 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Investigation of Particle Breakdown in the Production of Composite Magnesium Chloride and Zeolite Based Thermochemical Energy Storage Materials
Heriot Watt University, Institute of Mechanical, Process and Energy Engineering, Edinburgh, UK
* Corresponding Author: Louis F. Marie. Email:
Energy Engineering 2023, 120(10), 2193-2209. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2023.043075
Received 20 June 2023; Accepted 17 August 2023; Issue published 28 September 2023
Abstract
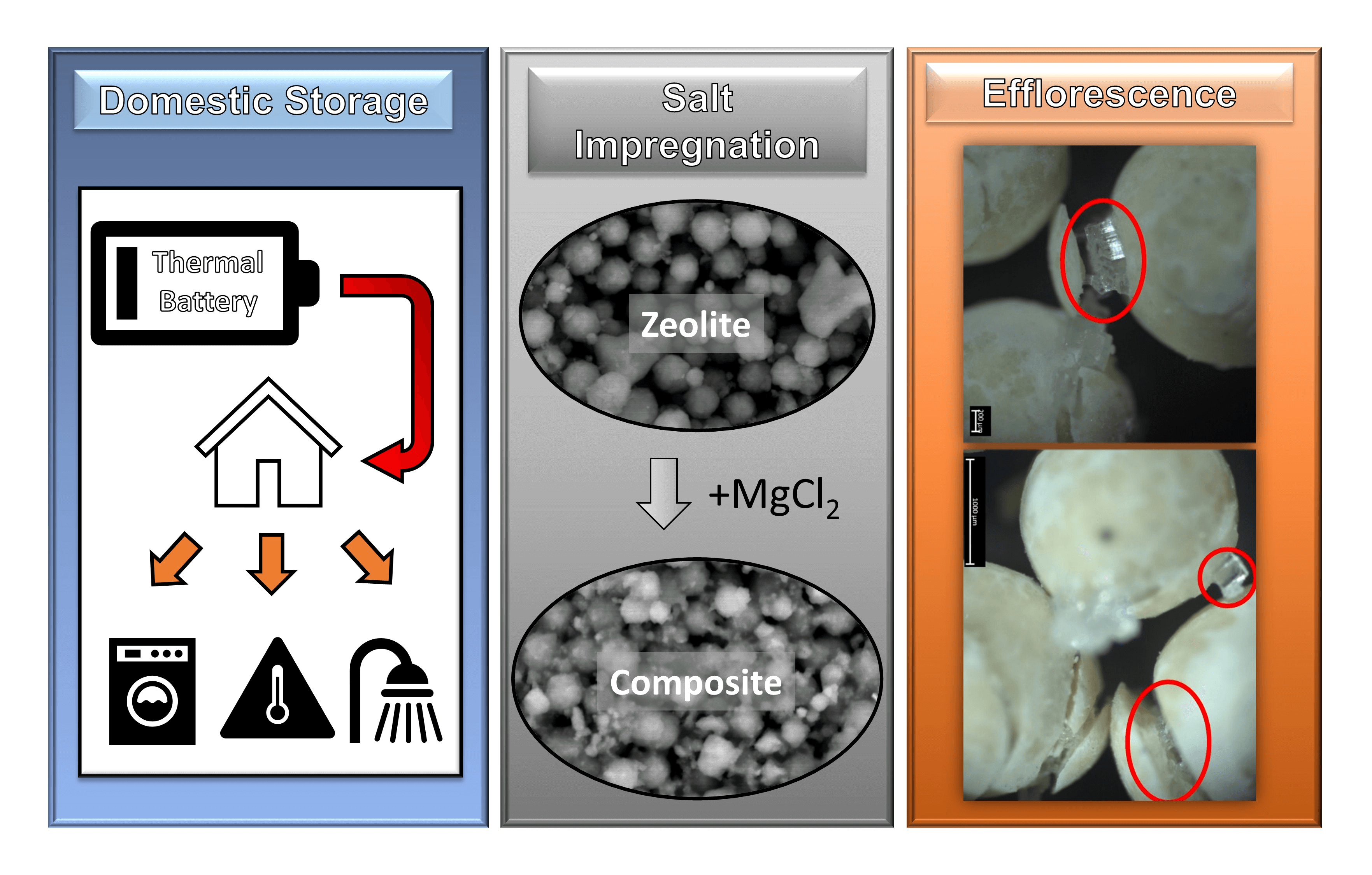
Composite thermochemical energy storage (TCES) represents an exciting field of thermal energy storage which could address the issue of seasonal variance in renewable energy supply. However, there are open questions about their performance and the root cause of some observed phenomena. Some researchers have observed the breakdown of particles in their production phase, and in their use. This study seeks to investigate the underlying cause of this breakdown. SEM and EDX analysis have been conducted on MgCl2 impregnated 13X zeolite composites of differing diameters, as well as LiX zeolite. This was done in order to study the level of impregnation of salt into the zeolite matrix, as well as the effect this impregnation process has on the morphology of the zeolite. Analysis was conducted using ImageJ software to study the effect of the impregnation process on the diameter of the particles. It has been found that a by weight impregnation concentration of magnesium chloride of 11.90% for the LiX zeolite, and 7.59% and 5.26% for the large diameter 13X zeolite and the small diameter 13X zeolite respectively has been achieved. It has been found that the impregnation process significantly affects the morphology of 13X zeolite particles, causing large fissures to form, and eventually resulting in the previously found breakdown of these particles. It has been verified that a primary factor influencing the breakdown of the 13X zeolite particles is the efflorescence and sub-fluorescence phenomena, which leads to a build-up of crystals in the zeolite pores. It has also been found that prolonged impregnation times and the use of high concentration salt solutions in the soaking process can induce significant crystal growth which also leads to the breakdown of these particles. Results demonstrate that LiX zeolite is the optimum host matrix choice in these conditions. These results will allow for the design of more resilient composite TCES particles.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools