 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Quantum Secure Direct Communication Protocol with Mutual Authentication Based on Single Photons and Bell States
1 School of Cybersecurity, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu, 610000, China.
2 Natural Resource Ecology Laboratory, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO 80523, USA.
* Corresponding Author: Lili Yan. Email: .
Computers, Materials & Continua 2020, 63(3), 1297-1307. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2020.09873
Received 23 January 2020; Accepted 26 February 2020; Issue published 30 April 2020
Abstract
Quantum secure direct communication (QSDC) can transmit secret messages directly from one user to another without first establishing a shared secret key, which is different from quantum key distribution. In this paper, we propose a novel quantum secure direct communication protocol based on signal photons and Bell states. Before the execution of the proposed protocol, two participants Alice and Bob exchange their corresponding identity IDA and IDB through quantum key distribution and keep them secret, respectively. Then the message sender, Alice, encodes each secret message bit into two single photons (| 01〉or|10〉) or a Bell state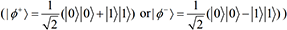 , and
composes an ordered secret message sequence. To insure the security of communication,
Alice also prepares the decoy photons and inserts them into secret message sequence on
the basis of the values of IDA and IDB. By the secret identity IDA and IDB, both sides of the
communication can check eavesdropping and identify each other. The proposed protocol
not only completes secure direct communication, but also realizes the mutual
authentication. The security analysis of the proposed protocol is presented in the paper.
The analysis results show that this protocol is secure against some common attacks, and
no secret message leaks even if the messages are broken. Compared with the two-way
QSDC protocols, the presented protocol is a one-way quantum communication protocol
which has the immunity to Trojan horse attack. Furthermore, our proposed protocol can be
realized without quantum memory.
, and
composes an ordered secret message sequence. To insure the security of communication,
Alice also prepares the decoy photons and inserts them into secret message sequence on
the basis of the values of IDA and IDB. By the secret identity IDA and IDB, both sides of the
communication can check eavesdropping and identify each other. The proposed protocol
not only completes secure direct communication, but also realizes the mutual
authentication. The security analysis of the proposed protocol is presented in the paper.
The analysis results show that this protocol is secure against some common attacks, and
no secret message leaks even if the messages are broken. Compared with the two-way
QSDC protocols, the presented protocol is a one-way quantum communication protocol
which has the immunity to Trojan horse attack. Furthermore, our proposed protocol can be
realized without quantum memory. Keywords
Cite This Article
Citations
 Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue Download PDF
Download PDF

 Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools