 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
FGD5 as a novel prognostic biomarker and its association with immune infiltrates in lung adenocarcinoma
1 Department of Respiratory Medicine, Central South University, Xiangya Hospital, Changsha, 410078, China
2 Xiangya School of Medicine, Department of Medical Microbiology, Central South University, Changsha, 410078, China
* Corresponding Authors: LING QIN. Email: ; YURONG TAN. Email:
BIOCELL 2023, 47(11), 2503-2516. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.031565
Received 11 July 2023; Accepted 14 September 2023; Issue published 27 November 2023
Abstract
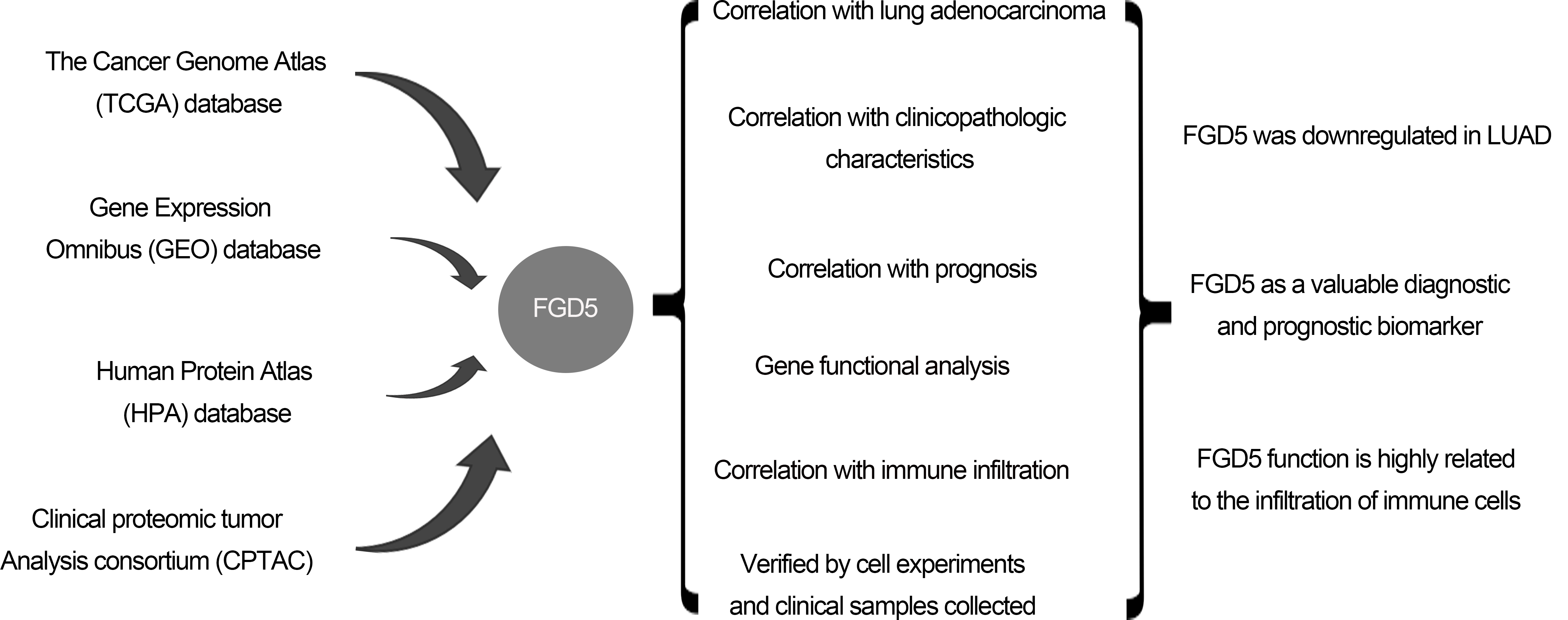
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has a poor prognosis with a low 5-year survival rate. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) accounts for 50%. Facio-genital dysplasia-5 (FGD5), a member of a subfamily of Rho GTP-GDP exchange factors, may be a good molecular biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis. Objective: To explore the clinical application of FGD5, the study was designed to investigate the prognosis value of FGD5 expression and its correlation with immune infiltrates in LUAD patients. Methods: Through the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and logistic regression, the correlation between clinical characteristics and FGD5 expression was analyzed. Kaplan–Meier plotter analysis, Cox regression, and a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were constructed to evaluate the influence of FGD5 on prognosis. The function of FGD5 in lung cancer was analyzed using Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and Single Sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (ssGSEA). Results: Compared to normal tissues, FGD5 was downregulated in LUAD. FGD5 may be a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of lung cancer for its association with improved overall survival (OS), progression-free interval (PFI), and disease-specific survival (DSS) in LUAD. Results of functional analysis suggested that FGD5 was involved in the immune response for its association with immune infiltration. Conclusion: FGD5 may be a significant molecular biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis, presenting as an independent prognostic risk factor for LUAD.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools