 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
An Embedded Computer Vision Approach to Environment Modeling and Local Path Planning in Autonomous Mobile Robots
Computer Engineering Department, Bilecik Şeyh Edebali University, Bilecik, 11100, Türkiye
* Corresponding Author: Hakan Üçgün. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Environment Modeling for Applications of Mobile Robots)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 145(3), 4055-4087. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.072703
Received 02 September 2025; Accepted 11 November 2025; Issue published 23 December 2025
Abstract
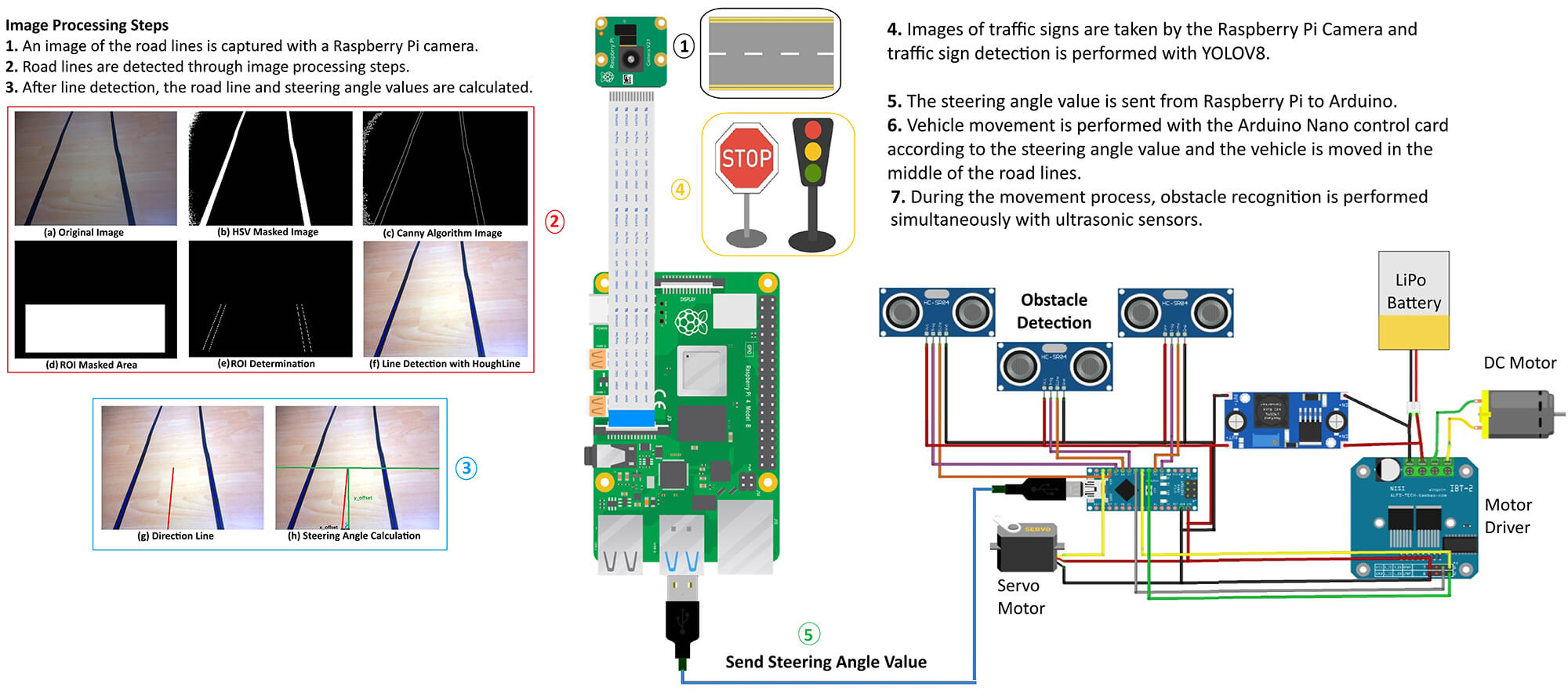
Recent advancements in autonomous vehicle technologies are transforming intelligent transportation systems. Artificial intelligence enables real-time sensing, decision-making, and control on embedded platforms with improved efficiency. This study presents the design and implementation of an autonomous radio-controlled (RC) vehicle prototype capable of lane line detection, obstacle avoidance, and navigation through dynamic path planning. The system integrates image processing and ultrasonic sensing, utilizing Raspberry Pi for vision-based tasks and Arduino Nano for real-time control. Lane line detection is achieved through conventional image processing techniques, providing the basis for local path generation, while traffic sign classification employs a You Only Look Once (YOLO) model optimized with TensorFlow Lite to support navigation decisions. Images captured by the onboard camera are processed on the Raspberry Pi to extract lane geometry and calculate steering angles, enabling the vehicle to follow the planned path. In addition, ultrasonic sensors placed in three directions at the front of the vehicle detect obstacles and allow real-time path adjustment for safe navigation. Experimental results demonstrate stable performance under controlled conditions, highlighting the system’s potential for scalable autonomous driving applications. This work confirms that deep learning methods can be efficiently deployed on low-power embedded systems, offering a practical framework for navigation, path planning, and intelligent transportation research.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools