The Journal of Renewable Materials (JRM) is an interdisciplinary journal publishing original research covering all aspects of renewable materials, namely bio-based materials, sustainable materials, green chemistry and including recycling and recovery of spent materials. The scope of the journal is devoted to reports of new and original experimental and theoretical research in the areas of materials, engineering, physics, bioscience, processing, environmental science and chemistry, which are related to renewable materials and their applications.
Ei Compendex/Engineering Village (Elsevier); Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 4.9; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.592; Google Scholar h5-index 31, ranking 5 in Wood Science &Technology; Chemical Abstracting Services; Polymer Library; Baidu Xueshu (China); Portico, etc...
Notice: Please make new submissions of JRM to the new system (ScholarOne) (https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/jrenewmater) from 25 September 2024. To view your previous submissions, please access TSP system (https://ijs.tspsubmission.com/homepage).
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0139 - 25 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Biomass-based Thermoset and Thermoplastic Polymers for Biomass-based Composites)
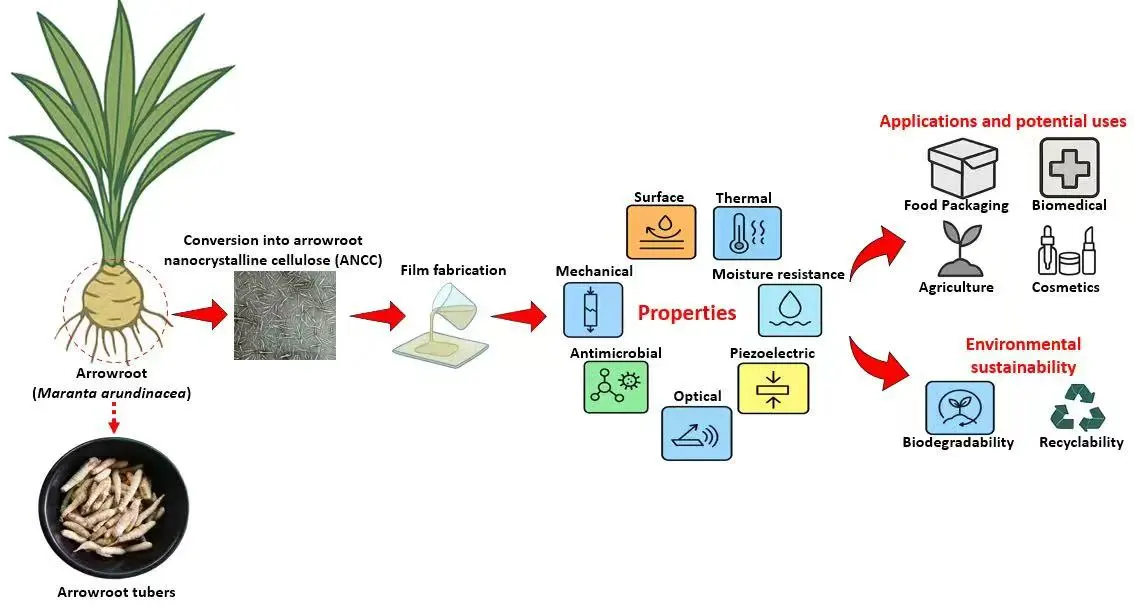
Abstract This review draws attention to the innovative use of arrowroot (Maranta arundinacea) fiber as a unique and underutilized biomass source for nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC)-based nanocomposites, presenting a noteworthy alternative to extensively researched materials like wood pulp, bacterial cellulose, and chemically modified NCCs. In contrast to traditional sources, arrowroot possesses a naturally elevated cellulose and diminished lignin content, facilitating more effective NCC extraction requiring reduced chemical input and enabling environmentally friendly processing techniques. The review evaluates the performance of arrowroot-derived nanocomposites against systems documented in the literature, including NCC-based shape memory composites and nanoparticle-reinforced films, demonstrating enhanced More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0151 - 25 February 2026
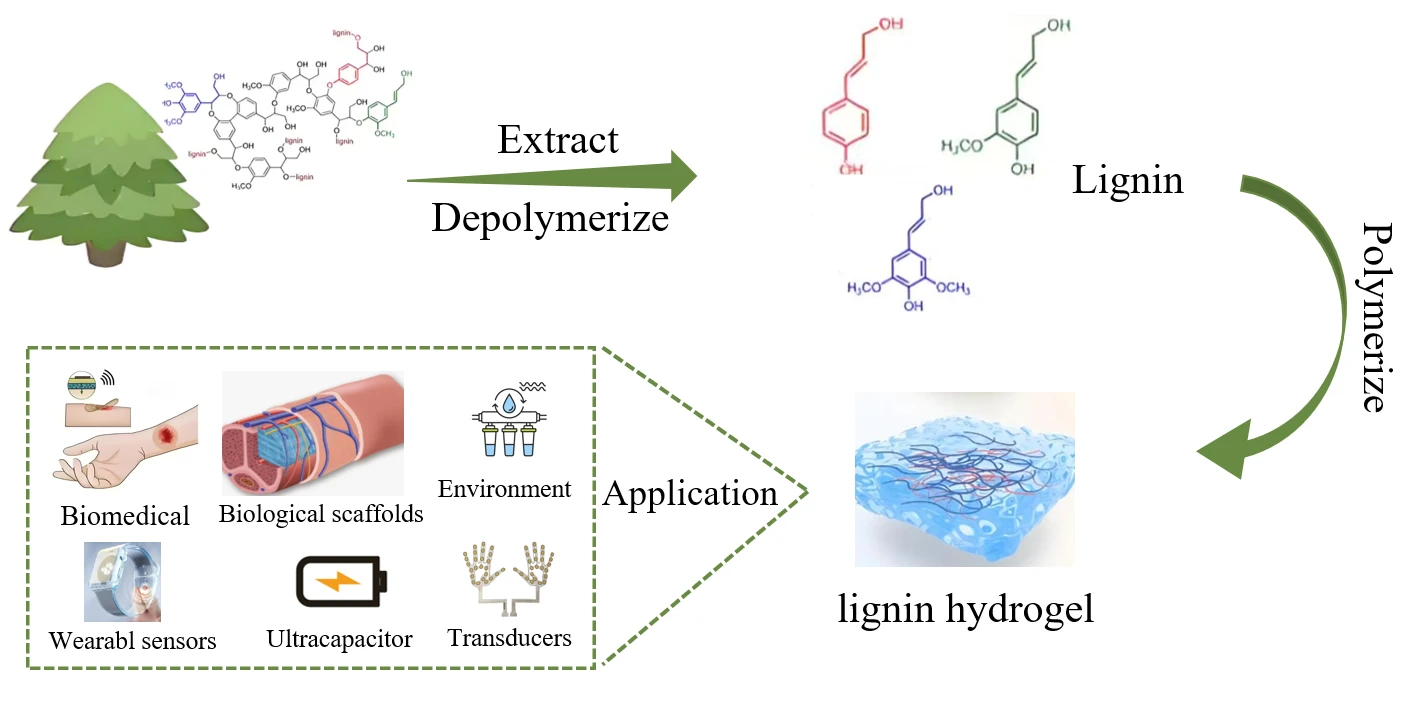
Abstract Lignin, the most abundant natural aromatic polymer globally, has garnered considerable interest due to its rich and diverse active functional groups and its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and adhesive properties. Recent research has significantly improved the performance of lignin-based hydrogels, suggesting their substantial potential in fields such as biomedicine, environmental science, and agriculture. This paper reviews the process of lignin extraction, systematically introduces synthesis strategies for preparing lignin-based hydrogels, and discusses the current state of research on these hydrogels in biomedical and environmental protection fields. It concludes by identifying the existing challenges in lignin hydrogel research and More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0152 - 25 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Eco-friendly Wood-Based Composites: Design, Manufacturing, Properties and Applications – Ⅱ)
Abstract Heat treatment is applied to wood to improve various properties of the material. The present study focuses on the colour changes of wood veneer samples due to heat treatment. Native wood species from Japan and Europe, such as Japanese oak (Quercus mongolica var. crispula), field maple (Acer campestre) and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) were used in the experiments. A laboratory-type oven was used to apply the heat at a temperature of 190°C, in the presence of oxygen, for different periods, gradually increasing from 5 to 40 min. The CIELab system (a colour space defined by the International Commission… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2026.02025-0066 - 25 February 2026
Abstract The growing demand for renewable energy has increased the use of wood pellets as a clean and efficient biomass fuel. This study aims to evaluate the physical properties of wood pellets produced from Acacia hybrid (AC) veneer waste and Pine wood (PW) waste mixed with varying ratios. The objectives are to investigate the effect of different blend ratios of Acacia hybrid veneer waste and pine wood waste on the physical properties, specifically moisture content, density, and pellet durability index (PDI) of wood pellets, and to identify the optimal ratio that yields the most desirable pellet quality. The… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0118 - 25 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Biomass-based Thermoset and Thermoplastic Polymers for Biomass-based Composites)
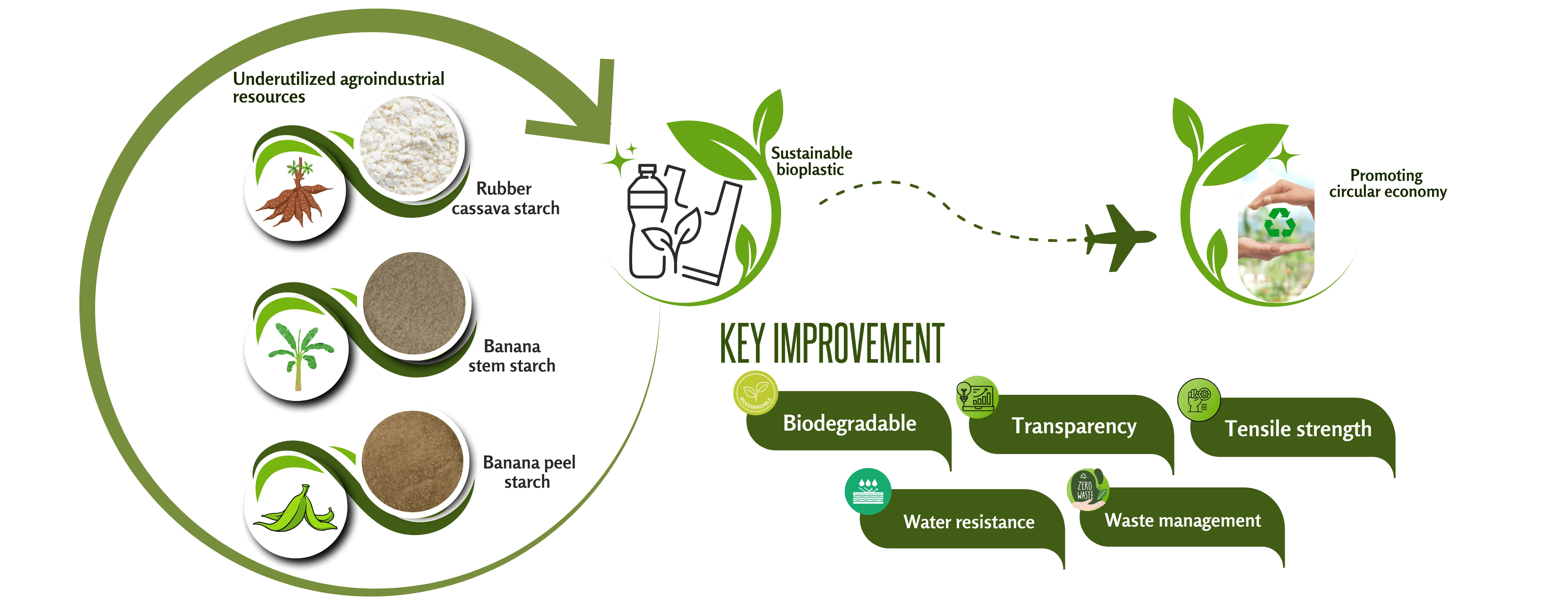
Abstract This study investigates the potential of starch extracted from underutilized agro-industrial resources as non-food-competing raw materials for the development of flexible bioplastics for food packaging applications. Starch was extracted from three biomass sources: rubber cassava (Manihot glaziovii), banana stem, and banana peel from Ambonese banana (Musa acuminata L.). Rubber cassava starch (SRC) exhibited the highest starch yield (50.68 ± 0.28%), significantly surpassing banana stem (SBS, 14.20 ± 0.25%) and banana peel (SBP, 3.07 ± 0.15%). The amylose contents of SRC, SBS, and SBP were 28.18%, 52.80%, and 56.57%, respectively, while their amylopectin contents were 71.83%, 47.20%, and 43.43%. FTIR spectra… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0132 - 25 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances on Renewable Materials)
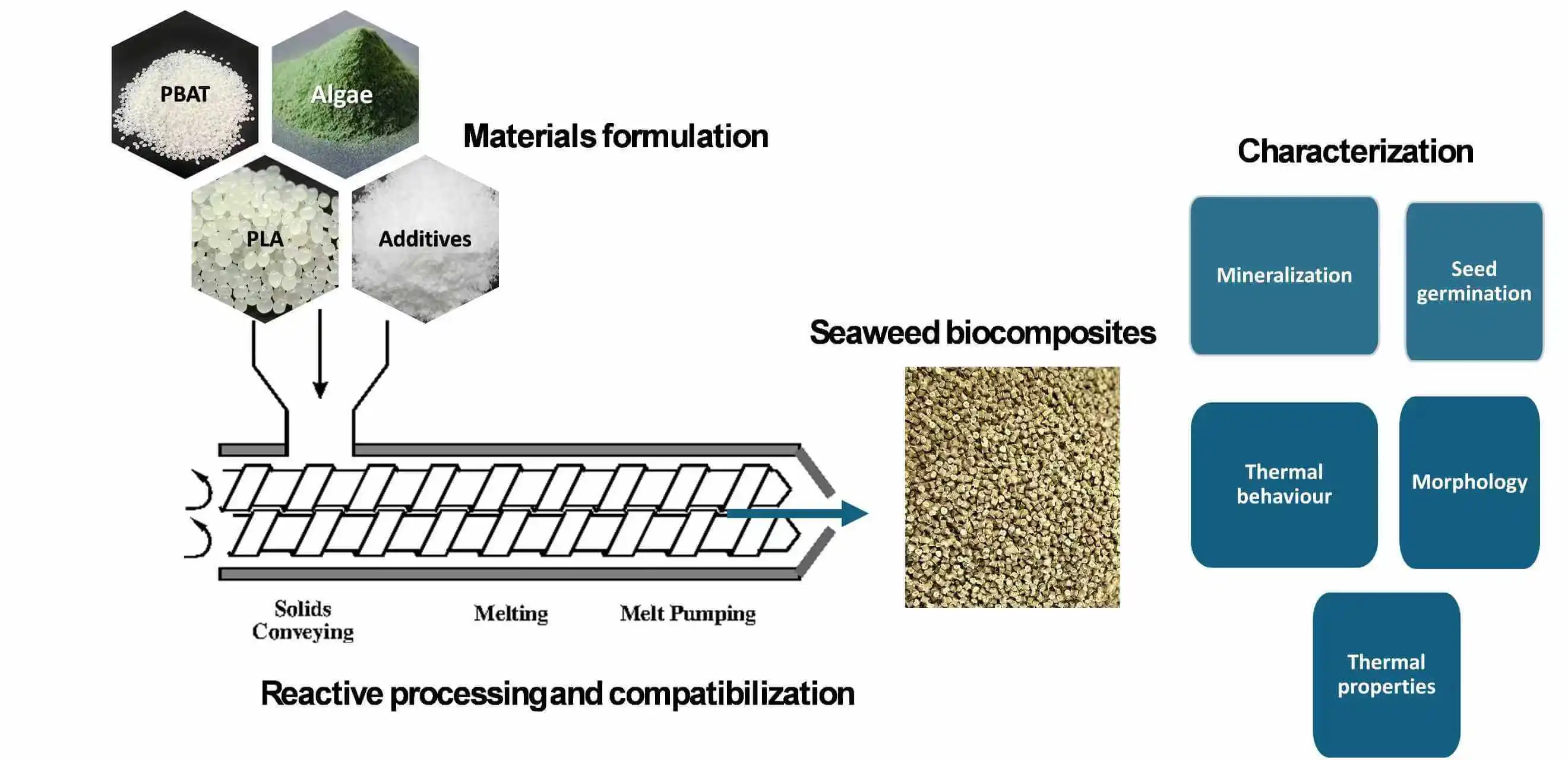
Abstract Melt blending of biodegradable polyesters such as poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and poly (butylene adipate co-terephthalate) (PBAT) with a compatibilizer and natural filler offers a chance to develop biodegradable bio-composites with improved performance. In this study, we examined how PLA/PBAT blends behave during ultimate biodegradation (mineralization), both with and without compatibilizer and algae as a reinforcement, under controlled composting conditions using carbon dioxide (CO2) respirometry techniques. Throughout the biodegradation process, the disintegration behaviour, thermal, chemical, and morphological properties of test samples before and after biodegradation were analyzed using FTIR, TGA, DSC, and SEM techniques. The results… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0138 - 25 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Biobased Nanoemulsions for a Sustainable Future)
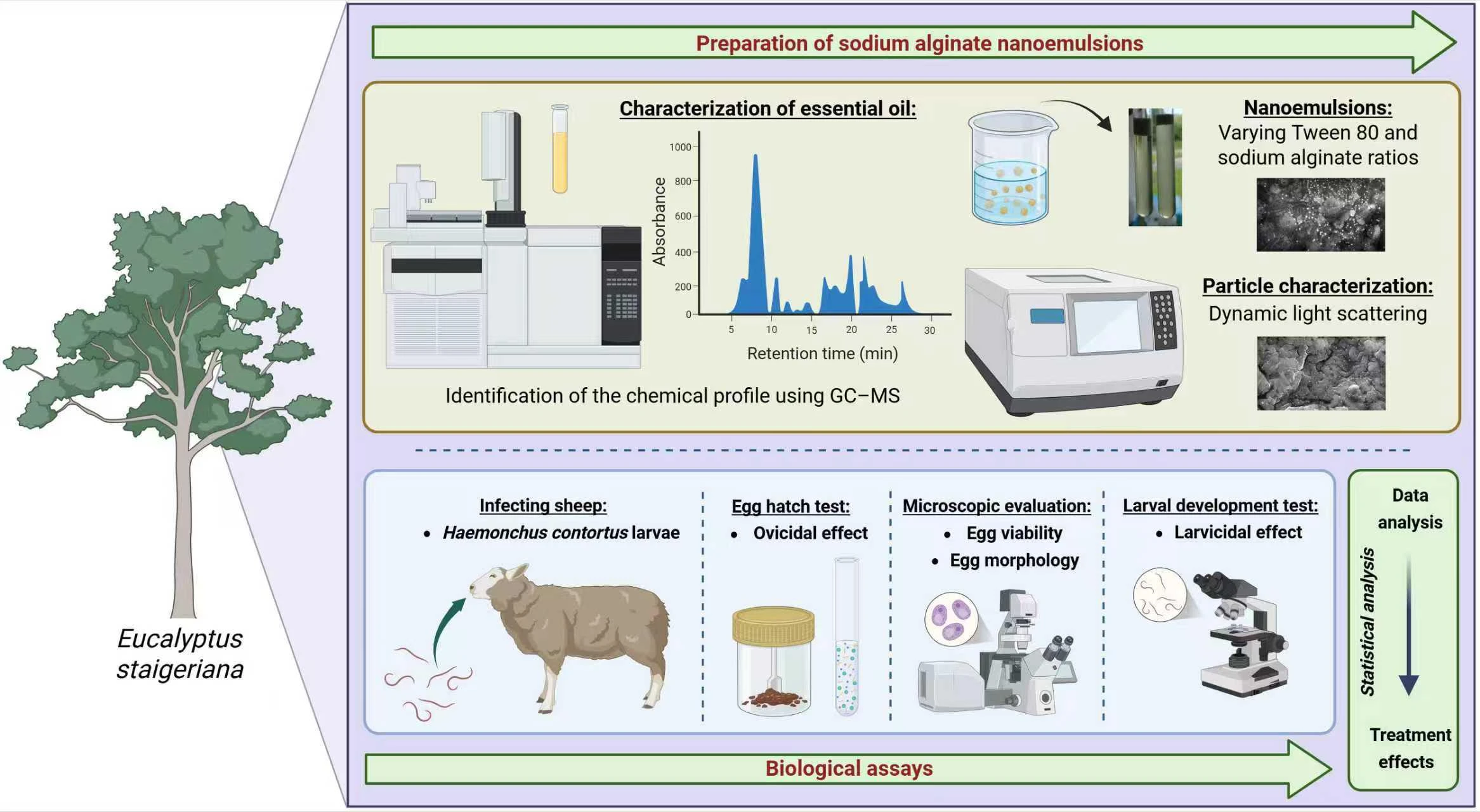
Abstract Eucalyptus staigeriana essential oil (EsEO) has well-known anthelmintic activity in small ruminants. However, its volatility limits its therapeutic action. The aim of this study was to develop a water-in-oil sodium alginate-based nanoemulsion with an effective in vitro effect on the eggs and larvae of Haemonchus contortus, a gastrointestinal parasite of sheep and goats. Four oil-in-water sodium alginate-based emulsions were prepared using a high-energy method with different proportions of Tween 80, EsEO, and sodium alginate (ALG) 4%. The physical-chemical characterization included stability, particle size, zeta potential and infrared spectra. The effects of the emulsions were evaluated against H. contortus via… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.2, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0163 - 25 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Nanostructured Porous Materials: Synthesis, Processing, and Applications)
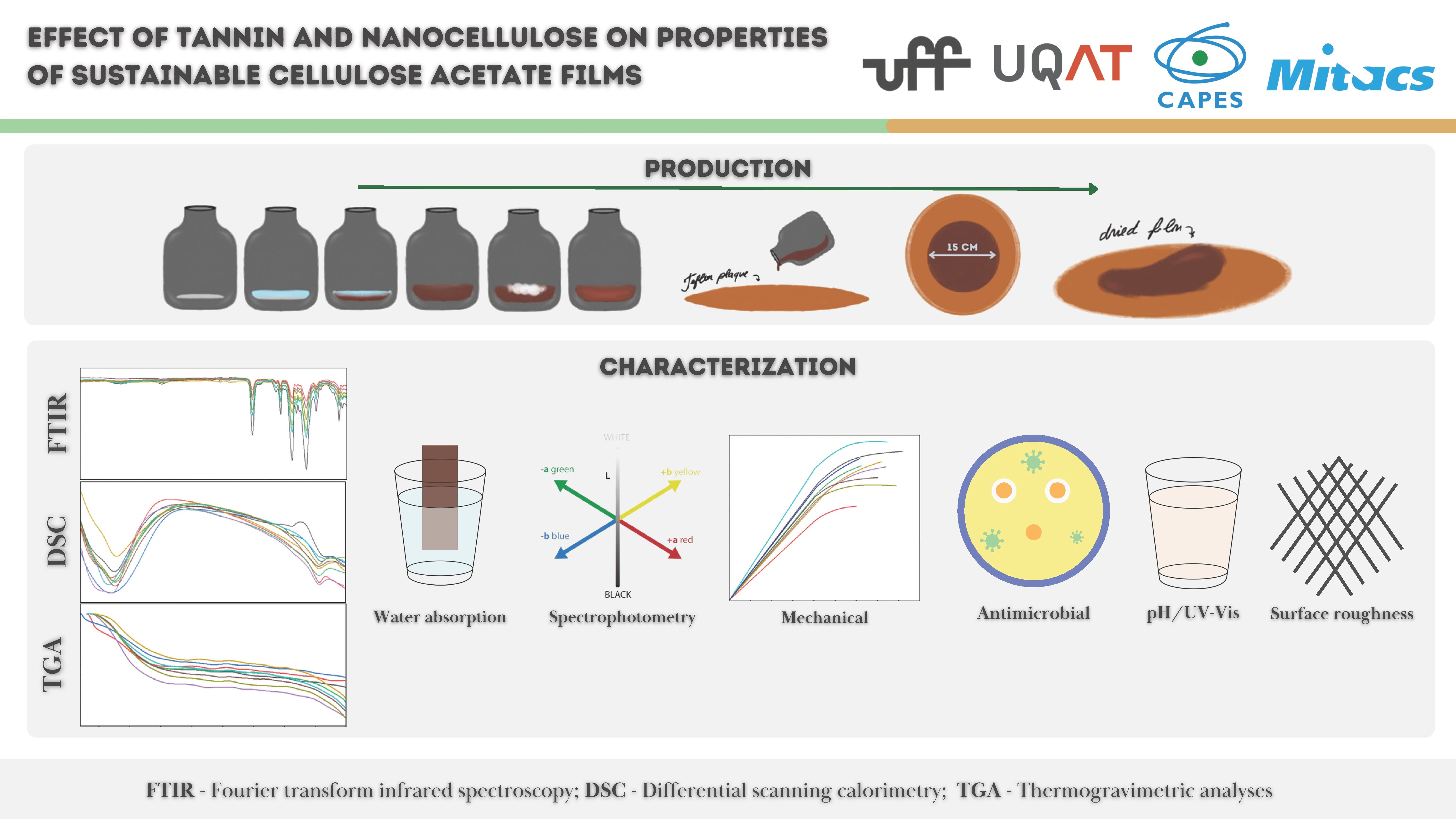
Abstract The development of sustainable materials has encouraged the use of biopolymers as alternatives to synthetic polymers. Polymeric films have stood out for their high potential in environmentally sustainable applications. Conventional cellulose acetate (CA)-based films are attractive due to their biodegradability and film-forming ability. However, their functional performance often requires enhancement through the incorporation of additives. In this context, two bio-based additives were investigated: condensed tannin (0%, 5% and 10%wt.), a natural polyphenol known for its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, and nanocrystalline cellulose (CNC) (0%, 0.5% and 1%wt.), which act as reinforcing agents to improve mechanical… More >
Graphic Abstract