 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Kaempferol ameliorated levodopa-induced dyskinesia in experimental rats: A role of brain monoamines, cFOS, FosB, Parkin, Pdyn, TH, and p-JNK
Geriatrics Department, Chengde Central Hospital, Chengde, 067000, China
* Corresponding Author: JIANHUA MA. Email:
BIOCELL 2024, 48(3), 513-523. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.045640
Received 02 September 2023; Accepted 21 November 2023; Issue published 15 March 2024
Abstract
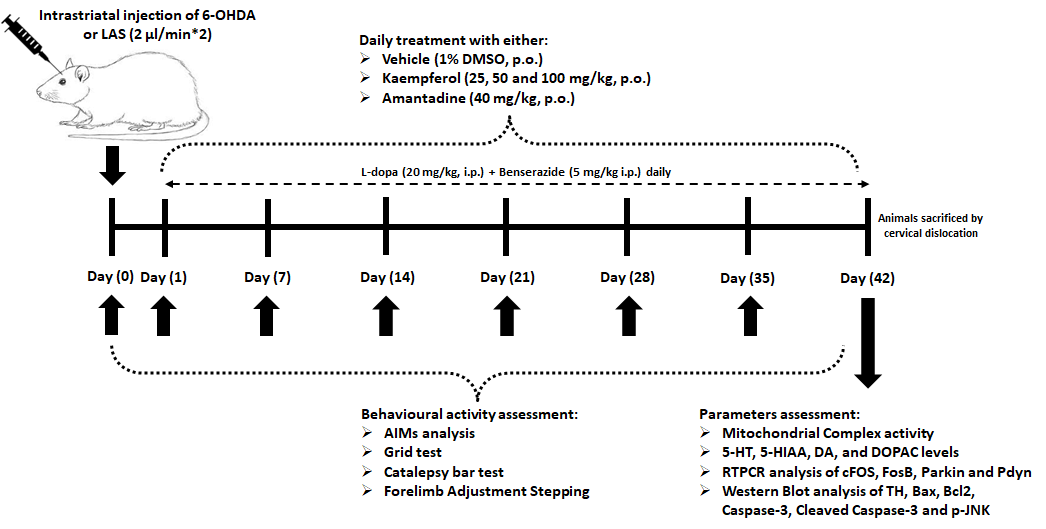
Background: L-dopa (Levodopa) is well known for managing PD (Parkinson’s disease); however, its prolonged use caused dyskinesia (LID). Due to the varied presentation of LID, effective treatment options are scarce. Flavonoids reported their neuroprotective activity by ameliorating acetylcholinesterase, monoamine oxidase, and neuroinflammation. Kaempferol is another flavonoid bearing these potentials. Aim: To evaluate neuroprotective activity of kaempferol in dyskinetic rats. Methods: PD was developed in Sprague-Dawley rats by injecting combination of L-ascorbic acid (10 µL) + 6-OHDA (12 µg) in medial forebrain bundle to induce neuronal damage in substantial nigra (SNr). LID was induced by administrating combination of L-dopa (20 mg/kg) + benserazide HCl (5 mg/kg) for 42 days. Rats were concomitantly treated with amantadine (40 mg/kg) or kaempferol (25, 50, and 100 mg/kg, p.o.). Results: Kaempferol (50 and 100 mg/kg) markedly (p < 0.05) inhibited LID-induced abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) and alternation in motor function. Kaempferol administration considerably (p < 0.05) inhibited reduced mitochondrial complex activities, serotonin and dopamine levels, Bcl-2, and Tyrosine hydroxylase protein expressions in SNr. Additionally, kaempferol considerably (p < 0.05) attenuated increased cFOS, FosB, Parkin, and Pdyn mRNAs expressions, Bax, cleaved caspase-3, caspase-3, and pJNK proteins levels; DOPAC and 5-HIAA levels in SNr. A positive correlation was reported between cFOS, FosB, Parkin, Pdyn, apoptosis, and TH with AIMs. Conclusion: Kaempferol effectively attenuated L-dopa-induced AIMs and dyskinesia via amelioration of alterations in cFOS, FosB, Parkin, Pdyn, Tyrosine hydroxylase, and apoptosis in the brain SNr.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools