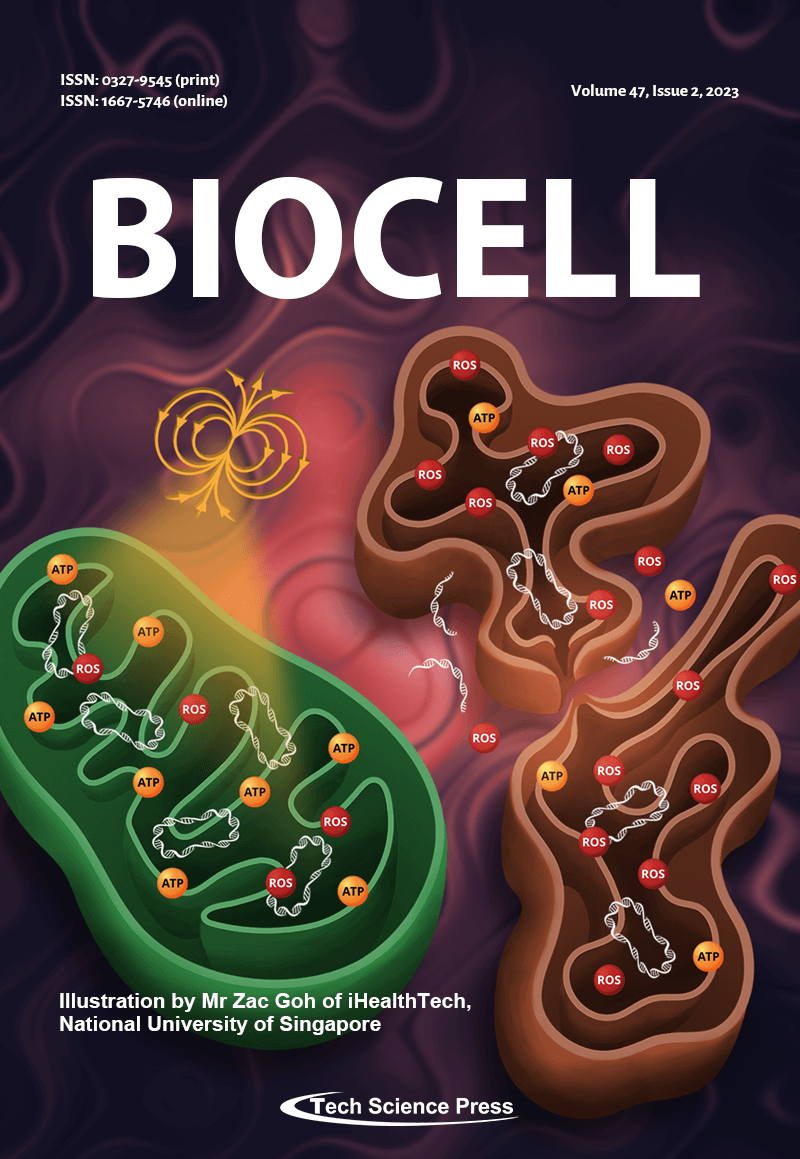
Artistic depiction of how brief and low energy magnetic field exposure of mitochondria may be exploited to improve their respiratory function. Via a process of mitohormesis, non-invasive exposure to weak magnetic fields may be used as a therapeutic means to improve mitochondrial respiratory efficiency (enhance ATP production and reduce associated ROS production) and prevent the release of mitochondrial DNA into the systemic circulation, which will have anti-inflammatory and general health repercussions. For clarity, the molecular machinery involved in mitochondrial fusion-fission dynamics and oxidative phosphorylation have been omitted. See: “Magnetic mitohormesis: A non-invasive therapy for inflammatory disorders?” for details.
View this paper