
A Proud Tradition
Established in 1904, Energy Engineering has a history of more than 120 years, making it one of the long-standing journals in the field. Throughout its long history, the journal has evolved alongside advances in energy science and technology, consistently serving as a catalyst for innovation and progress. In recent years, it has achieved steady improvements in academic quality, editorial standards, and international influence, and continues to move toward becoming a leading international journal.
Multi-faceted scholarship
Energy Engineering is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal focusing on the engineering aspects of energy research. It provides a global platform for researchers, engineers, scientists, and policy makers to publish original studies across a broad range of energy topics, including energy generation, conversion, conservation, utilization, storage, transmission, systems, technologies, management and sustainability. The journal also explores the societal impacts of energy use and policy, showcasing research that advances sustainable development and supports the transition to cleaner energy systems.
Ei Compendex/Engineering Village (Elsevier); Scopus (Elsevier); WorldCat (OCLC); Google Scholar; ResearchGate; SCImago (SJR); Crossref; Sherpa/RoMEO; Letpub; Elektronische; Genamics JournalSeek; Dimensions; Portico, etc...
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.075211 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Energy Transition in the Transport Sector: Challenges and Opportunities)
Abstract Discussions about the future of energy sources and environmental sustainability are becoming critical on a global scale. The energy sector plays a central role in the economy, as the availability and cost of energy influence the competitiveness of economies, while the level of energy consumption impacts the standard of living for individuals. This paper aims to examine environmental challenges and steps for a sustainable transition towards a hydrogen economy, focusing on its potential as an alternative to fossil fuels and the importance of developing the hydrogen paradigm. The research methodology is based on a combination… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071166 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Grid Integration of Intermittent Renewable Energy Resources: Technologies, Policies, and Operational Strategies)
Abstract An optimized volt-ampere reactive (VAR) control framework is proposed for transmission-level power systems to simultaneously mitigate voltage deviations and active-power losses through coordinated control of large-scale wind/solar farms with shunt static var generators (SVGs). The model explicitly represents reactive-power regulation characteristics of doubly-fed wind turbines and PV inverters under real-time meteorological conditions, and quantifies SVG high-speed compensation capability, enabling seamless transition from localized VAR management to a globally coordinated strategy. An enhanced adaptive gain-sharing knowledge optimizer (AGSK-SD) integrates simulated annealing and diversity maintenance to autonomously tune voltage-control actions, renewable source reactive-power set-points, and SVG output.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.072583 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Green Hydrogen Technologies)
Abstract Photoreforming is an emerging photocatalytic process that converts organic waste into hydrogen H2 using solar energy, offering a dual solution for waste valorization and sustainable fuel production. This review comprehensively examines the fundamental mechanisms of photoreforming, emphasizing the critical role of photocatalyst design in optimizing hydrogen evolution. Key criteria for effective photocatalysts including suitable band edge positions, broad spectrum solar absorption, and photostability are systematically analyzed alongside advances in heterojunction engineering and defect modulation. The review further explores diverse waste-derived feedstocks, such as biomass: alcohols, saccharides, lignin and plastics: PET, PLA, polyolefins, highlighting substrate, specific challenges More >
Graphic Abstract
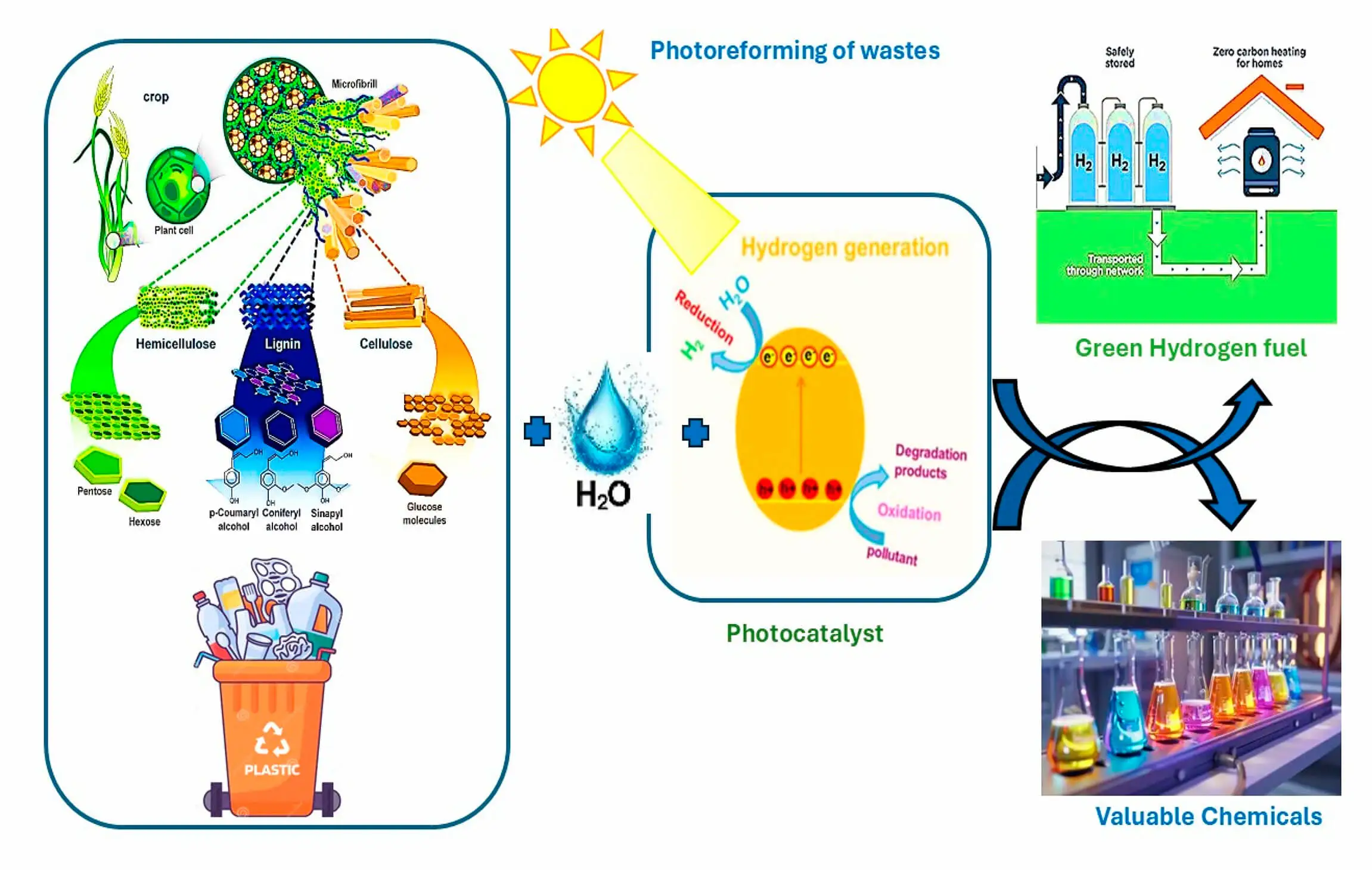
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.069610 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Construction and Control Technologies of Renewable Power Systems Based on Grid-Forming Energy Storage)
Abstract This paper presents an optimal operation method for embedded DC interconnections based on low-voltage AC/DC distribution areas (EDC-LVDA) under three-phase unbalanced compensation conditions. It can optimally determine the transmission power of the DC and AC paths to simultaneously improve voltage quality and reduce losses. First, considering the embedded interconnected, unbalanced power structure of the distribution area, a power flow calculation method for EDC-LVDA that accounts for three-phase unbalanced compensation is introduced. This method accurately describes the power flow distribution characteristics under both AC and DC power allocation scenarios. Second, an optimization scheduling model for EDC-LVDA… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.069764 - 27 February 2026
Abstract In order to solve the problems of slow dynamic response and difficult multi-source coordination of solar electric vehicle charging stations under intermittent renewable energy, this paper proposes a hardware-algorithm co-design framework: the T-type three-level bidirectional converter (100 kHz switching frequency) based on silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFET is deeply integrated with fuzzy model predictive control (Fuzzy-MPC). At the hardware level, the switching trajectory and resonance suppression circuit (attenuation resonance peak 18 dB) are optimized, and the total loss is reduced by 23% compared with the traditional silicon-based IGBT. At the algorithm level, the adaptive parameter update… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.074018 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract The utilisation of waste in green sustainable technology can provide a clean environment and support energy demand. This work aims to design and analyse the performance of a developed indirect flat-plate Solar Air Heater (SAH) integrated with an internal thermal storage unit using Waste Automotive Oil (WAO). The SAH was designed based on the circulation of confined air around the internal thermal storage unit due to the updraft effects of hot air. Two SAHs were tested to compare the performance of WAO and water, with the results being compared to previous work that utilised phase… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070023 - 27 February 2026
Abstract Distribution transformers play a vital role in power distribution systems, and their reliable operation is crucial for grid stability. This study presents a simulation-based framework for active fault diagnosis and early warning of distribution transformers, integrating Sample Ensemble Learning (SEL) with a Self-Optimizing Support Vector Machine (SO-SVM). The SEL technique enhances data diversity and mitigates class imbalance, while SO-SVM adaptively tunes its hyperparameters to improve classification accuracy. A comprehensive transformer model was developed in MATLAB/Simulink to simulate diverse fault scenarios, including inter-turn winding faults, core saturation, and thermal aging. Feature vectors were extracted from voltage,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070942 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery in Unconventional Reservoirs)
Abstract The shale gas development in China faces challenges such as complex reservoir conditions and high development costs. Based on the pore pressure and geostress coupling theory, this paper studies the geostress evolution laws and fracture network characteristics of shale gas infill wells. A mechanism model of CN platform logging data and geomechanical parameters is established to simulate the influence of parent well’s production on the geostress in the infill well area. It is suggested that with the increase of production time, normal fault stress state and horizontal stress deflection will occur. The smaller the parent… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074415 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract Despite significant advancements in solar collector technology, persistent challenges remain in improving the overall efficiency of solar systems. This paper investigates the use of mini-channel aluminum tubes mounted on the reflective surface as preliminary heating stages to enhance the overall system thermal performance. Experimental assessments were conducted with flow rates ranging from 0.1 to 0.8 LPM and tilt angles of 180° South and 225° Southwest in Al-Kut, Iraq, from 9:00 AM to 2:00 PM. Fluid flows sequentially through five flat aluminum tubes totaling 50 channels, named stage-1, then flows through four aluminum tubes totaling 40… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071006 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Grid Integration of Intermittent Renewable Energy Resources: Technologies, Policies, and Operational Strategies)
Abstract To address the high costs and operational instability of distribution networks caused by the large-scale integration of distributed energy resources (DERs) (such as photovoltaic (PV) systems, wind turbines (WT), and energy storage (ES) devices), and the increased grid load fluctuations and safety risks due to uncoordinated electric vehicles (EVs) charging, this paper proposes a novel dual-scale hierarchical collaborative optimization strategy. This strategy decouples system-level economic dispatch from distributed EV agent control, effectively solving the resource coordination conflicts arising from the high computational complexity, poor scalability of existing centralized optimization, or the reliance on local information… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071023 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations and Challenges in Smart Grid Technologies)
Abstract Owing to the development of communication technologies and control systems, the integration of numerous Internet of Things (IoT) nodes into the power grid has become increasingly prevalent. These nodes are deployed to gather operational data from various distributed energy sources and monitor real-time energy consumption, thereby transforming the traditional power grid into a smart grid (SG). However, the openness of wireless communication channels introduces vulnerabilities, as it allows potential eavesdroppers to intercept sensitive information. This poses threats to the secure and efficient operation of the IoT-driven smart grid. To address these challenges, we propose a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071144 - 27 February 2026
Abstract The accurate state of health (SOH) estimation in lithium-ion batteries represents a critical technological challenge with profound implications for electric vehicle performance and user experience. Precise SOH assessment not only enables reliable mileage prediction but also ensures operational safety. However, the complex and non-linear capacity fading process during battery cycling poses a challenge to obtaining accurate SOH. To address this issue, this study proposes an effective health factor derived from the local voltage range during the battery charging phase. First, the battery charging phase is divided evenly with reference to voltage intervals, and an importance… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.072899 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Global Intelligent Optimization and Advanced Control of Photovoltaic Systems Under Complex Operating Conditions)
Abstract Utility-scale PV plants increasingly operate under partial shading, soiling, temperature swings, and rapid irradiance ramps that depress yield and challenge stability on weak grids. This critical review addresses those conditions by (i) unifying a stressor-to-method taxonomy that links field stressors to global intelligent MPPT (metaheuristics and learning-based trackers) and to advanced inverter controls (adaptive/MPC and grid-forming), (ii) standardizing metrics and reporting aligned with IEC 61724-1 and IEEE 1547/1547.1 to enable fair, reproducible comparisons, and (iii) framing MPPT and grid support as a co-design problem with a DT→HIL→Field validation pathway and seedable scenarios. We identify persistent… More >
Graphic Abstract
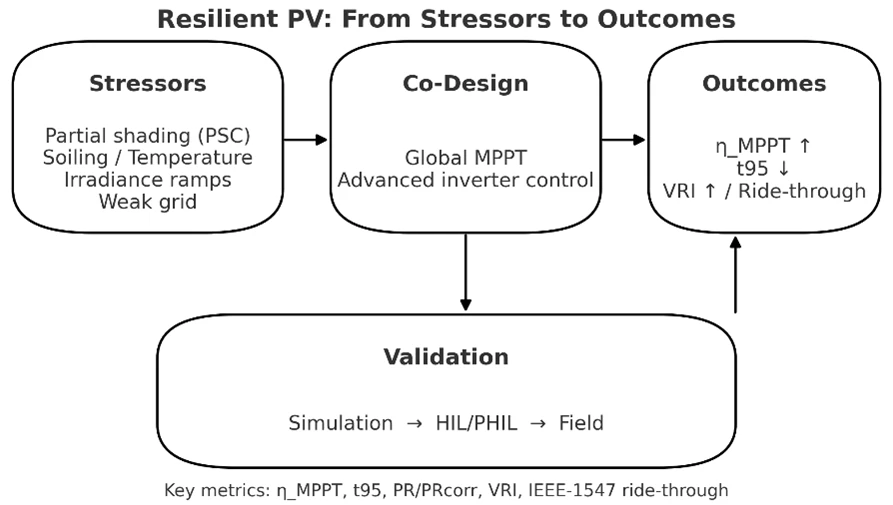
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.064770 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrated Geology-Engineering Simulation and Optimizationfor Unconventional Oil and Gas Reservoirs)
Abstract The migration, accumulation, and high yield of hydrocarbons in tight sandstone reservoirs are closely tied to the natural fracture systems within the reservoirs. Large-scale fracture networks not only enhance reservoir seepage capacity but also influence effective productivity and subsequent fracturing reconstruction. Given the diverse mechanical behaviors, such as migration, penetration, or fracture arrest, traditional assumptions about fracture interaction criteria fail to address this complexity. To resolve these issues, a global cohesive element method is proposed to model random natural fractures. This approach verifies intersection models based on real-time stress conditions rather than pre-set criteria, enabling… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070996 - 27 February 2026
Abstract To address the issues of high costs and low component utilization caused by the independent configuration of hybrid DC circuit breakers (HCBs) and DC power flow controllers (DCPFCs) at each port in existing DC distribution networks, this paper adopts a component sharing mechanism to propose a composite multi-port hybrid DC circuit breaker (CM-HCB) with DC power flow and fault current limitation abilities, as well as reduced component costs. The proposed CM-HCB topology enables the sharing of the main breaker branch (MB) and the energy dissipation branch, while the load commutation switches (LCSs) in the main… More >
Graphic Abstract
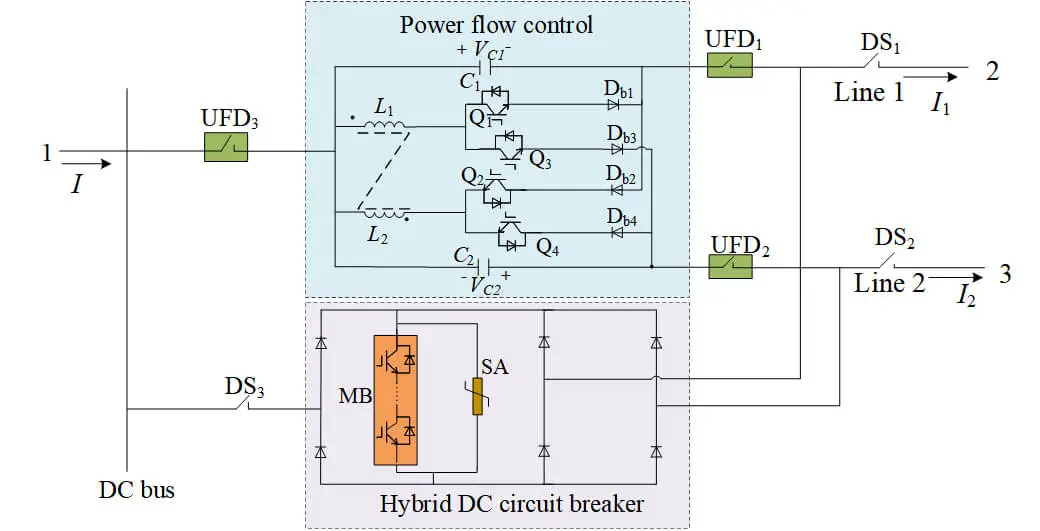
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.069004 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI in Green Energy Technologies and Their Applications)
Abstract The rapid digitalization of the energy sector has led to the deployment of large-scale smart metering systems that generate high-frequency time series data, creating new opportunities and challenges for energy anomaly detection. Accurate identification of anomalous patterns in building energy consumption is essential for optimizing operations, improving energy efficiency, and supporting grid reliability. This study investigates advanced feature engineering and machine learning modeling techniques for large-scale time series anomaly detection in building energy systems. Expanding upon previous benchmark frameworks, we introduce additional features such as oil price indices and solar cycle indicators, including sunset and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072679 - 27 February 2026
Abstract With the increasing penetration of renewable energy, the coordination of energy storage with thermal power for frequency regulation has become an effective means to enhance grid frequency security. Addressing the challenge of improving the frequency regulation performance of a thermal-storage primary frequency regulation system while reducing its associated losses, this paper proposes a multi-dimensional cooperative optimization strategy for the control parameters of a combined thermal-storage system, considering regulation losses. First, the frequency regulation losses of various components within the thermal power unit are quantified, and a calculation method for energy storage regulation loss is proposed,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071728 - 27 February 2026
Abstract The dense integration of residential distributed photovoltaic (PV) systems into three-phase, four-wire low-voltage (LV) distribution networks results in reverse power flow and three-phase imbalance, leading to voltage violations that hinder the growth of rural distributed PV systems. Traditional voltage droop-based control methods regulate PV power output solely based on local voltage measurements at the point of PV connection. Due to a lack of global coordination and optimization, their efficiency is often subpar. This paper presents a centralized coordinated active/reactive power control strategy for PV inverters in rural LV distribution feeders with high PV penetration. The… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073955 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract Thermal power plants are the main contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. The prediction of the emission supports the decision makers and environmental sustainability. The objective of this study is to enhance the accuracy of emission prediction models, supporting more effective real-time monitoring and enabling informed operational decisions that align with environmental compliance efforts. This paper presents a data-driven approach for the accurate prediction of gas emissions, specifically nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO), in natural gas power plants using an optimized hybrid machine learning framework. The proposed model integrates a Feedforward Neural Network (FFNN)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.071768 - 27 February 2026
Abstract The integration of a high proportion of renewable energy introduces significant challenges for the adaptability of traditional fault nature identification methods. To address these challenges, this paper presents a novel fault nature identification method for renewable energy grid-connected interconnection lines, leveraging wavelet packet decomposition and voltage waveform time-frequency morphology comparison algorithms. First, the paper investigates the harmonic injection mechanism during non-full-phase operation following fault isolation in photovoltaic renewable energy systems, and examines the voltage characteristics of faulted phases in renewable energy scenarios. The analysis reveals that substantial differences exist in both the time and frequency… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072333 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Grid Integration of Intermittent Renewable Energy Resources: Technologies, Policies, and Operational Strategies)
Abstract Thermal storage electric heating (TSEH), as a prevalent variable load resource, offers significant potential for enhancing system flexibility when aggregated into a cluster. To address the uncertainties of renewable energy and load forecasting in active distribution networks (ADN), this paper proposes a multi-timescale coordinated optimal dispatch strategy that incorporates TSEH clusters. It utilizes the thermal storage characteristics and short-term regulation capabilities of TSEH, along with the rapid and gradual response characteristics of resources in active distribution grids, to develop a coordinated optimization dispatch mechanism for day-ahead, intraday, and real-time stages. It provides a coordinated optimized… More >
Graphic Abstract
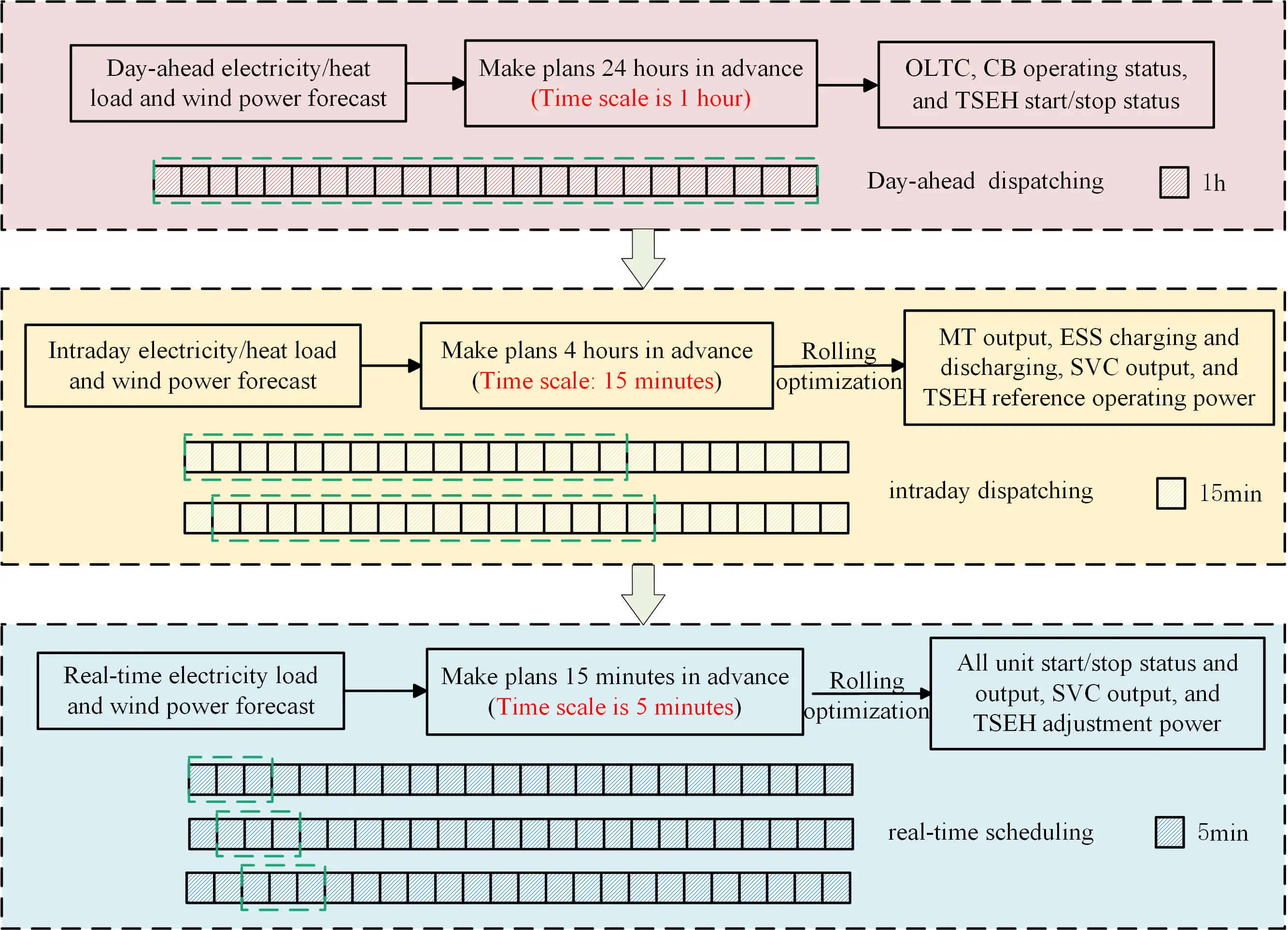
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073434 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Energy Transition in the Transport Sector: Challenges and Opportunities)
Abstract Synchronous reluctance motors (SynRM) are widely employed in industrial applications due to their high robustness, low cost, and absence of permanent magnets. In recent years, significant research efforts have focused on improving the controllability and efficiency of SynRM. Accurate rotor position information is essential for the controller to generate appropriate current and voltage references corresponding to the desired speed and load torque. Shaft-mounted position sensors are generally undesirable because of their high cost, sensitivity to harsh operating conditions, maintenance requirements, and reduced reliability in environments characterized by high vibration. Consequently, sensorless control techniques that estimate… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071911 - 27 February 2026
Abstract Air conditioning is a major energy-consuming component in buildings, and accurate air conditioning load forecasting is of great significance for maximizing energy utilization efficiency. However, the deep learning models currently used in the field of air conditioning load forecasting often suffer from issues such as distribution bias in load data and insufficient expression ability of nonlinear features in the model, which affect the accuracy of load forecasting. To address this, this paper proposes a novel load forecasting model. Firstly, the model employs the Dish-TS (DS) module to standardize the input window data through self-learning standardized… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071943 - 27 February 2026
Abstract Traditional oilfields face increasing extraction challenges, primarily due to reservoir quality degradation and production decline, which are further exacerbated by volatile international crude oil prices—illustrated by Brent Crude’s trajectory from pandemic-induced negative pricing to geopolitically driven surges exceeding USD 100 per barrel. This study addresses these complexities through an integrated methodological framework applied to medium-permeability sandstone reservoirs in the Xinjiang oilfield by combining advanced numerical simulations with multivariate regression analysis. The methodology employs Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS) to stratify geological parameter distributions and constructs heterogeneous reservoir models using Petrel software, rigorously validated through historical production… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Energy Engineering, Vol.123, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073971 - 27 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Analytics on Energy Systems)
Abstract The increasing integration of electric vehicle (EV) loads into power systems necessitates understanding their impact on stability. Small-magnitude perturbations, if persistent, can cause low-frequency oscillations, leading to synchronism loss and mechanical stress. This work analyzes the effect of voltage-dependent EV loads on this small-signal stability. The study models an EV load within a Single-Machine Infinite Bus (SMIB) system. It specifically evaluates the influence of EV charging through the DC link capacitor of a Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC), a key device for damping oscillations. The system’s performance is compared to a modified version equipped with More >