 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Numerical Analysis of Pressure Propagation Emitted by Collapse of a Single Cavitation Bubble near an Oscillating Wall
Quang-Thai Nguyen1,2,#, Duong Ngoc Hai3,4,#, The-Duc Nguyen1,3,4,*, Van-Tu Nguyen2,*, Jinyul Hwang2, Warn-Gyu Park2
1 Institute of Mechanics, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Hanoi, 100000, Vietnam
2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan, 46241, Republic of Korea
3 Graduate University of Science and Technology, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Hanoi, 100000, Vietnam
4 University of Engineering and Technology, Vietnam National University, Hanoi, 100000, Vietnam
* Corresponding Authors: The-Duc Nguyen. Email:  ; Van-Tu Nguyen. Email:
; Van-Tu Nguyen. Email: 
# These authors contributed equally to this work as the first author
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Modeling and Applications of Bubble and Droplet in Engineering and Sciences)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 145(3), 3433-3452. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.070570
Received 19 July 2025; Accepted 10 November 2025; Issue published 23 December 2025
Abstract
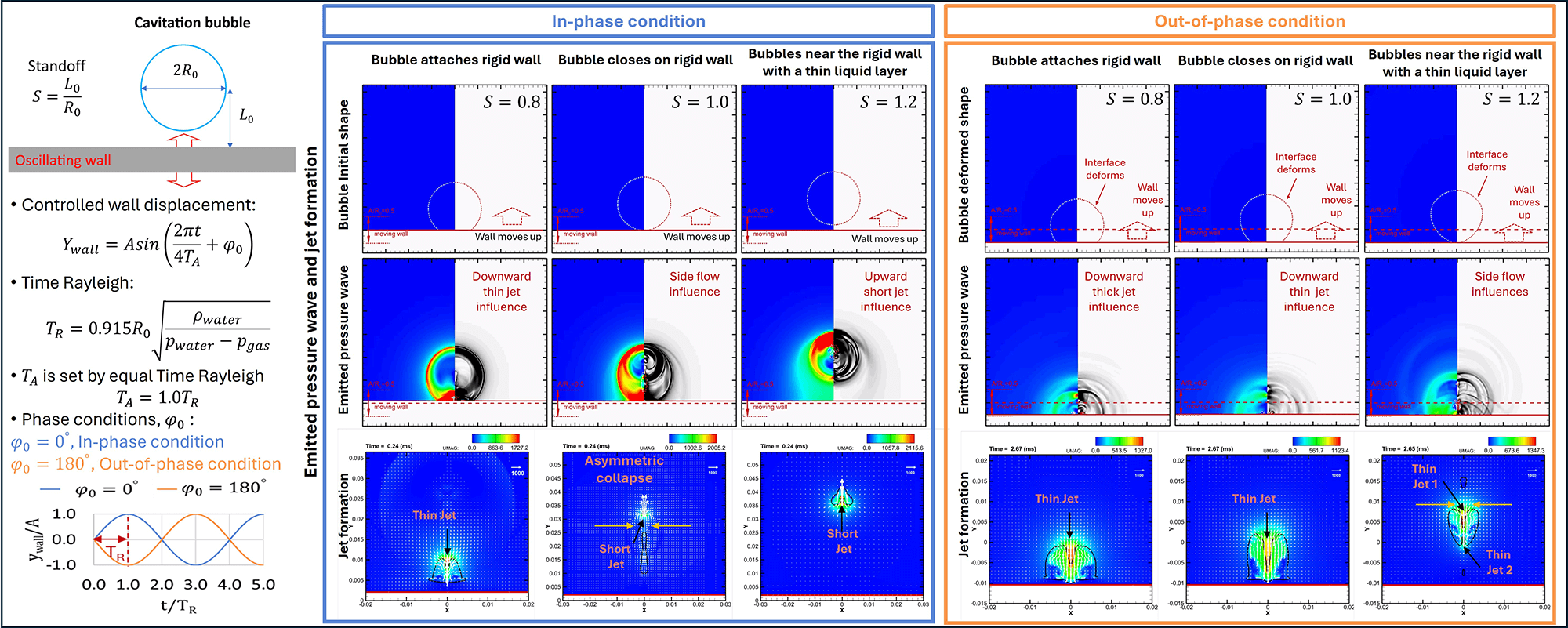
This study presents a numerical analysis of the effects of a rigid flat wall with oscillating motion on the pressure wave propagation during a single spherical cavitation bubble collapse at different initial bubble positions. Different nondimensional distances
S = 0.8, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.2 and 1.3 were considered to investigate the effects of initial in-phase and out-of-phase oscillations of the flat wall. Numerical simulations of cavitation bubble collapse near an oscillating wall were conducted using a compressible two-phase flow model. This model incorporated the Volume of Fluid (VOF) interface-sharpening technique on a general curvilinear moving grid. The numerical results were consistent with published experimental data. The simulation examined the impact of oscillating walls on bubble behavior and the resulting pressure peaks observed on the wall surface. The numerical results demonstrate the significant impact of wall oscillation conditions on bubble collapse and migration behavior, and consequently, the generation of pressure waves with significantly different propagation and pressure peaks induced by shock impact on the rigid wall. Different behaviors were observed in the trendlines of the pressure peaks and maximum jet velocity under in-phase and out-of-phase oscillating walls, with distinct values. At
S≥1.0, a higher-pressure peak on the wall was observed in the case of the out-of-phase oscillating condition, whereas a higher-pressure peak was found in the case of the in-phase condition at
S<1.0. The highest-pressure peak was found at
S=0.8 in trend lines of in-phase and
S=1.1 in trend lines of out-of-phase oscillation effects.
Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Pressure propagation; numerical analysis; cavitation bubble collapse; oscillating wall effects
Cite This Article
APA Style
Nguyen, Q., Hai, D.N., Nguyen, T., Nguyen, V., Hwang, J. et al. (2025). Numerical Analysis of Pressure Propagation Emitted by Collapse of a Single Cavitation Bubble near an Oscillating Wall.
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences,
145(3), 3433–3452.
https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.070570
Vancouver Style
Nguyen Q, Hai DN, Nguyen T, Nguyen V, Hwang J, Park W. Numerical Analysis of Pressure Propagation Emitted by Collapse of a Single Cavitation Bubble near an Oscillating Wall. Comput Model Eng Sci. 2025;145(3):3433–3452.
https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.070570
IEEE Style
Q. Nguyen, D. N. Hai, T. Nguyen, V. Nguyen, J. Hwang, and W. Park, “Numerical Analysis of Pressure Propagation Emitted by Collapse of a Single Cavitation Bubble near an Oscillating Wall,”
Comput. Model. Eng. Sci., vol. 145, no. 3, pp. 3433–3452, 2025.
https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.070570

Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
 Open Access
Open Access; Van-Tu Nguyen. Email:
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.

 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools