BIOCELL is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on molecular and cellular biosciences. The journal welcomes high quality original research articles, review papers, communications, perspectives, commentaries, etc. Topics of interests include but are not limited to: Cellular Biochemistry, Structural & Molecular Biology, Cellular/Molecular Biology, Immunology, Pathology & Neurobiology, Cell Signaling, Regenerative Biology & Stem Cells, Cancer Biology, RNA Biology, Genomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics & Metabolomics, Plant Molecular & Cellular Biology.
Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE): 2024 Impact Factor 1.0; Journal Citation Report/Science Edition (JCR); Scopus; Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 2.0; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.256; Sociedad Argentina de Investigaciones en Bioquímica y Biología Molecular (SAIB); Portico, etc.
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, pp. 1-22, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073776 - 14 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Melatonin and Mitochondria: Exploring New Frontiers)
Abstract Mitochondria are central regulators of cellular energy metabolism, redox balance, and survival, and their dysfunction contributes to neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, and metabolic diseases, as well as aging. Beyond its role as a circadian hormone, melatonin is now recognized as a key modulator of mitochondrial physiology. This review provides an overview of the mechanisms by which melatonin can preserve mitochondrial function through multifaceted mechanisms. Experimental evidence shows that melatonin enhances the activity of electron transport chain (ETC) complexes, stabilizes the mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψ), and prevents cardiolipin (CL) peroxidation, thereby limiting permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073221 - 14 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Melatonin and Mitochondria: Exploring New Frontiers)
Abstract As natural killer (NK) cells eliminate cancer cells and virus-infected cells, as well as modulate various other medical conditions, including aging-associated conditions such as neurodegenerative disorders, understanding NK cell regulation is of considerable clinical importance. This article reviews the role of circadian processes (melatonin and the cortisol system), aryl hydrocarbon receptor, and vagal nerve in the modulation of NK cell function, highlighting the importance of the endogenous mitochondrial melatonergic pathway in NK cells. As circadian and exogenous melatonin increase NK cell cytotoxicity, the presence of the endogenous melatonergic pathway may be of some importance not… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073252 - 14 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: The Role of γδ T Cells and iNKT Cells in Cancer: Unraveling Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential)
Abstract Gamma delta (γδ) T cells and invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells are unconventional T cells with limited T cell receptor (TCR) diversity. Both can recognize lipid or non-peptide antigens, often through cluster of differentiation 1d (CD1d), rapidly produce cytokines, express natural killer (NK) cell markers, and are mainly found in mucosal and barrier tissues. Acting as a bridge between innate and adaptive immunity, they show great promise for cancer immunotherapy. Developing γδ T and iNKT cells for treatment involves shared features like thymic origin, MHC-independent recognition, rapid cytotoxicity, low graft-vs.-host disease (GvHD) risk, ex vivo… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073551 - 14 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: The Role of γδ T Cells and iNKT Cells in Cancer: Unraveling Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential)
Abstract The paradigm of cancer treatment has been reshaped by chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) αβ T cell therapy, yet its full potential remains constrained by fundamental limitations. While conventional CAR αβ T cells have achieved notable success in hematological malignancies, their broader application is hindered by the high cost and delays of autologous manufacturing, as well as the critical risk of graft-vs-host disease (GvHD). In addition, their efficacy against solid tumors is often compromised by the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME). As a promising solution, γδ T cells are being developed as an alternative CAR platform. Their… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072780 - 14 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Cell Signaling Pathways in Health and Disease)
Abstract Atherosclerosis, characterized by the formation of fibrofatty lesions in the arterial wall, remains a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality. Emerging evidence highlights the critical regulatory roles of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) in atherogenesis. LncRNAs can function as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) by sponging miRNAs, thereby modulating the expression of downstream target mRNAs. This review summarizes current knowledge on lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks and their functional roles in the three major cell types involved in atherosclerotic plaque development: endothelial cells (ECs), vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), and macrophages. In ECs, these networks More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073576 - 14 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: NETs: A Decade of Pathological Insights and Future Therapeutic Horizons)
Abstract Objectives: Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) have emerged as critical effectors in immune defense but also as potential drivers of tissue damage in chronic inflammatory diseases. Their role in periodontitis, a highly prevalent condition characterized by dysregulated host–microbe interactions, remains incompletely defined. This systematic review aimed to synthesize, for the first time, ex vivo human evidence on the presence, activity, and clinical significance of NETs in periodontitis. Methods: A comprehensive search of Medline, Web of Science, and Scopus was conducted up to August 2025. Eligible studies included ex vivo human investigations assessing NETs or NET markers in gingival… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072227 - 14 February 2026
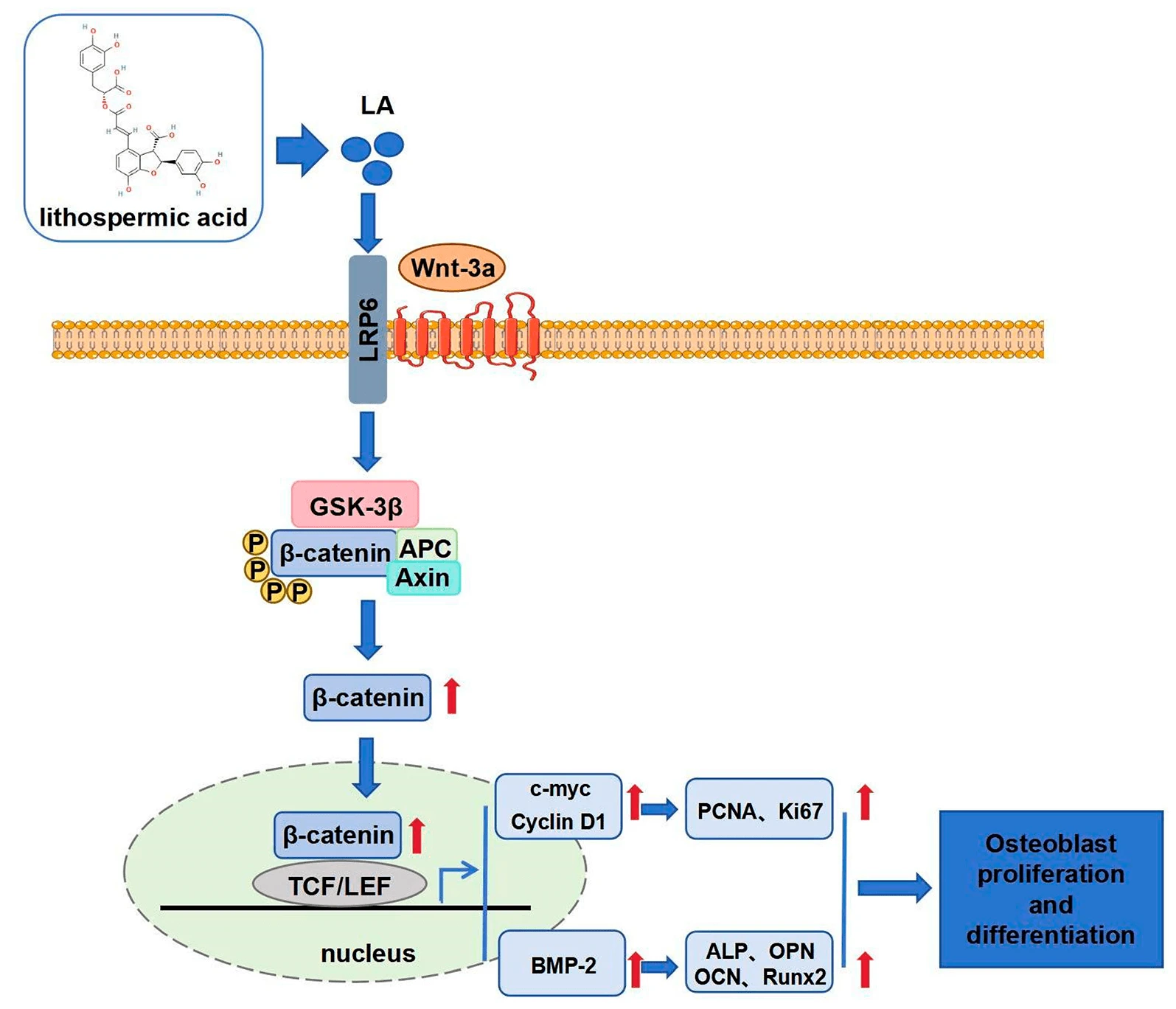
Abstract Objectives: Therapeutic strategies for enhancing bone regeneration and combating osteoporosis remain a significant unmet medical need. This study aims to elucidate Lithospermic acid (LA)’s regulatory effects on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, investigating its viability as a bone-healing agent. Methods: This study employed various cellular and molecular biology experiments to assess the effects of LA on the viability, proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, differentiation, mineralization, and migration of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Immunofluorescence and Western blot analyses were conducted to detect the expression of proteins related to the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, investigating the regulatory mechanisms by which LA promotes… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.074782 - 14 February 2026
Abstract Objectives: The discovery of novel molecular targets to enhance the osteogenesis of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (H-BMSCs) represents a promising strategy for preventing and treating osteoporosis. Thus, the primary objective of this study is to elucidate the mechanisms by which long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 (lncRNA FOXD2-AS1) regulates early osteogenic differentiation in H-BMSCs, thereby identifying potential therapeutic targets. Methods: Lentivirus-mediated vectors were constructed to either overexpress or silence FOXD2-AS1 in H-BMSCs. The effects of FOXD2-AS1 on osteogenesis were subsequently assessed by analyzing osteogenic marker expression and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining. To clarify the role… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.071651 - 14 February 2026
Abstract Objectives: Dysregulated osteoclast function contributes to skeletal diseases. However, the specific ubiquitination regulators of the osteoclastogenesis repressor MafB, particularly at the post-translational level, remain undefined. This study aims to identify ubiquitin-specific proteases (USPs) that deubiquitinate MafB and enhance its stability. Methods: We constructed a MafB-conjugated luciferase and overexpressed 40 individual USPs, measuring changes in luciferase activity. The identified USP was overexpressed in human CD14+ peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to evaluate its effect. Osteoclast differentiation was assessed through osteoclast marker Integrin alpha-V (CD51) staining and Western blot analysis. Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) was performed to assess the interplay.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073728 - 14 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: MitoROS: Exploring Mitochondria and Oxidative Stress)
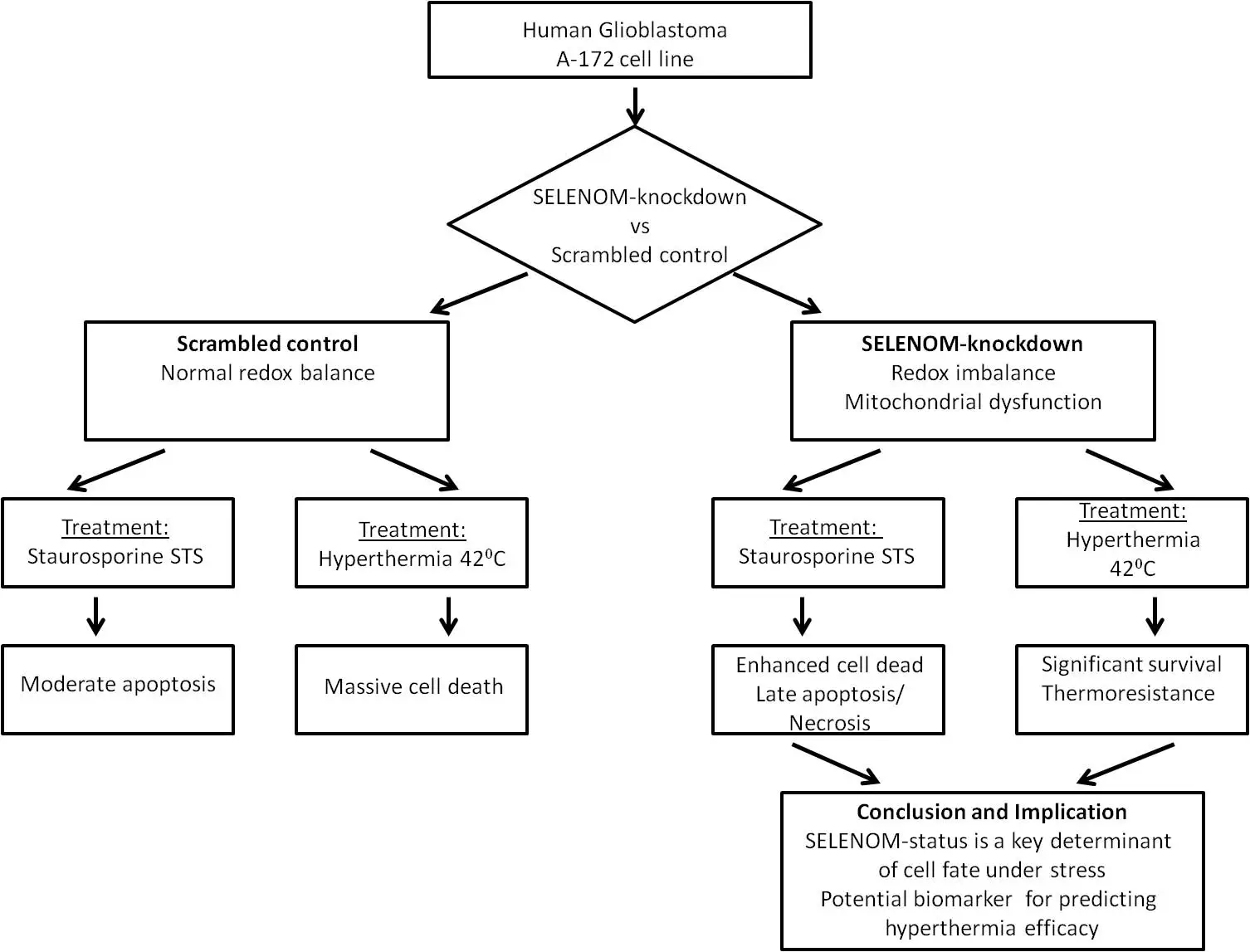
Abstract Objectives: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is highly resistant to apoptosis. This study investigates the role of Selenoprotein M (SELENOM), a redox-regulating protein, in the response of human glioblastoma A-172 cells to staurosporine (STS) and hyperthermia. Methods: A stable SELENOM-knockdown (SELENOM-KD) cell line was created. We measured reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), cell death, and apoptotic gene expression. Results: SELENOM-KD increased basal ROS levels and induced mitochondrial dysfunction. It sensitized cells to STS-induced apoptosis, enhancing the upregulation of pro-apoptotic genes. Conversely, under hyperthermia (42°C), SELENOM-KD cells exhibited significant thermoresistance, with 52% survival vs. 99% death More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.075574 - 14 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Natural Product-Based Anticancer Drug Discovery)
Abstract Objective: Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) contribute to chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), yet strategies to reprogram TAMs while enhancing chemotherapy efficacy remain limited. This study investigated whether Viscum album L. var. coloratum agglutinin (VCA) could sensitize TNBC cells to doxorubicin (DOX) and modulate TAM-mediated chemoresistance in three-dimensional (3D) co-culture models. Methods: MDA-MB-231 TNBC cells were co-cultured with RAW264.7 macrophages in collagen-embedded 3D spheroids. Spheroid viability was assessed using an ATP-based luminescent assay. Cytokine secretion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers were measured using ELISA and Western blotting. Drug synergy was evaluated using combination index (CI) calculations. Results: VCA-DOX More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.50, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.074128 - 14 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: The Role of γδ T Cells and iNKT Cells in Cancer: Unraveling Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential)
Abstract Objectives: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is characterized by progressive immune dysregulation. Invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells support immune surveillance, but the clinical relevance of their regulatory subsets remains unclear. FoxP3+ regulatory iNKT cells (iNKTreg) and E4BP4+IL-10+ (iNKT10) cells may reflect immunoregulatory changes associated with disease progression. The study aimed to quantify circulating iNKTreg and iNKT10 subsets and monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (M-MDSCs) in treatment-naïve CLL patients and evaluate their associations with disease characteristics and time to first treatment (TTFT). Methods: Peripheral blood samples from 60 untreated CLL patients and 20 healthy donors were analyzed by… More >