 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Predicting Soil Carbon Pools in Central Iran Using Random Forest: Drivers and Uncertainty Analysis
1 Department of Geography, Faculty of Geographical Sciences, Isfahan University, Isfahan, 81746-73441, Iran
2 State Key Laboratory of Desert and Oasis Ecology, Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Urumqi, 830011, China
3 Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan, 84156-83111, Iran
4 Soil Resource Management, Department of Soil Science, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Tehran, Karaj, 77871-31587, Iran
* Corresponding Author: Shamsollah Ayoubi. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in Environmental Monitoring and Management)
Revue Internationale de Géomatique 2025, 34, 809-829. https://doi.org/10.32604/rig.2025.069538
Received 25 June 2025; Accepted 27 August 2025; Issue published 06 November 2025
Abstract
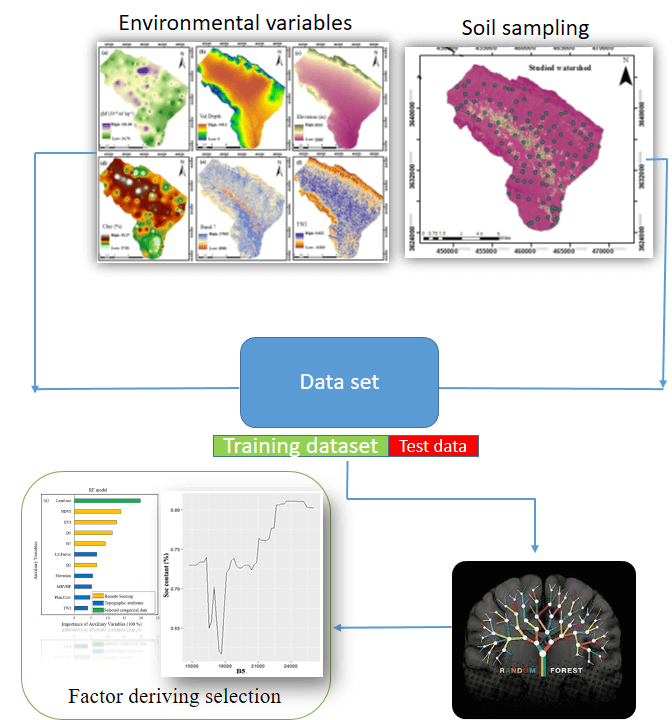
Accurate spatial prediction of soil organic carbon (SOC) and soil inorganic carbon (SIC) is vital for land management decisions. This study targets SOC/SIC mapping challenges at the watershed scale in central Iran by addressing environmental heterogeneity through a random forest (RF) model combined with bootstrapping to assess prediction uncertainty. Thirty-eight environmental variables—categorized into climatic, soil physicochemical, topographic, geomorphic, and remote sensing (RS)-based factors—were considered. Variable importance analysis (via) and partial dependence plots (PDP) identified land use, RS indices, and topography as key predictors of SOC. For SIC, soil reflectance (Bands 5 and 7, ETM+), topography, and geomorphic units were most influential. Climatic factors showed minimal impact in the studied semi-arid watershed. The RF model achieved moderate prediction accuracy (SOC: R2 = 0.43 ± 0.13, nRMSE = 0.28; SIC: R2 = 0.47 ± 0.11, nRMSE = 0.37). Via and PDP analyses enhanced model interpretability by clarifying environmental influences on SOC/SIC spatial distribution.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools