 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Pik3cb Antagonizes LPS/ATP-Induced Inflammatory Activation in Cardiomyocytes by Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB/NLRP3 Signaling Axis
1 College of Pharmacy, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, 250355, China
2 Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine Pharmacology, Shandong Academy of Chinese Medicine, Jinan, 250014, China
3 College of Animal Science and Technology, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, 271018, China
* Corresponding Authors: Cheng Wang. Email: ; Ping Wang. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Modulation of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Function: Therapeutic Perspectives Across Diseases)
BIOCELL 2025, 49(11), 2181-2194. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2025.070859
Received 25 July 2025; Accepted 08 October 2025; Issue published 24 November 2025
Abstract
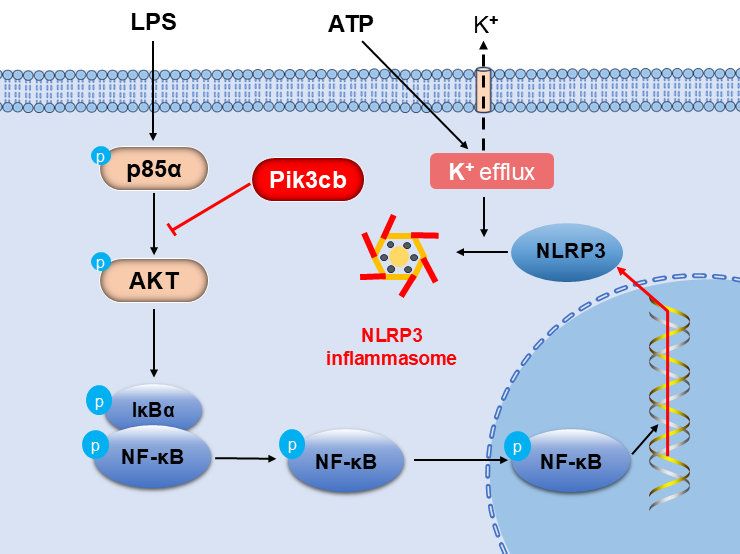
Objectives: PI3K plays a pivotal role in the inflammatory response by modulating the production and release of inflammatory factors. Pik3cb is one of the subunits of PI3K, and its specific role in myocardium inflammation remains unelucidated. This study aimed to investigate the role of Pik3cb in the inflammatory response and to elucidate the underlying mechanism. Methods: An inflammation model was established using H9c2 cells treated with LPS and ATP, and Pik3cb expression was evaluated in this model system. Subsequently, an overexpression model was constructed by transfecting cells with a Pik3cb overexpression plasmid, after which the effects of Pik3cb overexpression on the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammatory signaling pathways were assessed. Results: These analyses revealed that the expression and distribution of Pik3cb were significantly reduced in the LPS/ATP-induced cellular inflammation model group, whereas plasmid-mediated overexpression of Pik3cb significantly inhibited the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in response to LPS/ATP stimulation. Additionally, the LPS/ATP-induced activation of the NF-κB/NLRP3 axis was significantly inhibited following Pik3cb overexpression. Conclusion: This study demonstrates that Pik3cb acts as a negative regulator of LPS/ATP-induced inflammation in cardiomyocytes, exerting anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling axis. These findings provide a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of myocardial inflammation.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools