 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
An Efficient GPU Solver for Maximizing Fundamental Eigenfrequency in Large-Scale Three-Dimensional Topology Optimization
1 School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Beihang University, Beijing, 102206, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems, Beihang University, Beijing, 100191, China
* Corresponding Author: Junpeng Zhao. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods, and Engineering Applications)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 145(1), 127-151. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.070769
Received 23 July 2025; Accepted 09 September 2025; Issue published 30 October 2025
Abstract
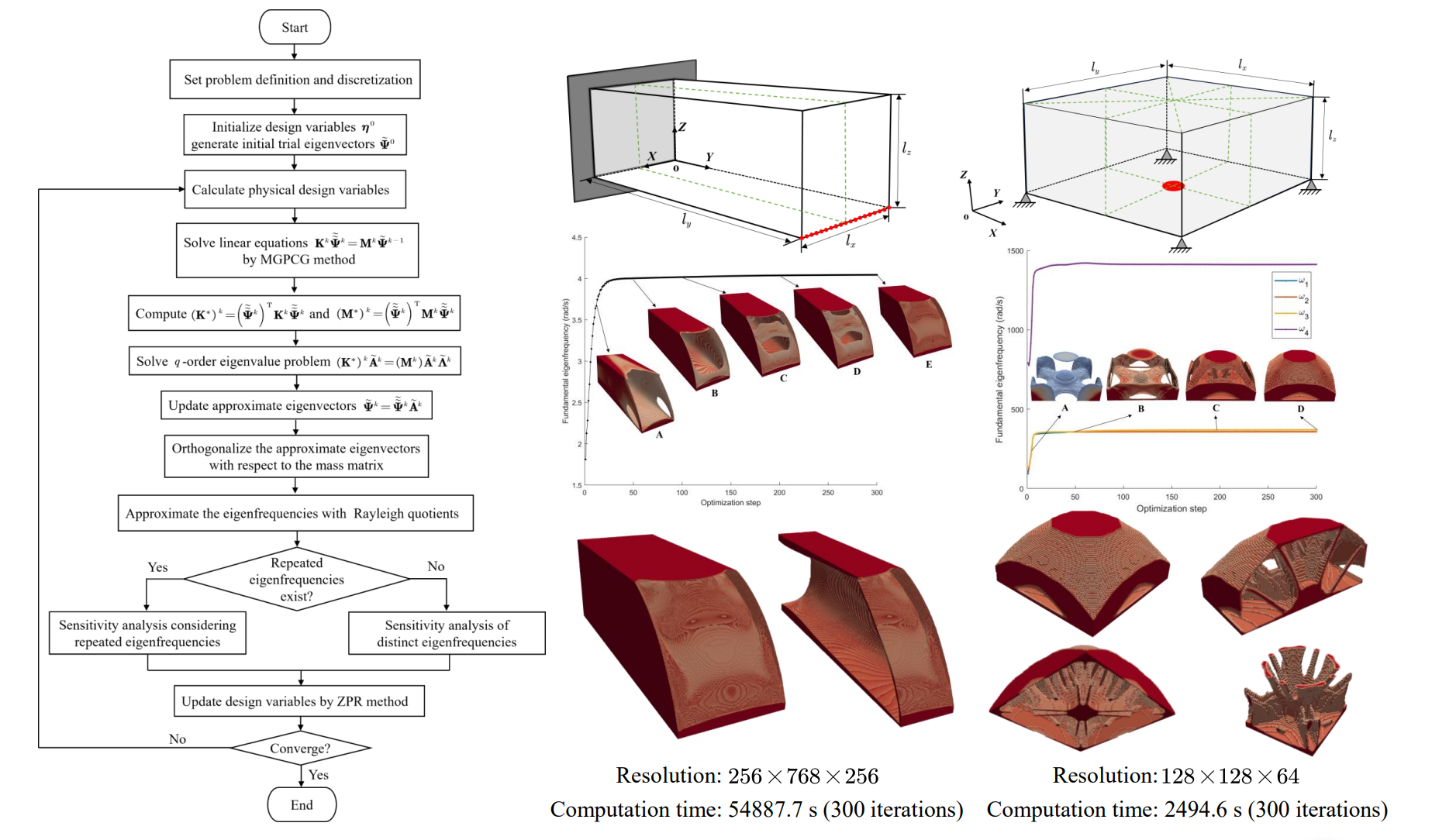
A major bottleneck in large-scale eigenfrequency topology optimization is the repeated solution of the generalized eigenvalue problem. This work presents an efficient graphics processing unit (GPU) solver for three-dimensional (3D) topology optimization that maximizes the fundamental eigenfrequency. The Successive Iteration of Analysis and Design (SIAD) framework is employed to avoid solving a full eigenproblem at every iteration. The sequential approximation of the eigenpairs is solved by the GPU-accelerated multigrid-preconditioned conjugate gradient (MGPCG) method to efficiently improve the eigenvectors along with the topological evolution. The cluster-mean approach is adopted to address the non-differentiability issue caused by repeated eigenfrequencies. The corresponding sensitivity analysis method is provided. The parallelized gradient-based Zhang-Paulino-Ramos Jr. (ZPR) algorithm is employed to update the design variables. The effectiveness of the proposed solver is demonstrated through two large-scale numerical examples. The first example demonstrates the accuracy, efficiency, and scalability of the proposed solver by solving a 3D optimization problem of 50.33 million elements being solved in approximately 15.2 h over 300 iterations on a single NVIDIA Tesla V100 GPU. The second example validates the effectiveness of the proposed solver in the presence of repeated eigenfrequencies. Our findings also highlight that higher-resolution models produce distinct optimized structures with higher fundamental frequencies, underscoring the necessity of large-scale topology optimization.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools