 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Rashid Mir1,*, Jameel Barnawi1, Naseh A. Algehainy1, Mohammed M. Jalal1, Malik A. Altayar1, Mohammad A. Alanazi1, Mamdoh Moawadh1, Faris J. Tayeb1, Syed Khalid Mustafa2, Abdullatif Taha Babakr3, Umair Manghrio4, Jaber Alfaifi5, Faisal H. Altemani1
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.076199
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Epigenetic and ncRNA Biomarkers in Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Value)
Abstract Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is one of the most complex hematological malignancies associated with the rapid production of immature myeloid cells and poor prognosis, even with the development of therapeutic options. Exosomes, which are extracellular vesicles with sizes ranging from 30 to 150 nm, have drawn a lot of interest because of their capacity to carry molecular cargoes, including DNA, mRNA, and non-coding RNAs. Various cells produce these vesicles, which have been shown to effectively transport their molecular contents to target cells via a variety of bodily fluids. This review comprehensively discusses the importance of More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Ralf Weiskirchen1, Amedeo Lonardo2,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.076177
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Insights into the Obesity-Cancer Nexus: From Cellular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Targets)
Abstract Obesity is a complex chronic condition characterized by an excess of body fat that manifests in various clinical pathophenotypes, each affecting liver health differently. One significant cause of chronic liver diseases among those living with obesity is metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), which is linked to one or more cardiometabolic risk factors in individuals who do not engage in harmful alcohol consumption. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common form of primary liver cancer and is increasingly being associated with MASLD through intricate immunological, cellular, proinflammatory, molecular, and genetic mechanisms. In this review, we More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Christoph Rehbach1, Patrick A. H. Ehm2,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075170
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Targeted Therapy in Oncology)
Abstract Despite improved overall prognosis, the treatment of high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) remains challenging due to the toxicity of intensive polychemotherapy and the limited efficacy of antibody-targeted therapies beyond cluster of differentiation 20 and 22 (CD20 and CD22). ALL is driven not only by genetic alterations but also by profound epigenetic dysregulation, including promoter hypermethylation that also silences surface receptor genes. This epigenetic repression can reduce the efficacy of targeted immunotherapies and contribute to relapse. Epigenetic reprogramming with DNA demethylating agents (e.g., decitabine) has the potential to restore the expression of key B cell receptors… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Desirée Victoria-Montesinos*, Pablo Barcina-Pérez*, Ana María García-Muñoz
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.077286
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: MitoROS: Exploring Mitochondria and Oxidative Stress)
Abstract Mitochondrial dysfunction is a central hallmark of metabolic, hepatic, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative diseases. Dietary polyphenols modulate mitochondrial pathways, but their integrated effects remain poorly appreciated. This narrative review synthesizes preclinical and clinical evidence on four polyphenols (resveratrol, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, quercetin, and oleuropein) and examines their mechanisms in mitochondrial biogenesis, mtDNA protection, and mitophagy. Experimental studies indicate that these compounds activate conserved adaptive pathways, including sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1α), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) with Parkin, therapy enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis, reducing oxidative stress, and promoting More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rihui Wang1,2,#, Wanlu Li3,#, Canyang Jiang1,2, Jianping Huang1,2, Kangwei Zhou1,2, Yan Jiang4,5, Junyang Zhang1,2, Li Huang1,2,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075875
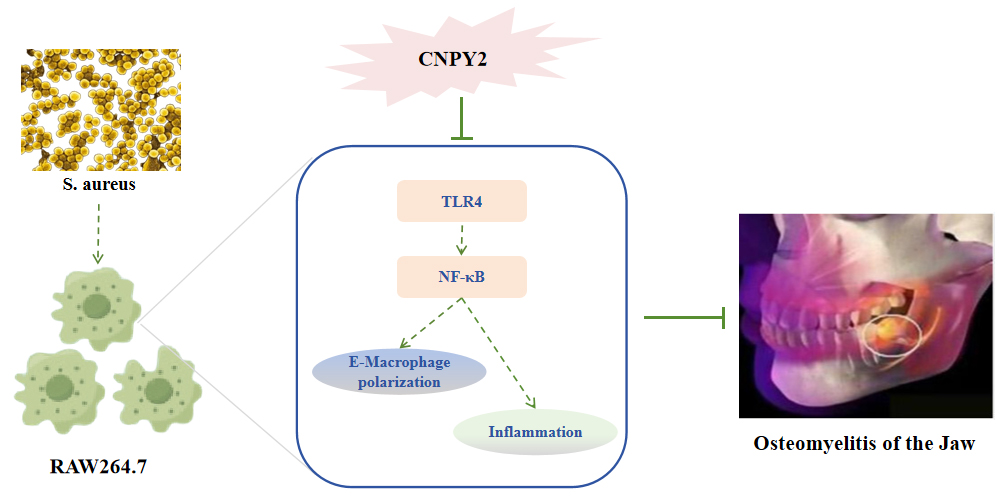
Abstract Background: Osteomyelitis of the jaw (OMJ) is a severe infectious bone disease. While Canopy FGF signaling regulator 2 (CNPY2) is known to regulate inflammatory diseases, its role in OMJ remains unclear. The study aimed to investigate the role of CNPY2 in the mandibular joint and its molecular mechanisms. Methods: An in vitro OMJ model was generated by stimulating RAW264.7 macrophages with S. aureus. CNPY2 knockdown and overexpression models were established using siRNA and plasmids. Functional assays assessed cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Macrophage polarization, cytokine secretion, and osteoclast differentiation were analyzed. The CNPY2-Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/Nuclear factor-kappa B… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ju Li1, Pengcheng Rao1, Dan Yang1, Tong Zhou1, Jianguo Gan1, Die Lv1, Shuting Zhou1, Yang Peng1, Xiaoqiang Xia1, Qianming Chen1, Yuchen Jiang1, Jian Jiang2, Xiaoping Xu1,*, Xiaodong Feng1,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075437
Abstract Objective: Multiple programmed cell death (PCD) pathways have been individually reported to be triggered by cisplatin, but whether and how they are co-regulated remains unclear. In this study, we comprehensively investigate the spectrum of cisplatin-induced PCD. Methods: We employed integrated in vitro and in vivo models, including human cancer cell lines, a Cal27 xenograft mouse model, and paired clinical specimens from an oral squamous cell carcinoma patient receiving neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy. A comprehensive methodological suite-encompassing cell death assays, Western blotting, Hematoxylin and eosin staining, immunofluorescence, Cyclic multiplexed tissue staining, and pathway-specific pharmacological inhibitors was utilized to dissect the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Andrew Scarborough1, Yvoni Kyriakidou1, Derek C. Lee2, Tomás Duraj2, Thomas N. Seyfried2, Isabella D. Cooper1,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.074152
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Homeostasis of Mitochondria: Unraveling its Multifaceted Role in Health and Disease)
Abstract The global rise in chronic, non-communicable diseases (NCDs) is inextricably linked to metabolic dysfunction, with hyperinsulinaemia acting as a potent upstream driver of ageing and age-related disease. Some of the most burdensome diseases of our time, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), are largely underpinned by insulin resistance as part of a broader system of metabolic and mitochondrial dysfunction. These pathologies are particularly pronounced in the developed world, where obesity and other lifestyle-related conditions are major contributors to disease burden and premature mortality. As an upstream… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xingchang Fu, Gang Yang*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.074951
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Modulation of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Function: Therapeutic Perspectives Across Diseases)
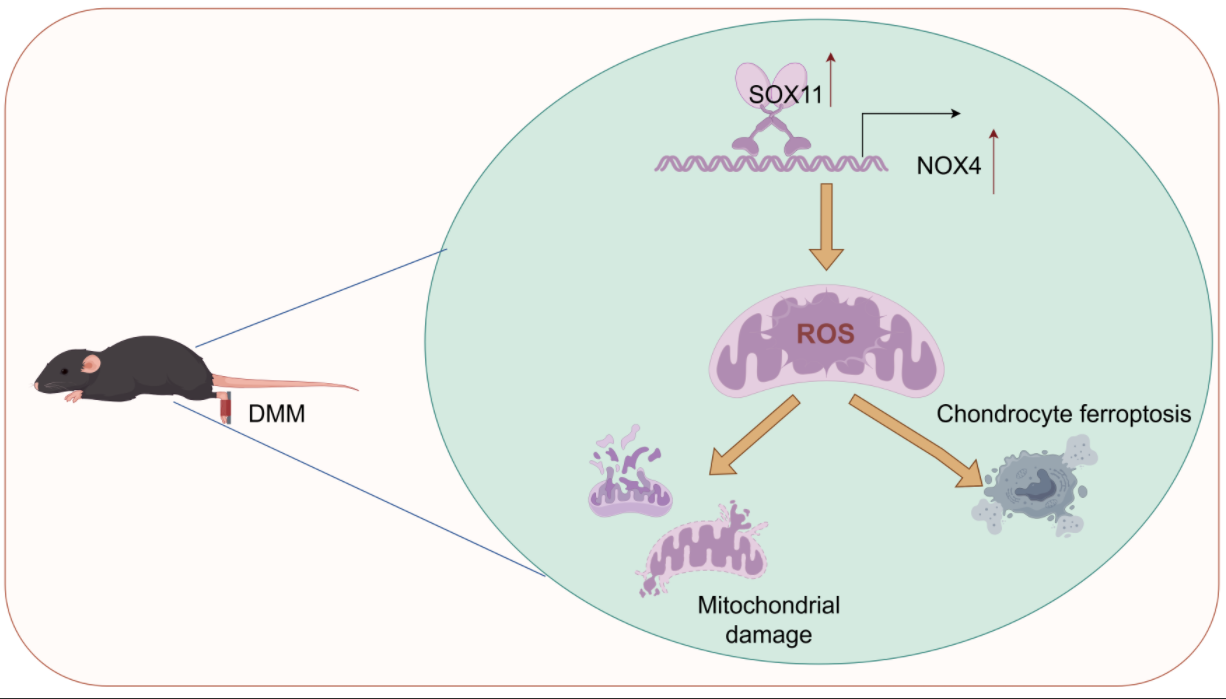
Abstract Objectives: Mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis play crucial roles in osteoarthritis (OA), but the mechanisms remain unclear. This study aims to investigate the mechanism of sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor (SOX) 11/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase 4 (NOX4) axis-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis in OA. Methods: Destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) induced knee OA in mice. Chondrocytes were stimulated with IL-1β. Ferroptosis and mitochondrial function-related indicators were detected by immunofluorescence, 5,5′,6,6′-Tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethyl-imidacarbocyanine iodide (JC-1) staining, flow cytometry, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), and Western blot. Results: OA mice had 4.4 and 1.1-fold increase in SOX11… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
YONG JIANG*, RUI MA, YU-GE WU, YI-MING HUO, HAN-ZHU ZHOU, JUN-XUAN ZHANG
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075982
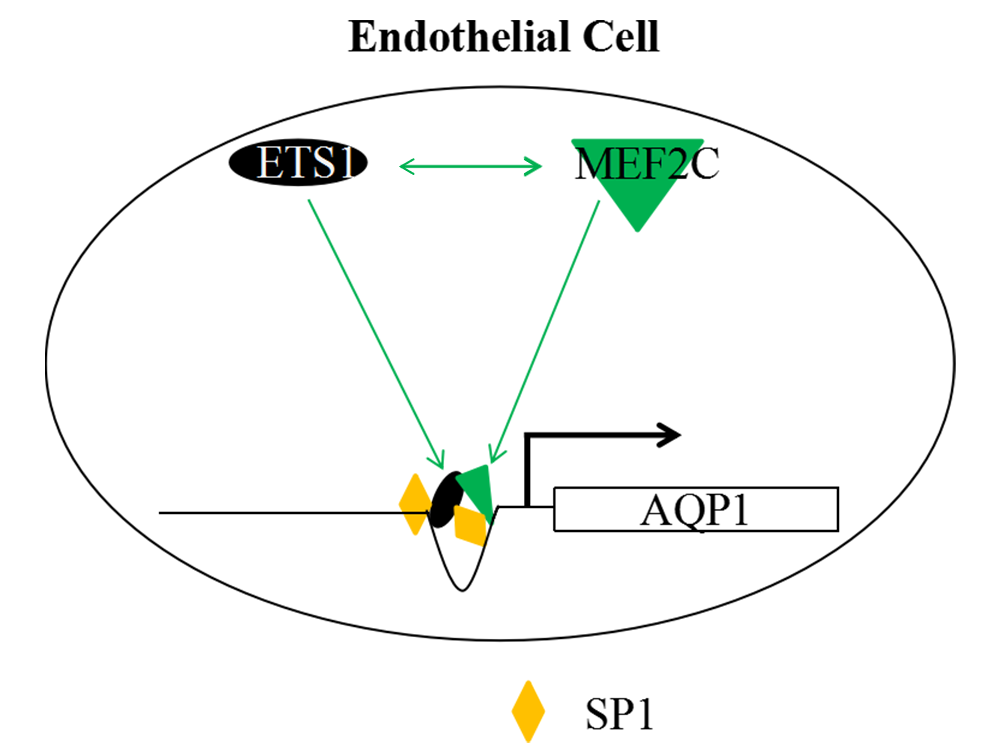
Abstract Background: Aquaporin 1 (AQP1) plays a key role in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. This study aimed to elucidate the mechanisms by which erythroblast transformation-specific 1 (ETS1) and myocyte enhancer factor 2C (MEF2C) regulated AQP1 transcription. Methods: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and rats with coronary heart disease were employed for in vitro and in vivo experiments, respectively. Expressions of ETS1, MEF2C, and AQP1 were analyzed by western blotting and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assays were performed to confirm the interactions between ETS1 and MEF2C. Scratch wound healing and… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Jernej Jorgačevski1,2, Maja Potokar1,2,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.077871
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Transporters and Channels in Brain Physiology: From Molecular Biophysics to Cellular Dynamics)
Abstract Astrocytes contribute to central nervous system (CNS) homeostasis by taking up and releasing various transmitters, ions, water, and energy molecules, thereby modulating neuronal function and maintaining the blood-brain barrier. The dynamic delivery, retrieval, and recycling of transporters, channels, receptors, and vesicular cargo at the astrocyte plasma membrane are regulated by the cytoskeleton networks composed of microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments. Increasing evidence indicates that changes in vesicle trafficking disrupt astrocyte–neuron communication and contribute to CNS dysfunction in pathological conditions. This review presents recent findings on vesicle trafficking in astrocytes with emphasis on the cytoskeletal More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Debasish Bandyopadhyay1,*, Romit Majumder1,2,#, Madhuri Datta1,2,#, Adrita Banerjee1,2, Aindrila Chattopadhyay2
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075963
Abstract Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are widely prescribed, but their long-term use frequently results in gastric mucosal injury. Emerging evidence indicates that, beyond cyclooxygenase inhibition, mitochondrial dysfunction represents a central mechanism driving NSAID-induced gastric epithelial damage. This review aims to critically synthesize current evidence on mitochondria-centered pathways involved in NSAID-induced gastric ulceration and to evaluate the therapeutic relevance of melatonin in this context. We highlight how NSAIDs impair mitochondrial bioenergetics, promote excessive reactive oxygen species generation, disrupt membrane potential, and activate apoptotic signaling, thereby compromising mucosal integrity. Importantly, melatonin exerts multifaceted gastroprotective actions by preserving mitochondrial More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Gyuri Han#, Yun Hee Jeong#, Ga Eun Kim, Jong-Sup Bae*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075139
Abstract Objectives: Plant-derived bioactive molecules are increasingly recognized as valuable therapeutic resources for managing diverse pathological conditions, particularly those involving vascular inflammation. This study aimed to determine whether veratramine (VRT), a naturally occurring steroidal alkaloid found in Veratrum species of the Liliaceae family, attenuates LPS-induced vascular and pulmonary inflammation by upregulating heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and modulating the Nrf2, nuclear factor (NF)-κB, and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT1) signaling pathways. Methods: The study assessed the modulatory effects of VRT on HO-1, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in LPS-activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Xing-Guo Li1,2,3,#, Lu-Kai Wang4,#, Fu-Ming Tsai5, Hsueh-Chun Wang1,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075492
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Natural and Synthetic Small Molecules in the Regulation of Immune Cell Functions)
Abstract Itaconate, produced by aconitate decarboxylase 1 (ACOD1, also known as IRG1), acts as a key immunometabolite that inhibits succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) and can engage reduction-oxidation (redox)-sensitive signaling programs. This review summarizes the emerging, context-dependent roles of the ACOD1-itaconate axis in cancer, while critically distinguishing between the effects of endogenous itaconate and its cell-permeable derivatives. In tumor cells, endogenous ACOD1 expression or uptake via solute carrier family 13 member 3 (SLC13A3) alters oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis. In the tumor microenvironment, myeloid-derived itaconate contributes to immune tolerance by reducing dendritic-cell cross-priming and limiting CD8+ T-cell metabolic activity. Moreover, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
PROTOCOL
Dalin Wang1, Mingcai Zhang1, Richard Hastings2, Patrick George1, Ryan Ranzau1, Jinxi Wang1,3,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.074572
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations in Musculoskeletal Biology, Disease, and Regeneration)
Abstract Objective: Although endplate (EP) injury may cause intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration and Modic changes (MCs) in the vertebral bone marrow (VBM), EP injury-induced synchronous cellular reactions and their crosstalk in the IVD and VBM remain unclear. This protocol-based study aimed to streamline and optimize the methods of tissue harvest and cell preparation for flow cytometry (FCM) analysis of T-cell and macrophage subpopulations in both VBM and IVD adjacent to the surgically induced EP microfracture in mice. Methods: EP injury or sham procedure was performed at the spinal levels L4-5 and L5-6 in male mice. Step-by-step… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Semin Lee1,2,#, Minjun Kim3,4,#, Seungmin Lee2,5, Jiyun Yoo1,5, Soo Seok Hwang6,7, Seongchan Kim8, Seung Pil Yun9,10, Dong Kyu Choi11,12,*, Sangdun Choi13,14,*, Hyuk-Kwon Kwon1,2,5,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.074555
Abstract Objective: Cisplatin is a widely used chemotherapeutic agent due to its ability to damage DNA in the treatment of cancer. However, its clinical application is often limited by adverse effects on normal tissues, especially the kidneys. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate its side effects. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying cisplatin-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in human renal epithelial cells, with a focus on key signaling pathways and mediators that drive nephrotoxicity. Methods: To explore these mechanisms, human proximal tubule epithelial… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jiangtao Yu*, Qingfeng Huo, Xinxin Duan
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.073331
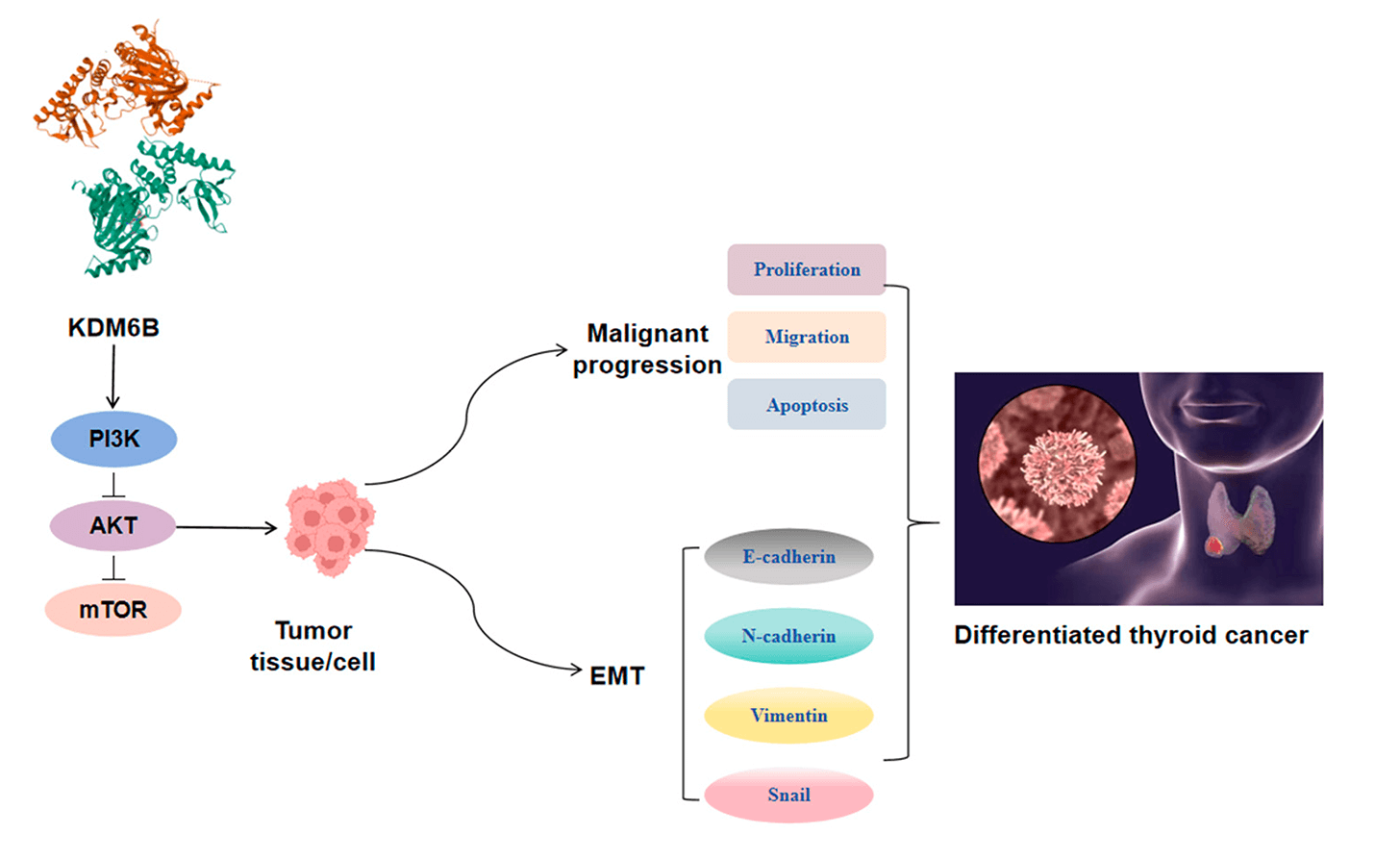
Abstract Objectives: The tumor microenvironment and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) are closely linked to the progression of differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC). However, the functional mechanisms of lysine-specific demethylase 6B (KDM6B) in carcinogenesis remain incompletely understood. This study aims to clarify whether KDM6B affects DTC progression and EMT through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of the rapamycin (PI3K/AKT/mTOR) pathway, providing a potential target for clinical treatment of DTC. Methods: Tissue samples from DTC patients (n = 39) were collected, and KDM6B expression was determined through Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot. Cell counting kit-8 assay, 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Gerardo Ramírez-Mejía1,#, Sofía Plata-Burgos1,#, Raquel Cuevas-Díaz Duran2, Adrian Ledesma-Beiza1, Cynthia Sámano1, Thalía Estefanía Sánchez-Correa3, Ernesto Soto-Reyes1,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075061
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cellular Mechanisms in Neurodegeneration, Injury, and Regeneration)
Abstract Objectives: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a highly aggressive brain tumor characterized by extensive transcriptional and epigenetic dysregulation. Brother of the Regulator of Imprinted Sites (BORIS/CTCFL) has been implicated in oncogenic transcriptional programs in several cancers, but its role in GBM remains poorly defined. This study aimed to characterize BORIS-associated transcriptional programs in GBM and to assess their functional relevance using integrative computational and experimental approaches. Methods: Transcriptomic data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)-GBM and Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTex) brain cortex were analyzed following batch correction, differential expression analysis, and gene ontology enrichment. TCGA-GBM samples were… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Kai Tang1, Shengxing Lu1, Cuie He2, Ruozeng Rong1,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.072154
Abstract Objectives: Prostate cancer (PCa) is a highly prevalent male malignancy with limited efficacy in advanced stages. Dysregulated modulation of necroptosis was reported to be tightly correlated with PCa initiation and progression. Herein, we aimed to identify necroptosis-associated long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and delineate their functional roles in PCa through an integrated approach combining bioinformatic analyses and in vitro experimental validation. Methods: RNA sequencing data and corresponding clinical information of PCa were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Differentially expressed necroptosis-related genes (NRGs) and lncRNAs were screened, and necroptosis activity was assessed by single-sample gene set… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
YUANHONG MAO#, YUNLAN YANG#, KUN YANG§, YONGQIANG SUN, KUN YANG*,,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075138
Abstract Objective: Intestinal barrier disruption is a critical event in sepsis and ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) injury. Enteric glial cells (EGCs) maintain barrier integrity by secreting glial cell line–derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). This study aimed to determine whether Dexmedetomidine (Dex) protects the intestinal barrier via α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7-nAChR) signaling in EGCs. Methods: An in vitro EGC-intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) co-culture system and a murine intestinal I/R model were established. EGCs were selectively ablated in vivo using benzalkonium chloride (BAC). Barrier integrity was evaluated by transmembrane electrical resistance (TEER) and plasma FITC-dextran permeability. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and Western blotting… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
JINGFEI SHI#, YI DING#, HUI LU*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.073956
Abstract Objective: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS). Soluble interleukin-2 receptor alpha (sIL-2Rα) has been implicated in MS pathogenesis, but its mechanisms remain unclear. This study investigates how sIL-2Rα exacerbates MS by modulating microglial activation and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mouse model. Methods: Female C57BL/6J mice were induced with EAE and treated with sIL-2Rα. Clinical symptoms, histopathology, and molecular changes were analyzed. Microglial activation was assessed via immunohistochemistry, Western blot, and RNA sequencing. In vitro, ADCC-mediated oligodendrocyte injury was evaluated using More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Abdullah Alattar1, Reem Alshaman1, Fawaz E. Alanazi1, Yusuf S. Althobaiti2, Ghareb M. Soliman3, Waleed Salman Khubrni1, Howaida S. Ali4, Fawad Ali Shah5,6,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.074865
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Neuroinflammation and Neuroprotection in CNS Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Targets)
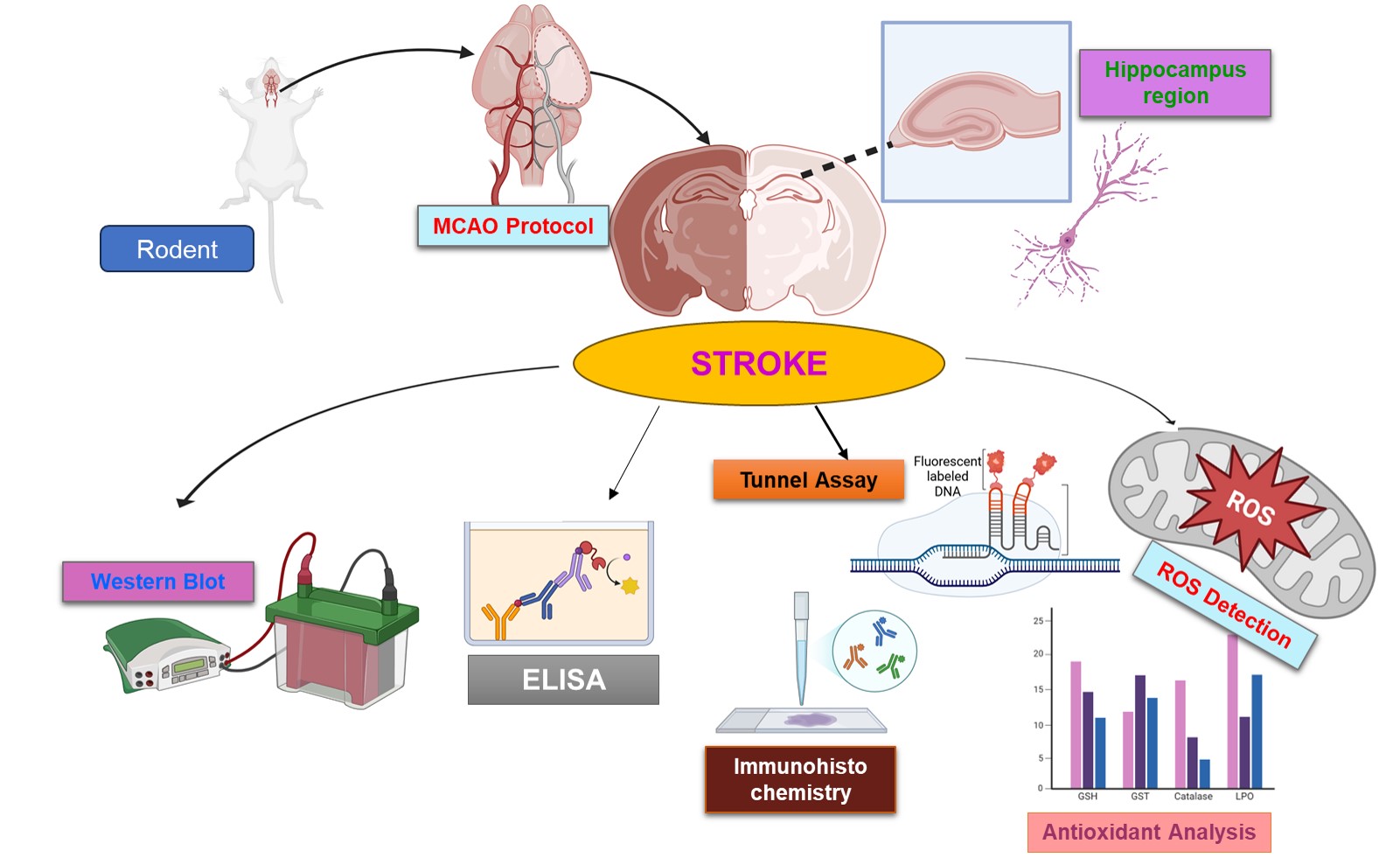
Abstract Objectives: Permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) can lead to hippocampal damage through multiple linked pathways such as reactive oxidative stress (ROS), neuroinflammation mediated by NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3), tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), and glutamate excitotoxicity involving N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits 2a and 2b (NR2a/NR2b) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR/GluR1). The hippocampus, which is essential for memory and cognition, is at a substantial risk of ischemic degeneration. The aim of this study was to investigate the neuroprotective potential of melatonin in regulating these… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
ANDREA DE MATTHAEIS1, LAURA REHAK2,*, MARIA BIANCHI3, ROSSANA PUTZULU3, NICOLA PICCIRILLO3,4, GIULIO MACCAURO1
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.073783
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Tissue Regeneration and Vascularization: From Stem Cells to Functional Tissues)
Abstract For over two decades, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been recognised as the cornerstone of orthobiologic treatments for musculoskeletal diseases. However, clinical evidence increasingly indicates that MSC engraftment in inflamed tissues is minimal and transient, with effects mainly driven by paracrine and immunomodulatory mechanisms induced by macrophage efferocytosis. This evolving paradigm emphasises the immune system as the central orchestrator of tissue repair. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMNCs) have emerged as potent effectors of regenerative inflammation, mediating apoptotic cell clearance through efferocytosis, facilitating the transition of macrophages from pro-inflammatory (M1) to reparative (M2) phenotypes, and releasing… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
YINGJIAN WANG1, CHEN JIN1, YIXUE QIN1, XINGHONG YAO2, YE ZENG1,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.076298
Abstract Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B1 (AKR1B1) was historically characterized as the first and generally rate-limiting enzyme of the polyol pathway and, consequently, was primarily implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Recent advances, however, have repositioned AKR1B1 as a pleiotropic signaling hub whose biological functions extend far beyond glucose metabolism. This review systematically integrates the complex regulatory network governing AKR1B1, including transcriptional control by tumor protein p53 (p53) and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), and its dual functionality as both a metabolic enzyme and a non-catalytic signaling scaffold. We elucidate its role More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Sebastián Jaurreteche1,2,*, María Luana Brajkovic2, María Victoria Del Rosal2, Graciela Venera3, Carlos Daniel De La Vega Elena4
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.073790
Abstract Protein misfolding has emerged as a central mechanism in the pathogenesis of human kidney diseases. Normally, proteins achieve their native conformation through highly regulated folding processes in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and cytoplasm, assisted by molecular chaperones and quality-control pathways. However, genetic variants, environmental stressors, or cellular overload can destabilize this system, resulting in unfolded or misfolded proteins that trigger aggregation, amyloid formation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR). These events may ultimately lead to loss of function, gain of toxic function, and apoptosis. This review summarizes the structural basis… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Michael I. Bukrinsky1, Alessio L. Ravani2, Anastasia V. Poznyak3,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.072752
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Basis for the Involvement of Inflammation and Lipids in Pathologies)
Abstract Atherosclerosis (AS) is a key contributor to ischemic heart disease, resulting in significant cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality worldwide. Despite advancements in managing conventional risk factors, including the utilization of statins, recurrent adverse cardiovascular events remain prevalent, emphasizing the need for novel therapeutic strategies. This review explores the critical role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease (CAD) and highlights potential atheroprotective approaches targeting inflammatory pathways. We discuss the multifaceted interplay between immune responses and AS, detailing the contributions of myeloid cells, T lymphocytes, and various cytokines in plaque formation and instability. Recent More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
SHUYU YUAN1,#, GUOXIAO HAN1,#, HUIMIN QIU1, HENAN ZHENG2, RONGZHI FANG1, WANGMIAO XIE1, WANGUI YU1,*, XIAOCHUN PENG1,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2026.075338
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Gut Microbiota, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Health and Disease)
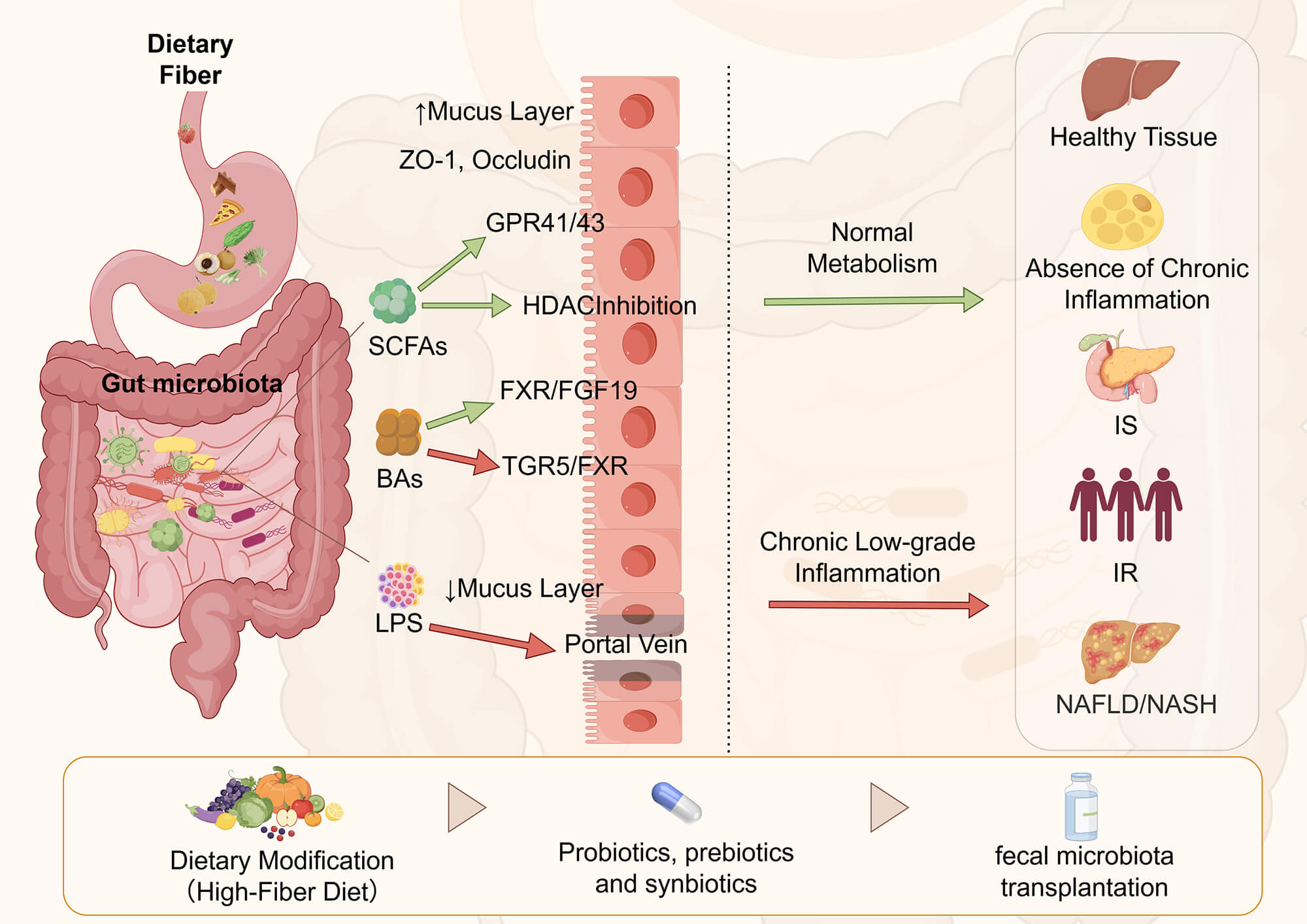
Abstract The gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in maintaining host metabolic homeostasis. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that dysbiosis of the gut microbiota is closely associated with metabolic disorders, including obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). These alterations affect energy harvest, bile acid and short-chain fatty acid metabolism, intestinal barrier integrity, and low-grade inflammation, thereby contributing to insulin resistance and ectopic fat accumulation. In this narrative review, we summarize current knowledge on microbiome-host interactions in metabolic diseases, with a focus on energy metabolism, immune regulation, and inflammatory pathways. We further More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
YIWEI HAO1,#, YAODONG PING2,#, YAN YANG3, CHENG QU3, YUAN CHEN1, XUEYAN JIANG1, RONG FU1, HAILONG ZHAO4,*, LEI YU4,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.074863
Abstract Myocardial ischemia, a core pathological process underlying diverse cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, poses a severe threat to global human health by frequently leading to acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and even sudden cardiac death. A comprehensive understanding of its intricate underlying pathogenic mechanisms is not only crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies but also essential for accelerating the translation of basic research findings into clinical practice. However, the complex regulatory networks that drive myocardial ischemia remain to be systematically clarified. These networks encompass the intricate interactions among multiple pathological processes, including energy… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Yung-Chieh Huang1,2,3, Wen-Chien Cheng4,5, Ya-Hsuan Chao6, Tzu-Ting Chen7,*, Chi-Chen Lin8,9,10,11,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072732
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Natural and Synthetic Small Molecules in the Regulation of Immune Cell Functions)
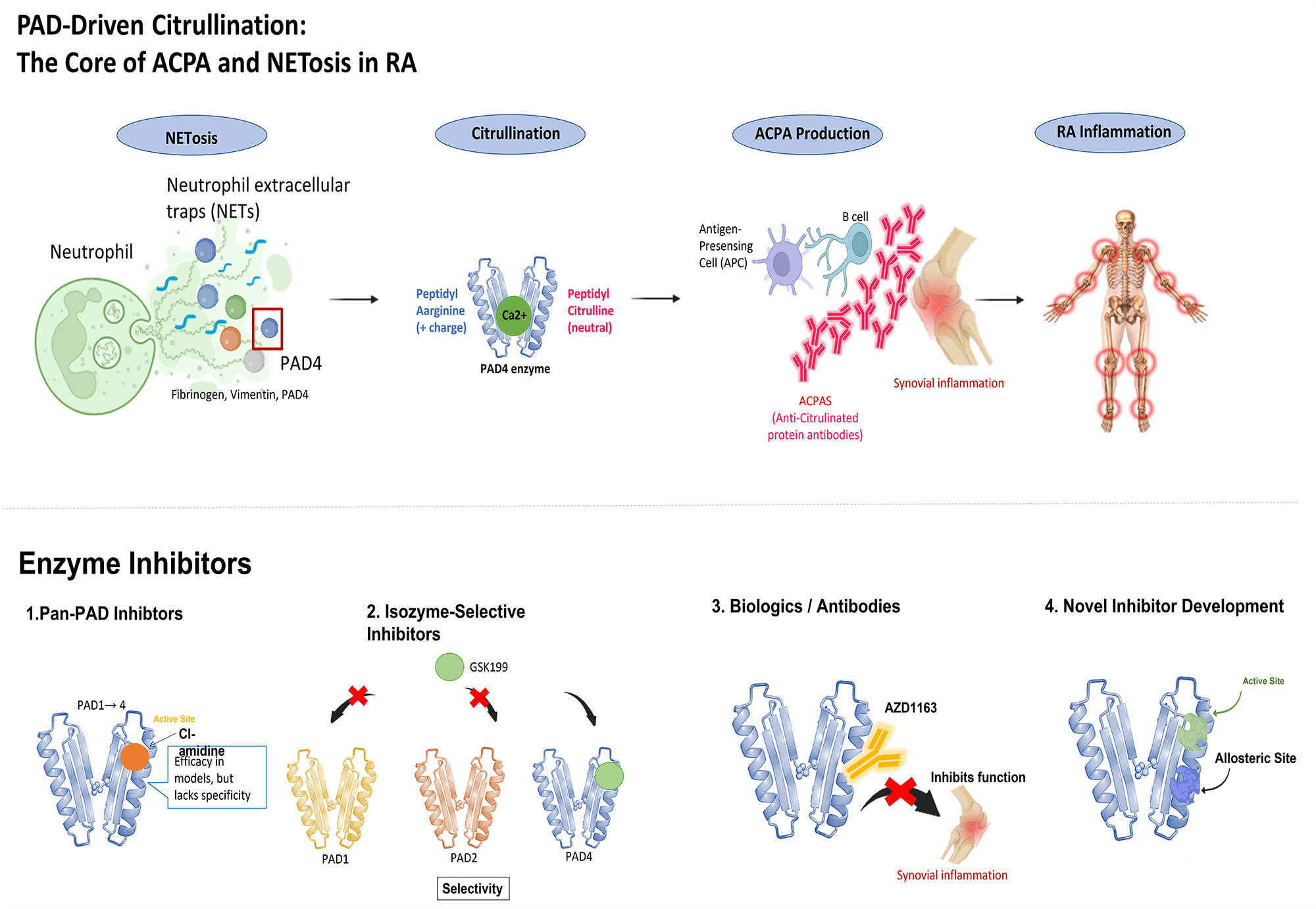
Abstract Protein arginine deiminases (PADs) are key enzymes in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), catalyzing the conversion of arginine to citrulline in a process called citrullination. This post-translational modification is crucial to RA pathogenesis as it creates neo-antigens that trigger the production of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs). These ACPAs are highly specific to RA and often appear before clinical symptoms, making them valuable biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis. Beyond ACPA production, PADs, particularly PAD4, play a vital role in forming neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). NETs contribute to inflammation and joint damage, further highlighting the importance… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Alessio L. Ravani1, Michael I. Bukrinsky2, Anastasia V. Poznyak3,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.074266
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Basis for the Involvement of Inflammation and Lipids in Pathologies)
Abstract Atherosclerosis (AS) remains a major contributor to cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality worldwide. Its development involves dysregulated lipid handling, persistent vascular inflammation, and endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction, influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Increasing evidence highlights a pivotal role of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress as a molecular link between lipid dysregulation and inflammatory signaling in AS pathogenesis. ER stress is triggered by modified LDL, oxidized lipids, hyperhomocysteinemia, oxidative stress (OS), and disrupted calcium (Ca2+) homeostasis, leading to activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR). Core UPR mediators—inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1), protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK),… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
HUAN ZHOU1, JIAMI JIANG2, YUQING ZOU1, JIAHUI ZHANG1,*, ZHIWEI YU3,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073989
Abstract Obesity-related asthma is a distinct clinical phenotype, characterized by severe respiratory symptoms, reduced responsiveness to conventional glucocorticoid therapy, and a significantly increase in disease burden. With the rising global prevalence of obesity, the number of individuals affected by obesity-related asthma is steadily growing, presenting a pressing public health issue. The pathogenesis of obesity-related asthma is multifactorial, involving a complex interplay of metabolic and immune pathways. Key mechanisms include dysregulated T-cell differentiation, pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization, oxidative stress, and altered cytokines and adipokines secretion, all contributing to airway inflammation and remodeling. Additionally, metabolic factors, such as adiposity… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Congwei You1,#, Anwen Yin2,#, Jia Xia3, Le Zhang4,*, Xiaolei Wang1,*, Yutong Hou4,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072971
Abstract Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) have shown a marked global increase in prevalence, placing a substantial burden on public health and healthcare systems worldwide. Epidemiological data demonstrate a significant overlap between these two conditions, with further evidence from research identifying common pathophysiological features, such as lipid metabolism dysregulation, disrupted energy balance, and chronic systemic inflammation. Mitochondria are central to the pathophysiology of both diseases. In addition to their role in energy production, mitochondria are involved in numerous critical cellular processes, including biosynthesis, lipid metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation, signal transduction, and More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Chung-Che Tsai1,#, Chih-Hung Lin2,#, Katherine Lin3,4, Jia Hong Hubert Chen4,5, Ying Jie Celia Chen4,5, Ilyssa Ting-Ying Chang3,4, Hsu-Hung Chang6, Jin-Yin Chang7, Tin-Yi Chu8, Po-Chih Hsu4,8,*, Chan-Yen Kuo8,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073698
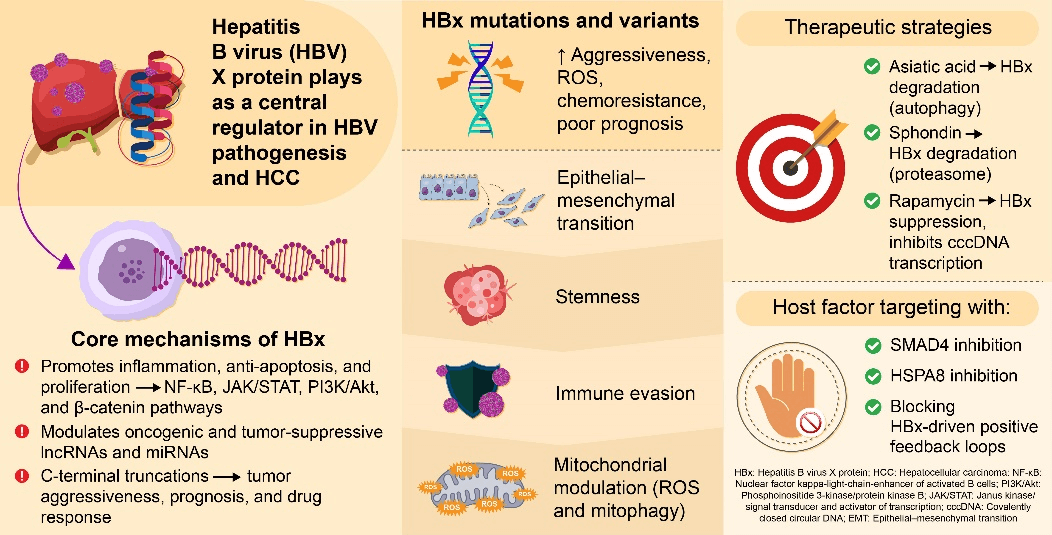
Abstract Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide, most commonly driven by chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The HBV X protein (HBx) plays a central role in hepatocarcinogenesis by regulating transcription, signal transduction, epigenetic modification, and interactions with noncoding RNAs. This review summarizes current advances in HBx-mediated signaling pathways and mutation-specific functions, highlighting its potential as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target, and providing insights for future strategies in HCC treatment and HBV eradication. Activation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), cAMP response element binding protein/activating transcription factor More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
KAWALJIT KAUR*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.073340
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Targeted Therapy in Oncology)
Abstract Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is a pediatric brainstem tumor with a very poor prognosis, characterized by immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) that limits immune infiltration, including a significant reduction in circulating natural killer (NK) cells. This drop in NK cell levels and activity may promote tumor growth and immune evasion, making NK cells a promising target for immunotherapy. NK cells can attack and eliminate DIPG tumor cells, including glioma stem cells, while counteracting certain immune evasion strategies. Although the DIPG microenvironment and blood-brain barrier present challenges, NK cell-based therapies have shown encouraging tumor control and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
ANNA PAWłOWSKA-ŁACHUT*, DOROTA SUSZCZYK, IWONA WERTEL
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072104
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: The Role of γδ T Cells and iNKT Cells in Cancer: Unraveling Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential)
Abstract Ovarian cancer (OC) remains the most lethal gynecological malignancy, and it is characterized by high heterogeneity, early metastatic dissemination, and frequent recurrence within 12–18 months after primary therapy. Despite progress in clinical management and drug development, the mortality rate remains high, and the biological drivers of OC aggressiveness are not fully understood. A major contributor to therapeutic resistance and disease progression is the ovarian tumor microenvironment (TME), which supports tumor growth and immune evasion. Its complexity poses significant challenges to the development of effective therapies. Current treatments, especially in advanced or recurrent stages, have limited… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
JOONGBUM MOON1, JI HYEON AHN2, MOO-HO WON3,*
BIOCELL, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2025.072635
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cellular and Molecular Insights into Brain Ischemic Insults)
Abstract Ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury induces region-specific neuronal vulnerability within the hippocampus, with the cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) subfield particularly prone to delayed neuronal death. While intrinsic neuronal factors have been implicated, emerging evidence highlights the decisive contribution of astrocyte endfeet (AEF)—specialized perivascular structures that regulate ion and water homeostasis, glutamate clearance, and blood–brain barrier (BBB) stability. This review synthesizes structural and molecular alterations of AEF across the CA1–CA3 subfields following I/R and their correlation with neuronal fate. In CA1, AEF undergo early-onset swelling and detachment from the vascular basal lamina due to dysfunction of critical proteins… More >