 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Activated Carbon from Nipa Palm Fronds (Nypa fruticans) with H3PO4 and KOH Activators as Fe Adsorbers
1 Physics Study Program, FMIPA, Universitas Lambung Mangkurat, Banjarbaru, 70714, Indonesia
2 Department of Physics, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Surabaya, 60111, Indonesia
* Corresponding Author: Ninis Hadi Haryanti. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Eco-Friendly Waste-Base Materials for Pollution Control Sustainable Technologies)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(2), 203-214. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.043549
Received 05 July 2023; Accepted 18 October 2023; Issue published 11 March 2024
Abstract
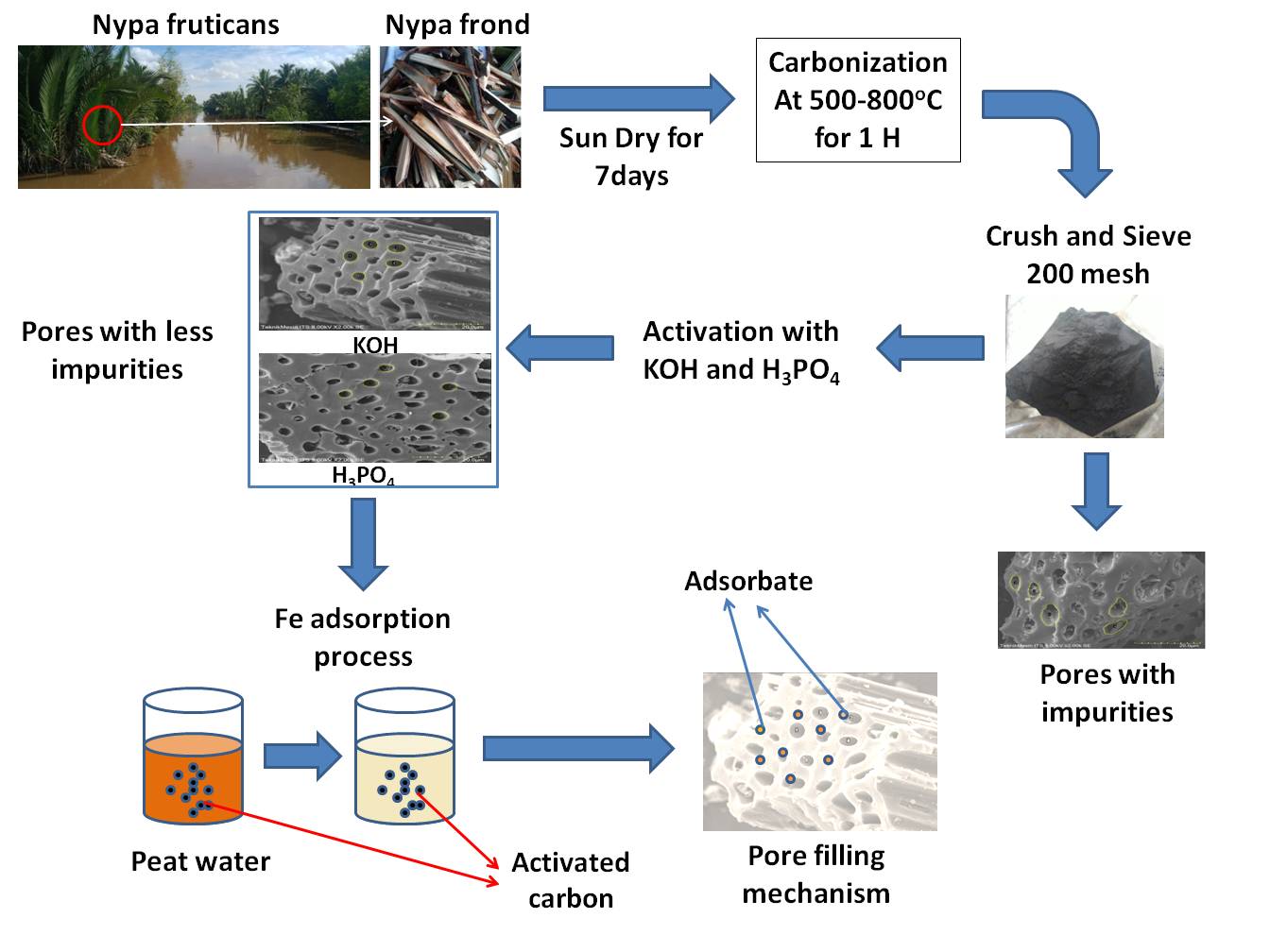
Nipa palm is one of the non-wood plants rich in lignocellulosic content. In this study, palm fronds were converted into activated carbon, and their physical, chemical, and morphological properties were characterized. The resulting activated carbon was then applied as an adsorbent of Fe metal in peat water. The carbonization process was carried out for 60 min, followed by sintering at 400°C for 5 h with a particle size of 200 mesh. KOH and H3PO4 were used in the chemical activation process for 24 h. KOH-activated carbon contained 6.13% of moisture, 4.55% of ash, 17.02% of volatile matter, and 78.84% of fixed carbon, while its Fe reduction efficiency was 28.09%. The H3PO4-activated carbon contained 4.67% of moisture, 2.84% of ash, 16.41% of volatile matter, and 80.57% of bonded carbon, and the Fe reduction efficiency was 52.25%. KOH-activated carbon and H3PO4-activated carbon contained fixed carbon of 78.84% and 80.57%, respectively, while their average rates of efficiency of Fe reduction were 22.82% and 39.23%, respectively. Overall, the characteristics of activated nipa carbon met the Indonesian standards (SNI No. 06-3730-1995). However, H3PO4-activated carbon was found to be better at adsorbing Fe metal from peat water.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools