 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Enhancing 3D U-Net with Residual and Squeeze-and-Excitation Attention Mechanisms for Improved Brain Tumor Segmentation in Multimodal MRI
1 International Ph.D. Program in Innovative Technology of Biomedical Engineering and Medical Devices, Ming Chi University of Technology, New Taipei City, 243303, Taiwan
2 Department of Computer Engineering, College of Computer and Information Sciences, King Saud University, P.O. Box 51178, Riyadh, 11543, Saudi Arabia
* Corresponding Author: Nisar Ahmad. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Healthcare: Insights into Data Management, Integration, and Ethical Considerations)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 144(1), 1197-1224. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.066580
Received 11 April 2025; Accepted 26 June 2025; Issue published 31 July 2025
Abstract
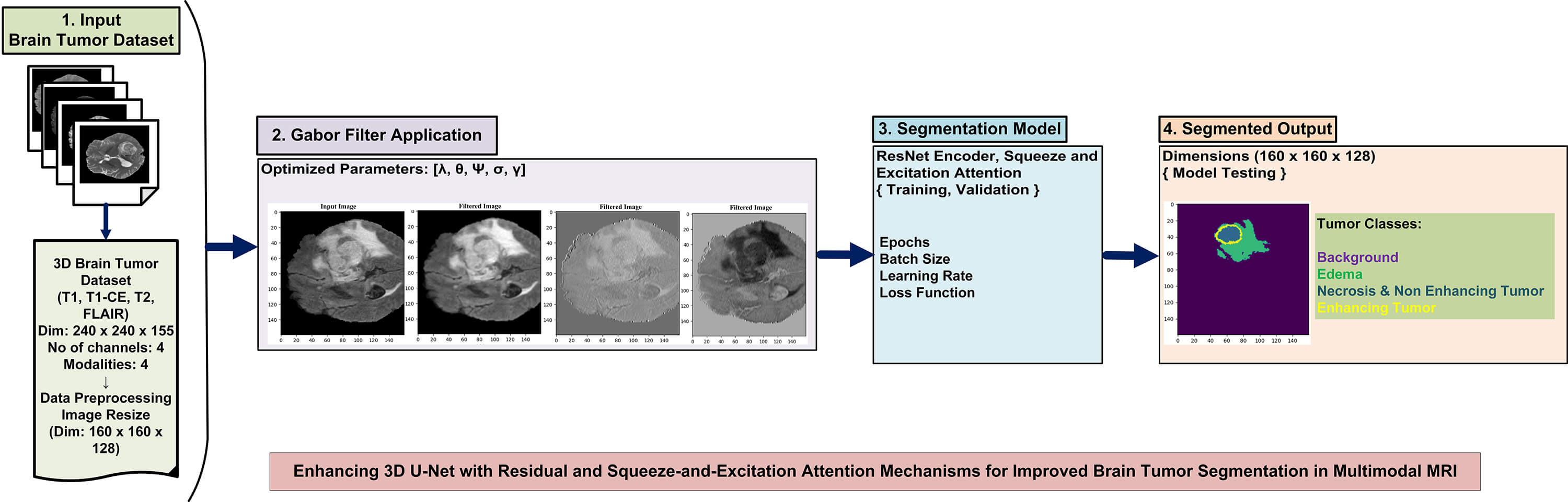
Accurate and efficient brain tumor segmentation is essential for early diagnosis, treatment planning, and clinical decision-making. However, the complex structure of brain anatomy and the heterogeneous nature of tumors present significant challenges for precise anomaly detection. While U-Net-based architectures have demonstrated strong performance in medical image segmentation, there remains room for improvement in feature extraction and localization accuracy. In this study, we propose a novel hybrid model designed to enhance 3D brain tumor segmentation. The architecture incorporates a 3D ResNet encoder known for mitigating the vanishing gradient problem and a 3D U-Net decoder. Additionally, to enhance the model’s generalization ability, Squeeze and Excitation attention mechanism is integrated. We introduce Gabor filter banks into the encoder to further strengthen the model’s ability to extract robust and transformation-invariant features from the complex and irregular shapes typical in medical imaging. This approach, which is not well explored in current U-Net-based segmentation frameworks, provides a unique advantage by enhancing texture-aware feature representation. Specifically, Gabor filters help extract distinctive low-level texture features, reducing the effects of texture interference and facilitating faster convergence during the early stages of training. Our model achieved Dice scores of 0.881, 0.846, and 0.819 for Whole Tumor (WT), Tumor Core (TC), and Enhancing Tumor (ET), respectively, on the BraTS 2020 dataset. Cross-validation on the BraTS 2021 dataset further confirmed the model’s robustness, yielding Dice score values of 0.887 for WT, 0.856 for TC, and 0.824 for ET. The proposed model outperforms several state-of-the-art existing models, particularly in accurately identifying small and complex tumor regions. Extensive evaluations suggest integrating advanced preprocessing with an attention-augmented hybrid architecture offers significant potential for reliable and clinically valuable brain tumor segmentation.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools