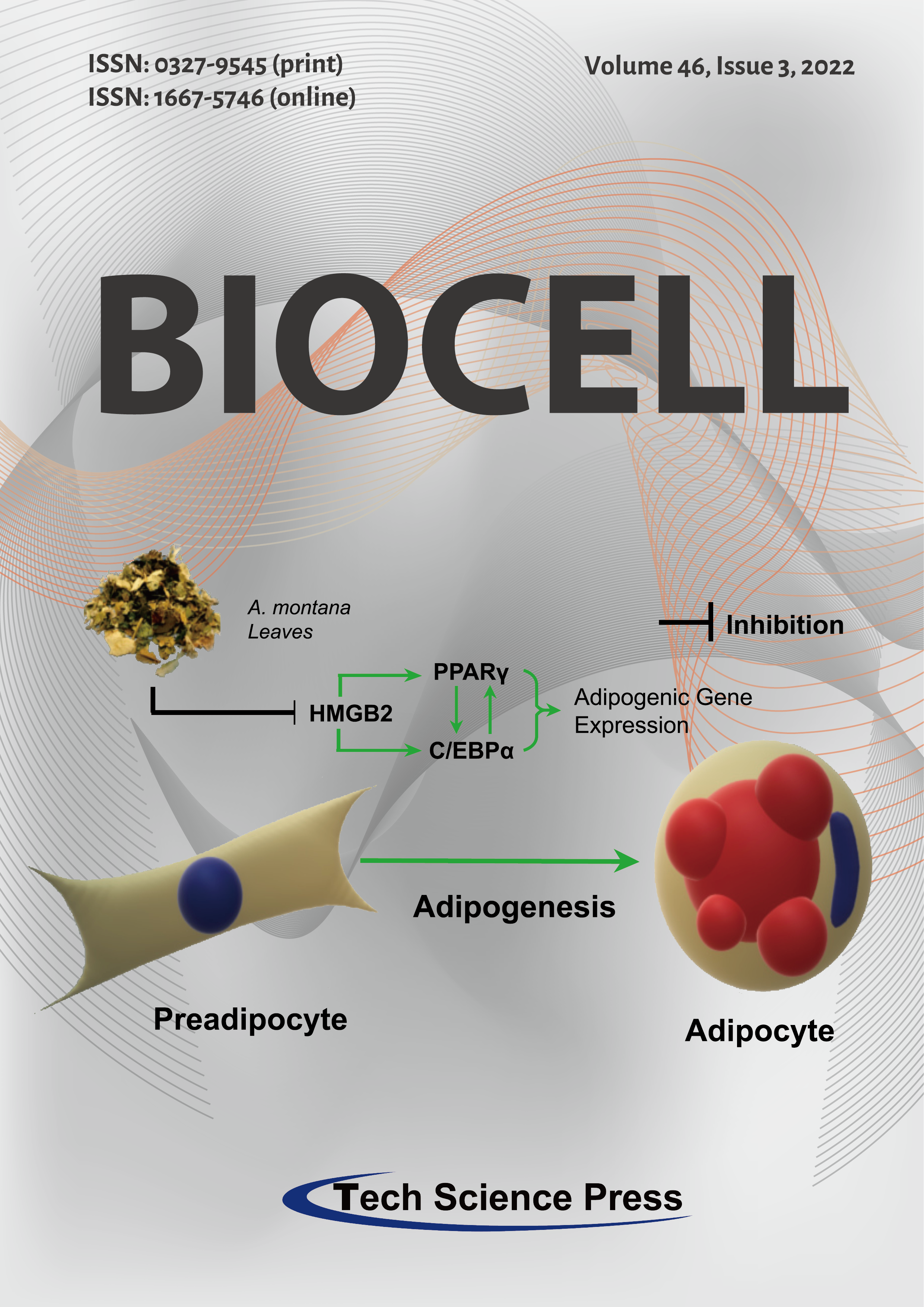
Annona montana-mediated inhibitory effect on both human and murine adipogenesis was shown to be exerted via a significant decrease in the accumulation of lipid content by both a dramatic reduction of size and number of lipid droplets. Annona montana leaves’ extract strongly attenuated the expression of HMGB2, which correlate with the decrease of the expression of CEBPα, and PPARγ via the modulation of the Akt signaling pathway. Thus, Annona montana leaves’ extract blocks adipogenesis of fibroblasts by selectively altering expression of several adipogenic factors.
View this paper