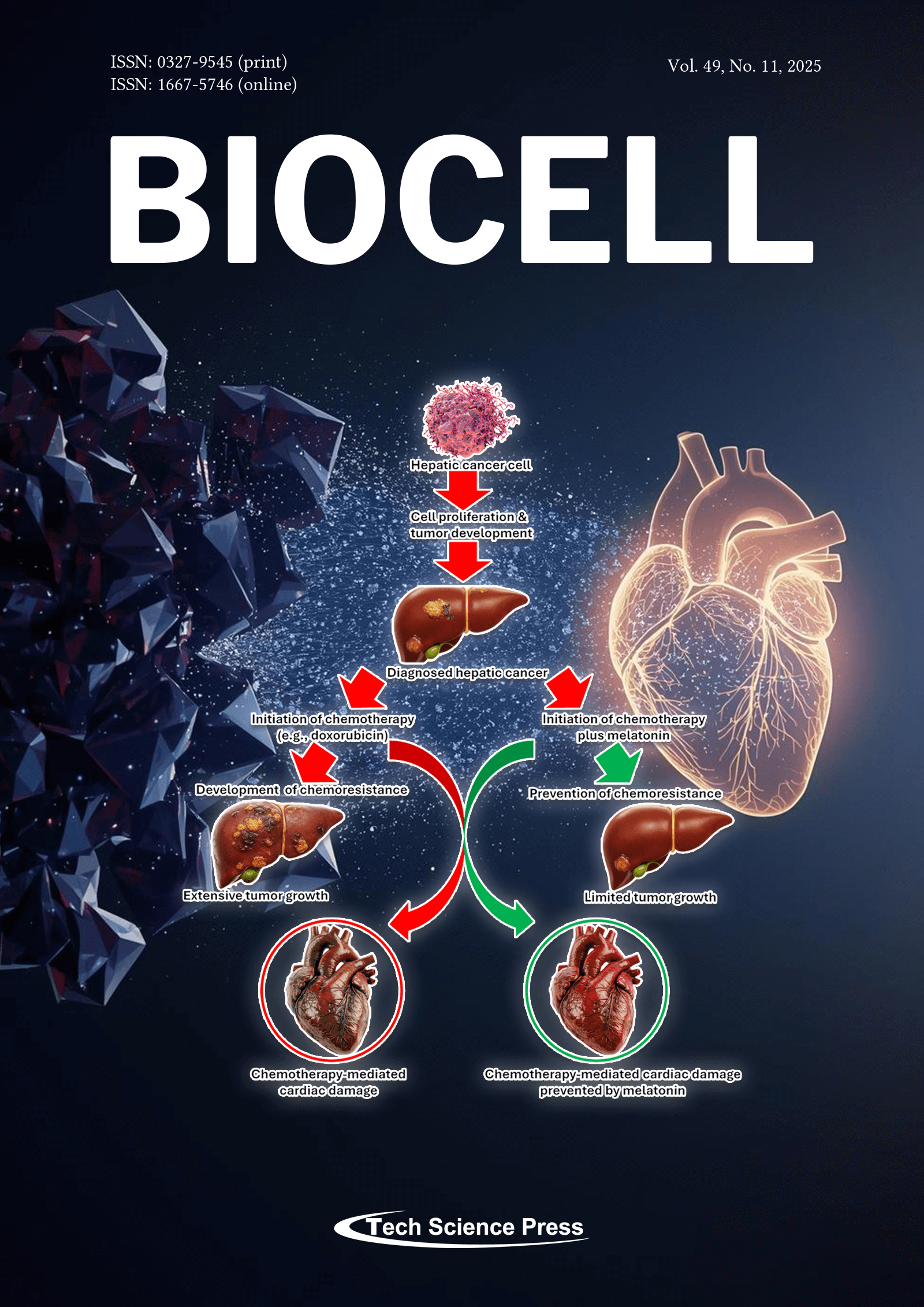
Many tumors become insensitive to the drugs used to inhibit their growth. Means of overcoming the chemoresistance of cancer cells to treatment is of paramount importance in improving cancer-related therapies. Melatonin treatment reverses cancer cell chemo insensitivity in many experimental settings making tumors responsive to the corresponding drugs. Also, melatonin limits the collateral toxicity of chemotherapies, especially at the level of the heart.
This cover image is a composite of original author-created central artwork and AI-generated peripheral elements produced via Canva. The final composition contains no copyrighted material or misleading representations.
View this paper