 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Structural Health Monitoring Using Image Processing and Advanced Technologies for the Identification of Deterioration of Building Structure: A Review
1 Department of Computer Engineering, Veermata Jijabai Technological Institute, Mumbai, 400019, India
2 Department of Structural Engineering, Veermata Jijabai Technological Institute, Mumbai, 400019, India
* Corresponding Author: Kavita Bodke. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning Approaches for Real-Time Damage Detection and Structural Monitoring in Civil Structures)
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring 2025, 19(6), 1547-1562. https://doi.org/10.32604/sdhm.2025.069239
Received 18 June 2025; Accepted 20 August 2025; Issue published 17 November 2025
Abstract
Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) systems play a key role in managing buildings and infrastructure by delivering vital insights into their strength and structural integrity. There is a need for more efficient techniques to detect defects, as traditional methods are often prone to human error, and this issue is also addressed through image processing (IP). In addition to IP, automated, accurate, and real- time detection of structural defects, such as cracks, corrosion, and material degradation that conventional inspection techniques may miss, is made possible by Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies like Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL). This review examines the integration of computer vision and AI techniques in Structural Health Monitoring (SHM), investigating their effectiveness in detecting various forms of structural deterioration. Also, it evaluates ML and DL models in SHM for their accuracy in identifying and assessing structural damage, ultimately enhancing safety, durability, and maintenance practices in the field. Key findings reveal that AI-powered approaches, especially those utilizing IP and DL models like CNNs, significantly improve detection efficiency and accuracy, with reported accuracies in various SHM tasks. However, significant research gaps remain, including challenges with the consistency, quality, and environmental resilience of image data, a notable lack of standardized models and datasets for training across diverse structures, and concerns regarding computational costs, model interpretability, and seamless integration with existing systems. Future work should focus on developing more robust models through data augmentation, transfer learning, and hybrid approaches, standardizing protocols, and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration to overcome these limitations and achieve more reliable, scalable, and affordable SHM systems.Graphic Abstract
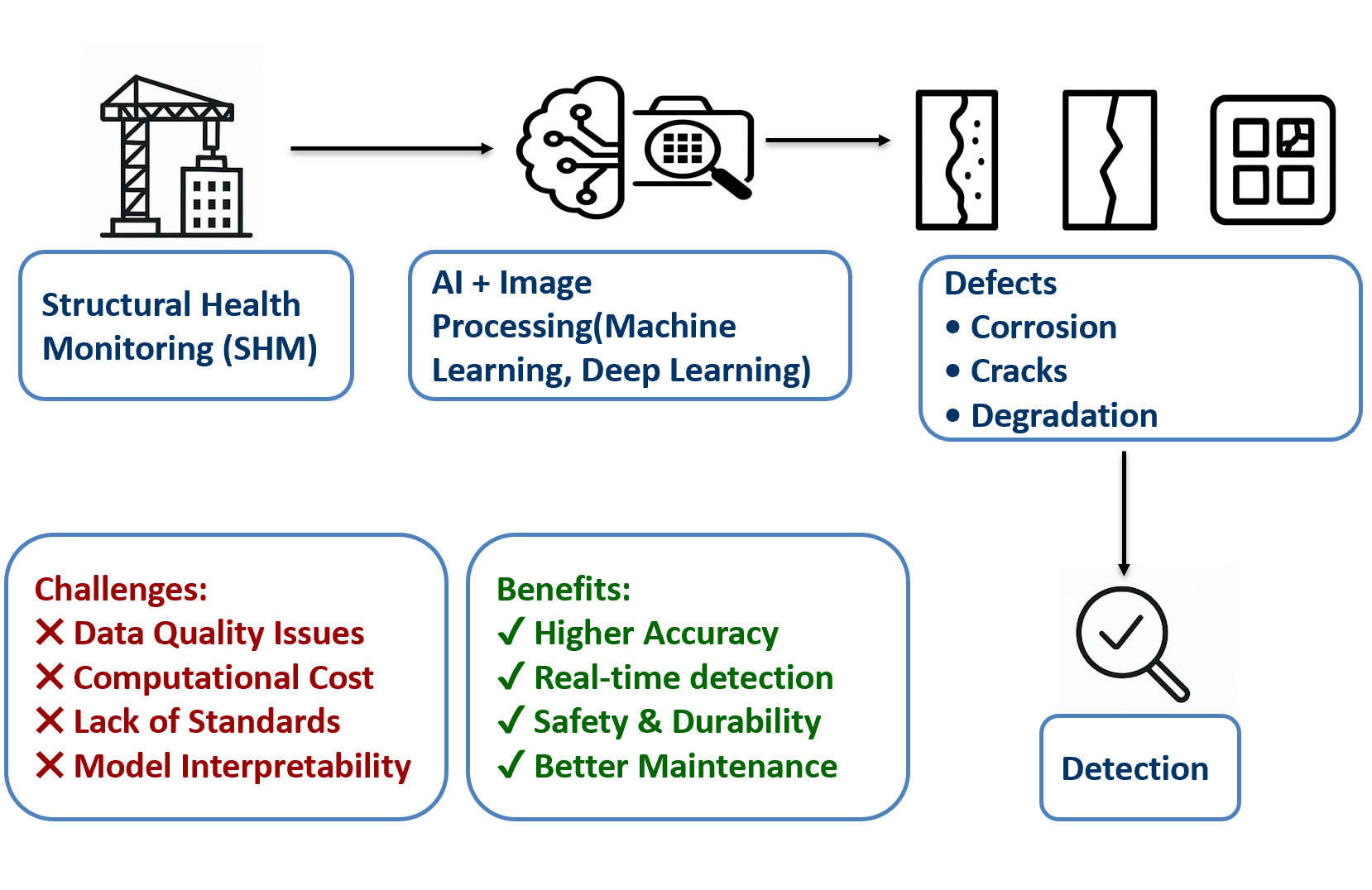
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools