 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Feature Selection Optimisation for Cancer Classification Based on Evolutionary Algorithms: An Extensive Review
1 Faculty of Computing and Meta-Technology, Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris, Tanjong Malim, 35900, Malaysia
2 Faculty of Science and Technology, Universitas Islam Negeri Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau, Pekanbaru, 28293, Indonesia
3 Centre for Global Sustainability Studies, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang, 11800, Malaysia
4 Premier Integrated Lab, Pantai Hospital Ampang, Kuala Lumpur, 59100, Malaysia
5 Sunway Medical Centre, Subang Jaya, Selangor, 47500, Malaysia
6 Fakultas Teknologi Informasi, Universitas Islam Kalimantan Muhammad Arsyad Al-Banjar, Banjarmasin, 70123, Indonesia
7 Data Intelligence and Knowledge Management Special Interest Group, Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris, Tanjong Malim, 35900, Malaysia
* Corresponding Author: Shir Li Wang. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Computational Intelligence Techniques, Uncertain Knowledge Processing and Multi-Attribute Group Decision-Making Methods Applied in Modeling of Medical Diagnosis and Prognosis)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 143(3), 2711-2765. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.062709
Received 25 December 2024; Accepted 19 May 2025; Issue published 30 June 2025
Abstract
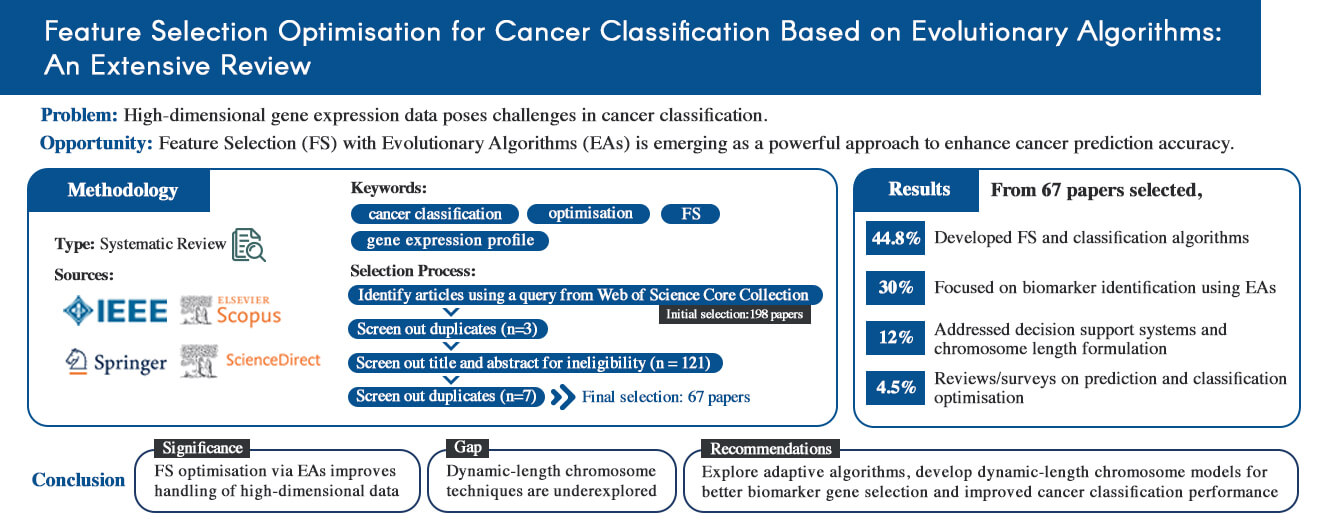
In recent years, feature selection (FS) optimization of high-dimensional gene expression data has become one of the most promising approaches for cancer prediction and classification. This work reviews FS and classification methods that utilize evolutionary algorithms (EAs) for gene expression profiles in cancer or medical applications based on research motivations, challenges, and recommendations. Relevant studies were retrieved from four major academic databases–IEEE, Scopus, Springer, and ScienceDirect–using the keywords ‘cancer classification’, ‘optimization’, ‘FS’, and ‘gene expression profile’. A total of 67 papers were finally selected with key advancements identified as follows: (1) The majority of papers (44.8%) focused on developing algorithms and models for FS and classification. (2) The second category encompassed studies on biomarker identification by EAs, including 20 papers (30%). (3) The third category comprised works that applied FS to cancer data for decision support system purposes, addressing high-dimensional data and the formulation of chromosome length. These studies accounted for 12% of the total number of studies. (4) The remaining three papers (4.5%) were reviews and surveys focusing on models and developments in prediction and classification optimization for cancer classification under current technical conditions. This review highlights the importance of optimizing FS in EAs to manage high-dimensional data effectively. Despite recent advancements, significant limitations remain: the dynamic formulation of chromosome length remains an underexplored area. Thus, further research is needed on dynamic-length chromosome techniques for more sophisticated biomarker gene selection techniques. The findings suggest that further advancements in dynamic chromosome length formulations and adaptive algorithms could enhance cancer classification accuracy and efficiency.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools