 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fuzzy Logic-Based Robust Global Consensus in Leader-Follower Robotic Systems under Sensor and Actuator Attacks Using Hybrid Control Strategy
1 Metaverse Research Institute, School of Computer Science and Cyber Engineering, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou, 510006, China
2 Department of Mathematics, College of Sciences, Northern Border University, Arar, 91431, Saudi Arabia
3 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of Lahore, Sargodha, 40100, Pakistan
4 Department of Mathematics, College of Sciences and Arts (Muhyil), King Khalid University, Muhyil, 61421, Saudi Arabia
5 Department of Mathematics, College of Sciences and Humanities, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, Alkharj, 11942, Saudi Arabia
6 School of Engineering Sciences, Lappeenranta-Lahti University of Technology, Lappeenranta, 53850, Finland
* Corresponding Authors: Fathia Moh. Al Samman. Email: ; Azmat Ullah Khan Niazi. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Control and Machine Learning for Renewable Energy Systems and Industries)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 144(2), 1971-1999. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.068240
Received 23 May 2025; Accepted 11 July 2025; Issue published 31 August 2025
Abstract
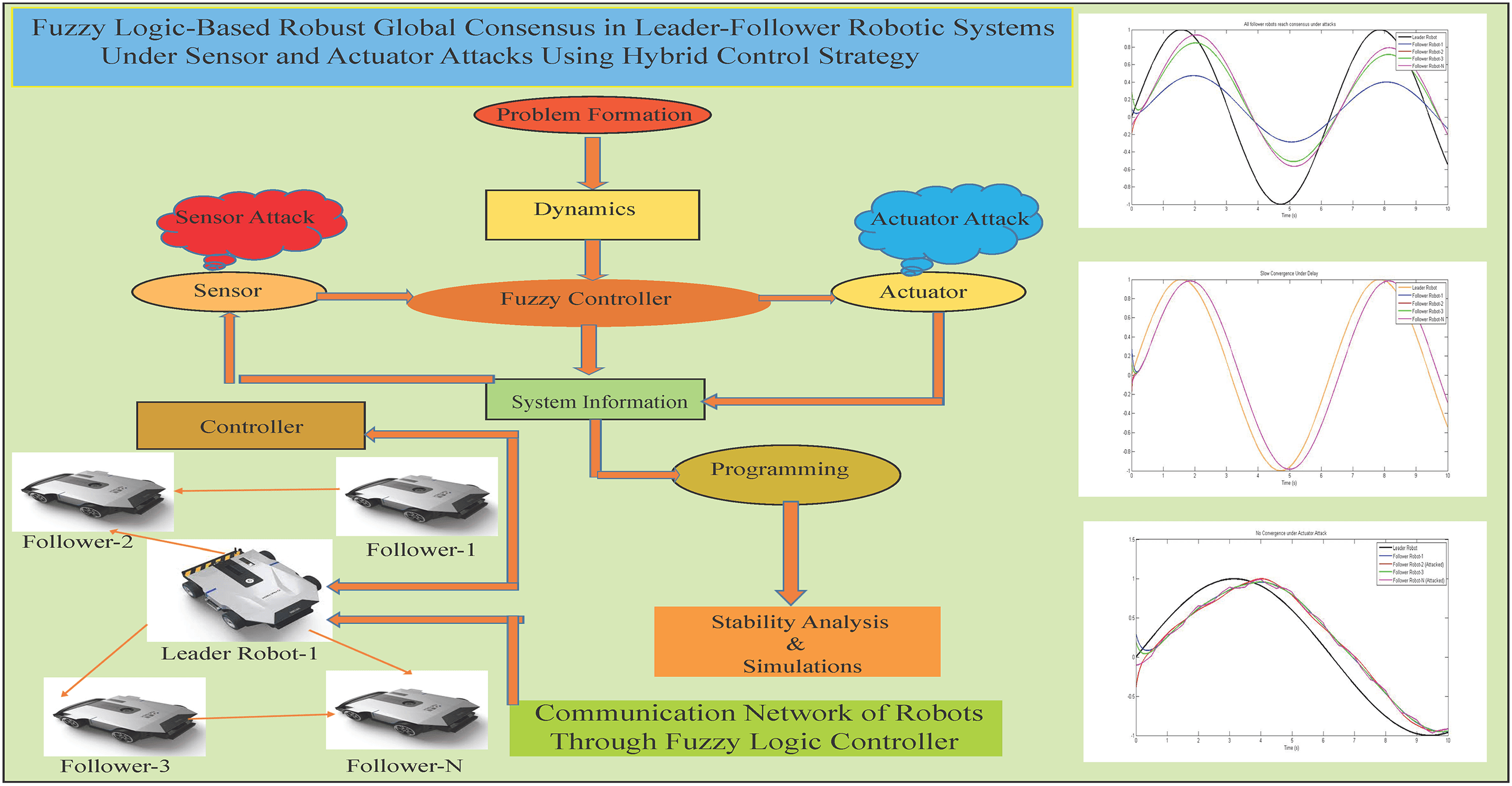
This research paper tackles the complexities of achieving global fuzzy consensus in leader-follower systems in robotic systems, focusing on robust control systems against an advanced signal attack that integrates sensor and actuator disturbances within the dynamics of follower robots. Each follower robot has unknown dynamics and control inputs, which expose it to the risks of both sensor and actuator attacks. The leader robot, described by a second-order, time-varying nonlinear model, transmits its position, velocity, and acceleration information to follower robots through a wireless connection. To handle the complex setup and communication among robots in the network, we design a robust hybrid distributed adaptive control strategy combining the effect of sensor and actuator attack, which ensures asymptotic consensus, extending beyond conventional bounded consensus results. The proposed framework employs fuzzy logic systems (FLSs) as proactive controllers to estimate unknown nonlinear behaviors, while also effectively managing sensor and actuator attacks, ensuring stable consensus among all agents. To counter the impact of the combined signal attack on follower dynamics, a specialized robust control mechanism is designed, sustaining system stability and performance under adversarial conditions. The efficiency of this control strategy is demonstrated through simulations conducted across two different directed communication topologies, underscoring the protocol’s adaptability, resilience, and effectiveness in maintaining global consensus under complex attack scenarios.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools