícola y Forestal, Universidad de Valladolid, Campus Duques de Soria, Soria, 42004, Spain
* Corresponding Authors: Carlos Torres-Aguilar. Email: ; Pedro Moreno. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovative Computational Models for Smart Cities)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 145(3), 3859-3881. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.069996
Received 05 July 2025; Accepted 03 November 2025; Issue published 23 December 2025
Abstract
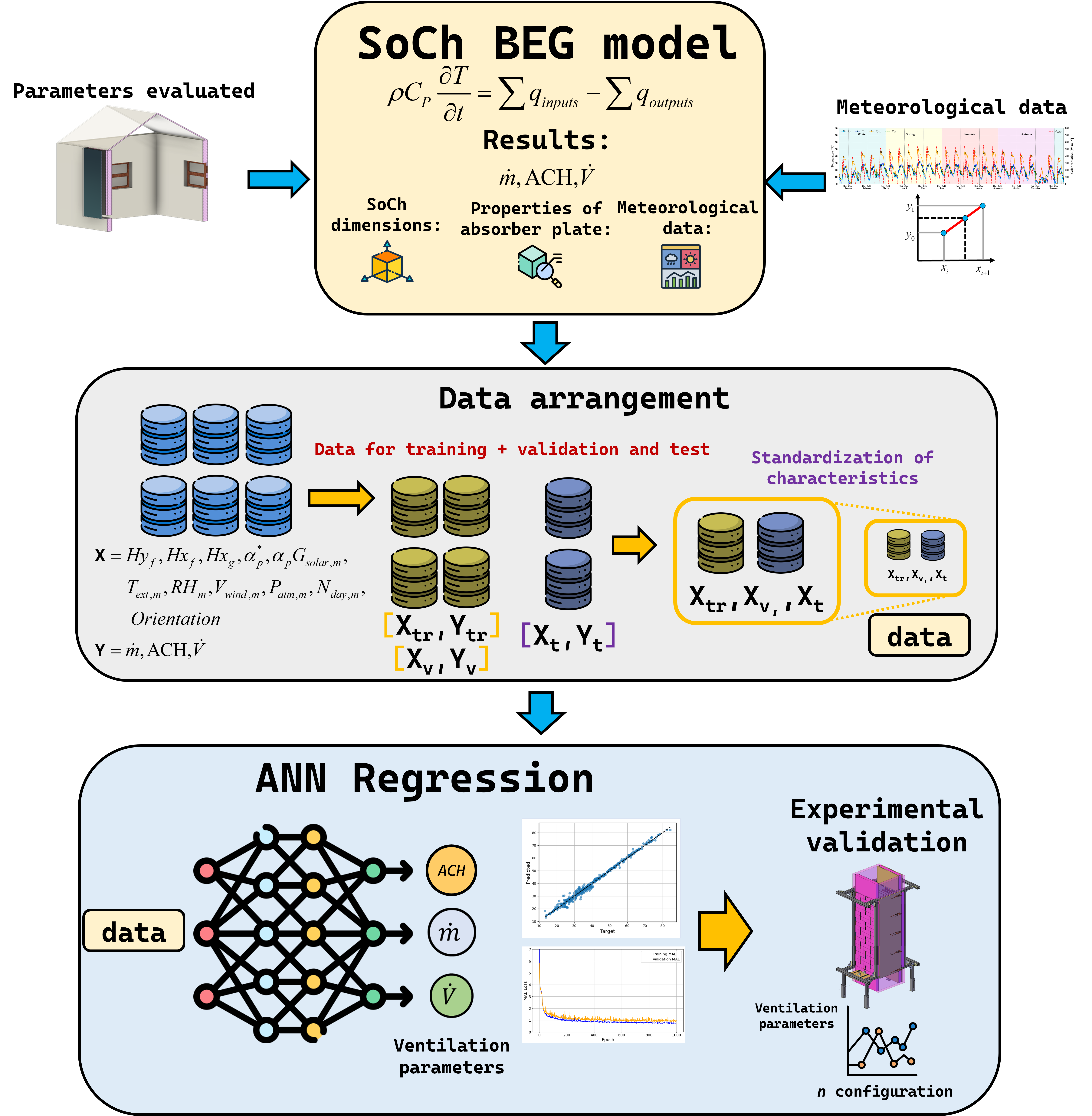
Solar chimneys are renewable energy systems designed to enhance natural ventilation, improving thermal comfort in buildings. As passive systems, solar chimneys contribute to energy efficiency in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way. The effectiveness of a solar chimney depends on its design and orientation relative to the cardinal directions, both of which are critical for optimal performance. This article presents a supervised learning approach using artificial neural networks to forecast the performance indicators of solar chimneys. The dataset includes information from 2784 solar chimney configurations, which encompasses various factors such as chimney height, channel thickness, glass thickness, paint, wall material, measurement date, and orientation. The case study examines the four cardinal orientations and weather data from Mexico City, covering the period from 01 January to 31 December 2024. The main results indicate that the proposed artificial neural network models achieved higher coefficient of determination values (0.905-0.990) than the baseline method across performance indicators of the solar chimney system, demonstrating greater accuracy and improved generalization. The proposed approach highlights the potential of using artificial neural networks as a decision-making tool in the design stage of solar chimneys in sustainable architecture.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools