 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Robustness and Performance Comparison of Generative AI Time Series Anomaly Detection under Noise
1 Department of Computer Education/Data Science, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, 03063, Republic of Korea
2 Department of Computer Education/Social Innovation Convergence Program, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, 03063, Republic of Korea
* Corresponding Author: Moohong Min. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 145(3), 3913-3948. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.072261
Received 22 August 2025; Accepted 23 October 2025; Issue published 23 December 2025
Abstract
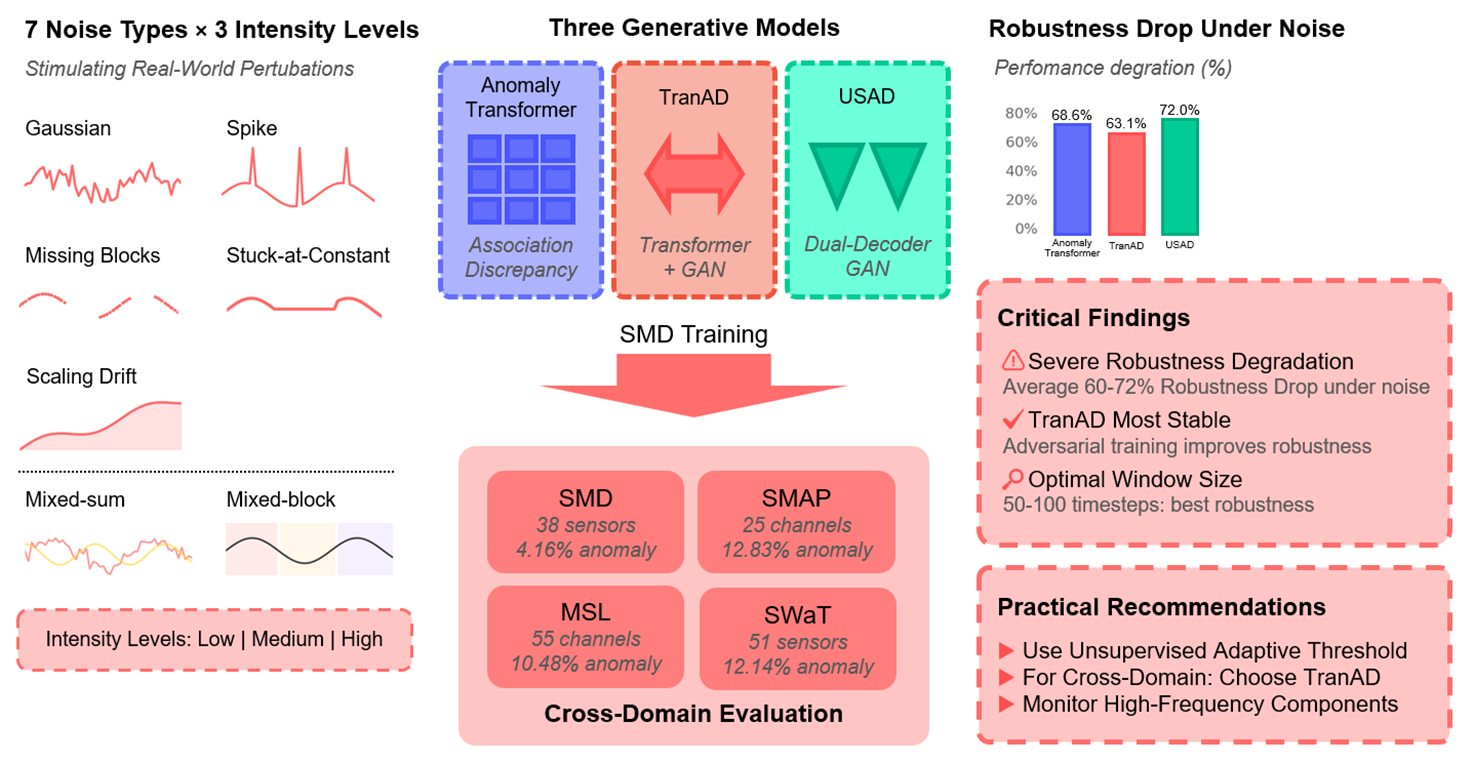
Time series anomaly detection is critical in domains such as manufacturing, finance, and cybersecurity. Recent generative AI models, particularly Transformer- and Autoencoder-based architectures, show strong accuracy but their robustness under noisy conditions is less understood. This study evaluates three representative models—AnomalyTransformer, TranAD, and USAD—on the Server Machine Dataset (SMD) and cross-domain benchmarks including the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) dataset, the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) dataset, and the Secure Water Treatment (SWaT) testbed. Seven noise settings (five canonical, two mixed) at multiple intensities are tested under fixed clean-data training, with variations in window, stride, and thresholding. Results reveal distinct robustness profiles: AnomalyTransformer maintains recall but loses precision under abrupt noise, TranAD balances sensitivity yet is vulnerable to structured anomalies, and USAD resists Gaussian perturbations but collapses under block anomalies. Quantitatively, F1 drops 60%–70% on noisy SMD, with severe collapse in SWaT (F1Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools