 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Finite Element Analysis of the Influence of End Grouting Defects in Grouted Sleeve on the Structural Performance of Precast Reinforced Concrete Columns
1 Institute of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Ural Federal University, Yekaterinburg, 620062, Russia
2 Faculty of Mechanics and Mathematics, Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, 119991, Russia
* Corresponding Author: Shuoting Xiao. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Frontiers in Computational Modeling and Simulation of Concrete)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 145(3), 2821-2847. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.071961
Received 16 August 2025; Accepted 20 November 2025; Issue published 23 December 2025
Abstract
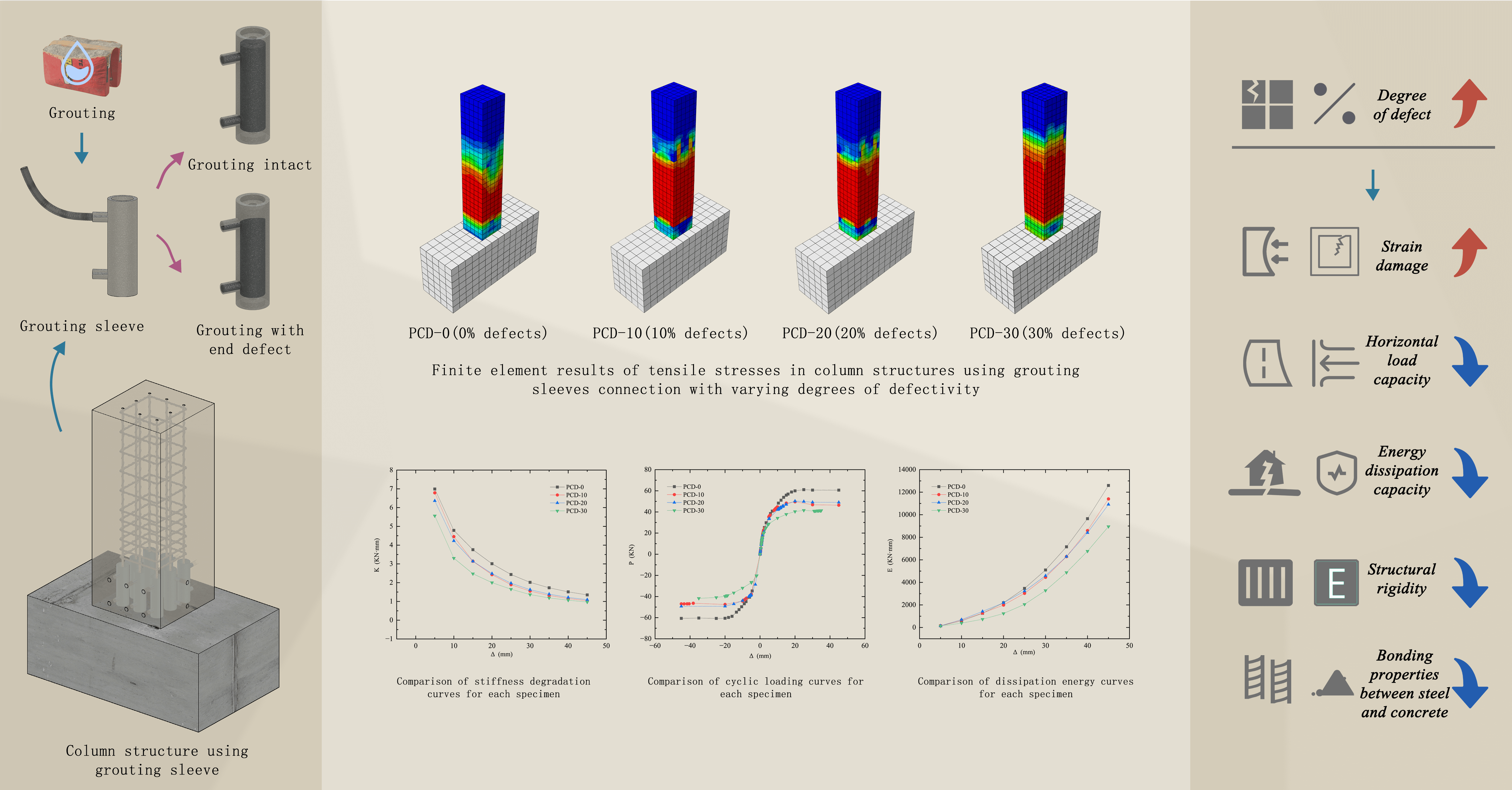
Precast concrete structures have gained popularity due to their advantages. However, the seismic performance of their connection joints remains an area of ongoing research and improvement. Grouted Sleeve Connection (GSC) offers a solution for connecting reinforcements in precast components, but their vulnerability to internal defects, such as construction errors and material variability, can significantly impact performance. This article presents a finite element analysis (FEA) to evaluate the impact of internal grouting defects in GSC on the structural performance of precast reinforced concrete columns. Four finite element models representing GSC with varying degrees of defects were used to investigate the effects on mechanical properties, including bearing capacity, stress-deformation behavior, and stiffness degradation. The study highlights the significant impact of internal grouting defects on the mechanical performance of GSC, with findings indicating a decrease in stiffness, increased plastic deformation, and reduced energy dissipation as the proportion of internal defects rises. The analysis reveals that the internal defects in GSC act as stress concentration points, leading to early crack formation and accelerated damage under cyclic loading. By improving construction quality and reducing the prevalence of grouting defects, the adverse effects on the performance of GSC can be mitigated. Compared to defect-free specimens, those with defects of 30% exhibited a 31.23% reduction in horizontal bearing capacity, highlighting the importance of minimizing defects in practical engineering applications.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools