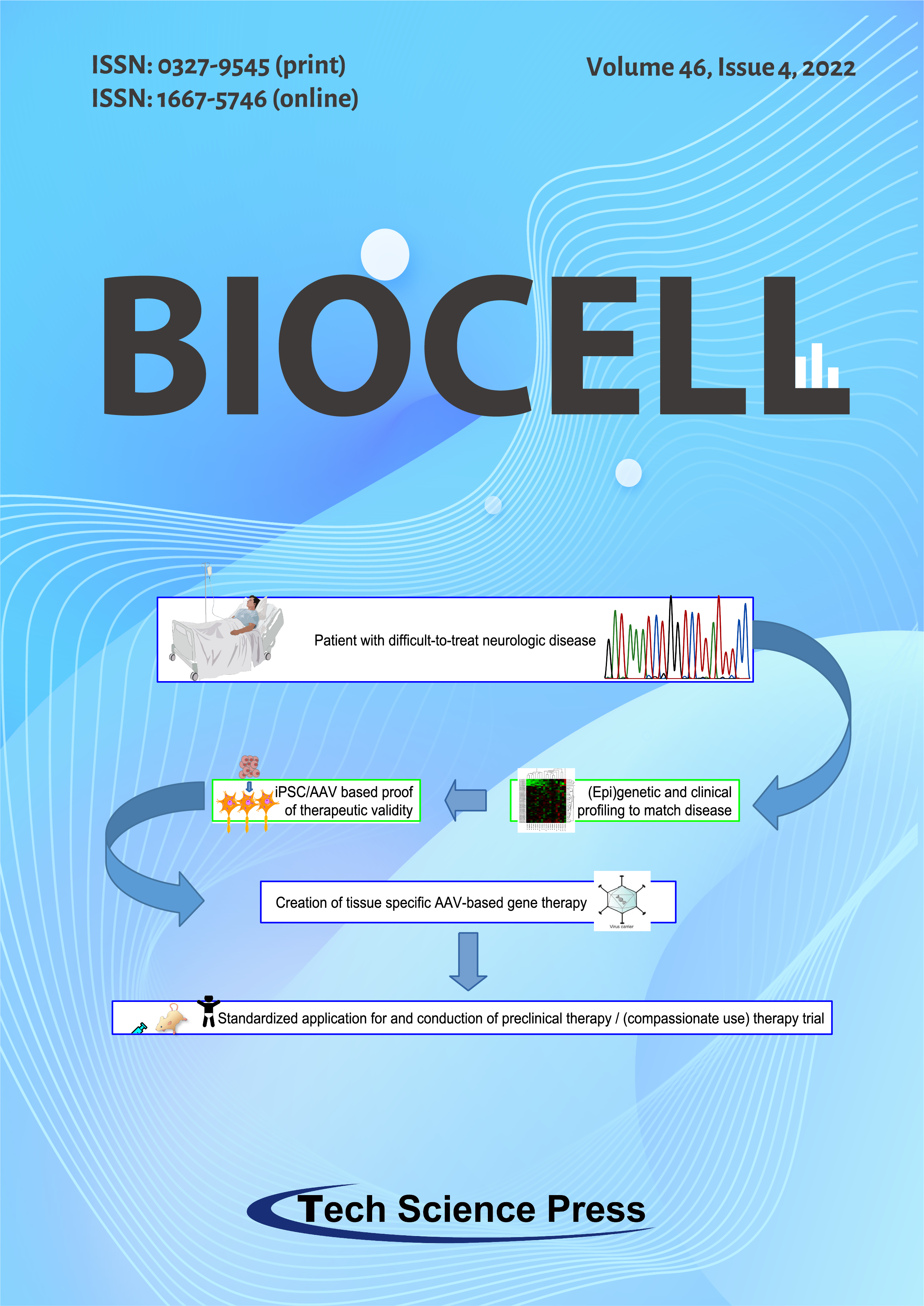
Tauopathies comprise a spectrum of genetic and sporadic neurodegenerative diseases mainly characterized by hyperphosphorylated TAU protein accumulations and aggregations in neurons and/or glia. Gene-therapy, in particular adeno-associated virus/AAV-based, is an effective medical approach for difficult-to-treat genetic diseases for which there are no convincing traditional therapies, such as tauopathies. We outline a future vision for the application of this promising therapeutic approach for genetic and sporadic tauopathies: Upon admission, patients suffering from a difficult to treat neurologic disease will be subjected to (epi)genetic and clinical profiling to match their disease entity to a known genetic disease. Next, iPSC/AAV-based studies will help to design and validate (patient-tailored if necessary) gene-therapy approach, with a pipeline set up for fast (pre-)clinical studies.
View this paper