 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Analysis of functional hub genes indicates DLGAP5 is linked to lung adenocarcinoma prognosis
1 Department of Thoracic Surgery, Thoracic Cancer Center, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510655, China
2 Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, 515041, China
3 Department of Microbiology, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Key Laboratory for Tropical Diseases Control of the Ministry of Education, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
* Corresponding Authors: XIANYU QIN. Email: ; HONGYING LIAO. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
BIOCELL 2023, 47(11), 2453-2469. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.030032
Received 19 March 2023; Accepted 22 June 2023; Issue published 27 November 2023
Abstract
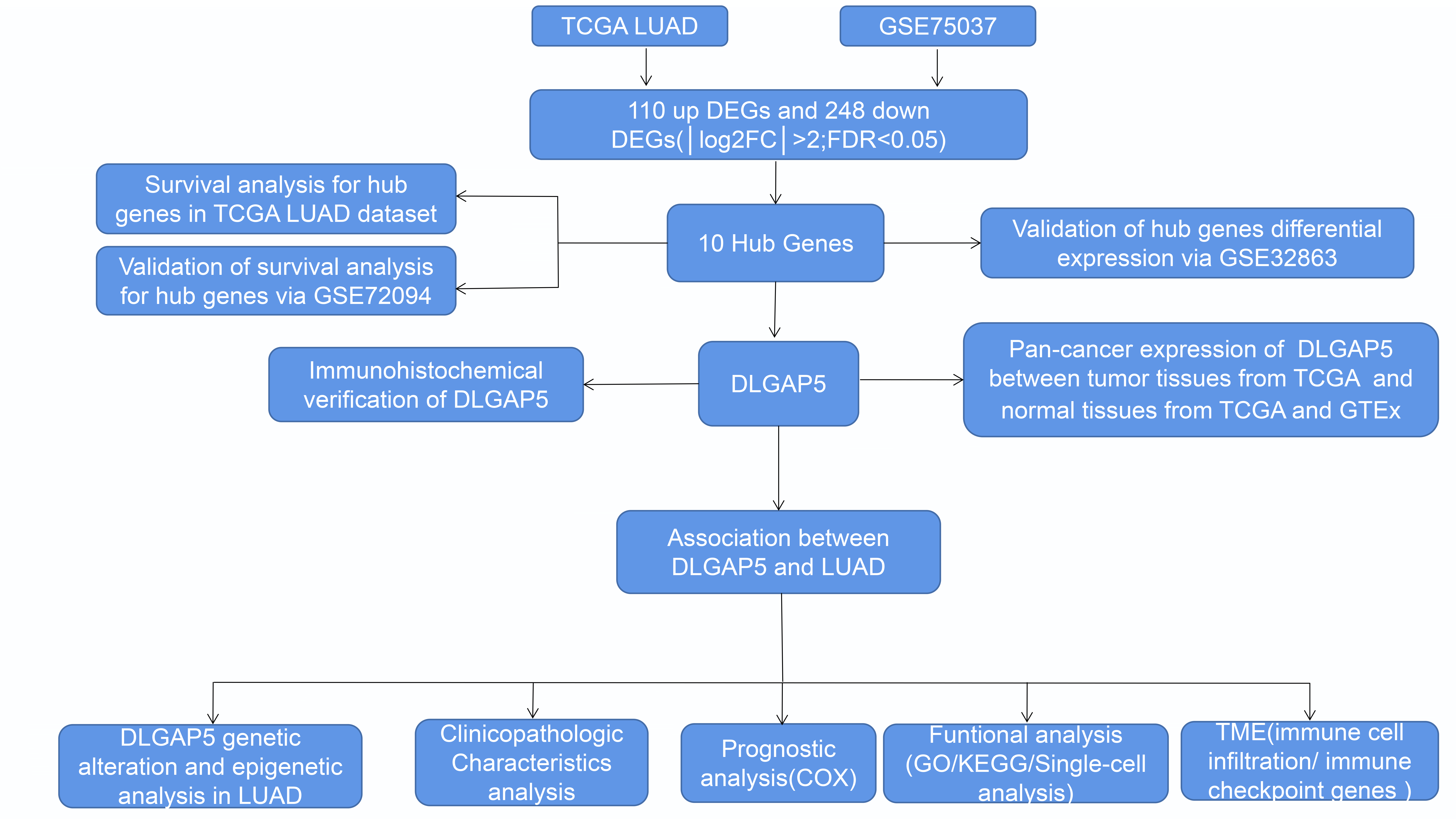
Introduction: The difficulty in treating lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is caused by a shortage of knowledge about the biological mechanisms and a lack of treatment choices. Objectives: The aim of this study was to identify a valuable molecular target for the treatment of LUAD. Methods: Using multiple databases, we screened for hub genes in LUAD using Cytoscape and explored the expression and prognosis of DLG associated protein 5 (DLGAP5) in LUAD. We investigated the genetic variation, functional enrichment, and epigenetic activity of DLGAP5. Furthermore, we evaluated the relationship between the tumor microenvironment (TME) and DLGAP5. Results: Our study identified 10 hub genes in LUAD: CDC45, KIAA0101, DLGAP5, CDT1, NCAPG, CCNB1, CDCA5, CDC20, KIF11, and AURKA. We discovered that DLGAP5 was overexpressed and associated with poor prognosis in LUAD. DLGAP5 exhibited an overall genetic variation frequency of 2%, and its DNA promoter was hypomethylated in LUAD (p < 0.05). The expression of DLGAP5 in LUAD showed a positive correlation with the majority of N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-methylation genes. Additionally, DLGAP5 was primarily associated with the cell cycle in LUAD. Notably, there was a significant favorable association between DLGAP5 and CD274, CTLA4, HAVCR2, and LAG3 in LUAD. Conclusion: DLGAP5 may be a therapeutic target for LUAD, as it affects cancer cells proliferation and development through the regulation of cell-cycle checkpoints and modulation of immune cell infiltration and immune checkpoints in the TME.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools