 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Protective Effects of Probiotics against Methotrexate-Induced Intestinal Toxicity in the Mice Model
1 Department of Genetics, Cytology and Bioengineering, Biomedical faculty, Voronezh State University, Voronezh, 394018, Russia
2 Experimental Pharmacology Department, All-Russian Scientific Research Veterinary Institute of Pathology of Pharmacology and Therapy, Voronezh, 394087, Russia
3 Department of Service and Restaurant Business, Voronezh State University of Engineering Technology, Voronezh, 394000, Russia
4 Department of Quality Management, Hospitality and Tourism, Voronezh State University of Engineering Technology, Voronezh, 394000, Russia
5 Laboratory of Metagenomics and Food Biotechnology, Voronezh State University of Engineering Technology, Voronezh, 394000, Russia
* Corresponding Author: ARTEM P. GUREEV. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Metabolic and Neuromuscular Diseases: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies)
BIOCELL 2025, 49(1), 7-20. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2024.058339
Received 10 September 2024; Accepted 28 November 2024; Issue published 24 January 2025
Abstract
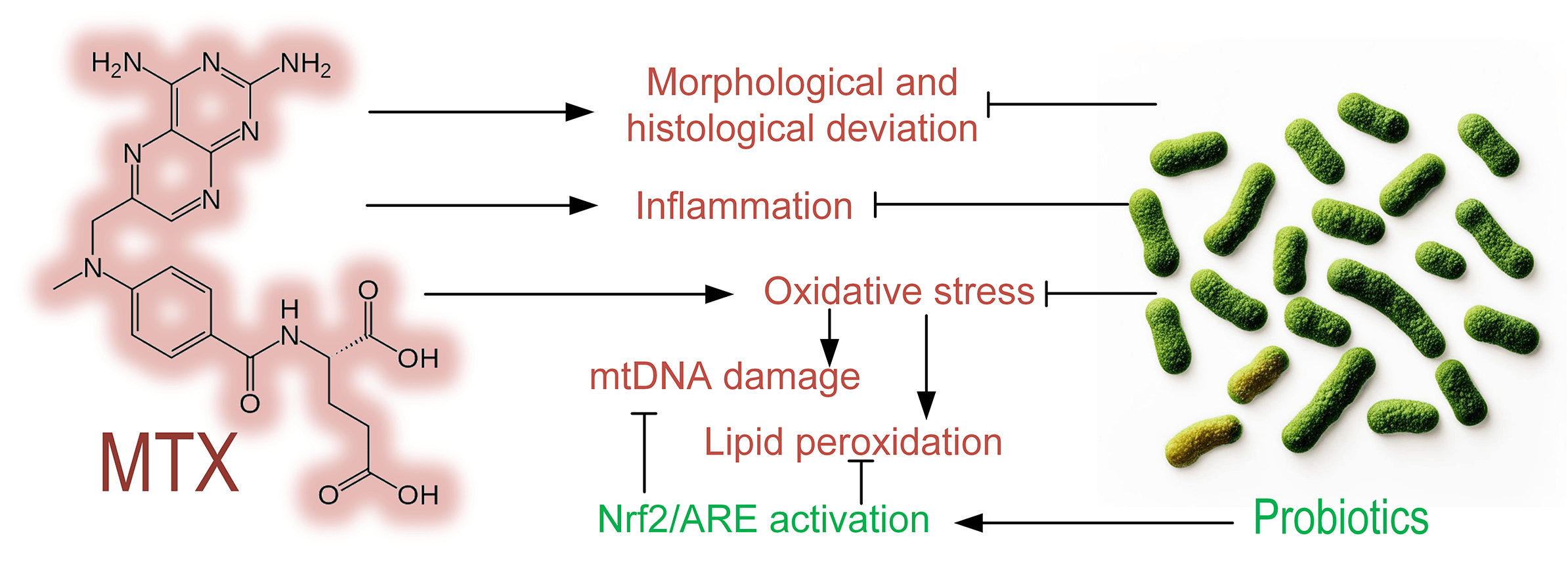
Objective: The objective of this study was to determine the level of methotrexate (MTX) toxicity in the intestines of mice and to evaluate the protective effect of probiotics composed of Streptococcus, Bifidobacterium, and Lactobacillus species on intestinal cells during MTX treatment. Methods: Mice were divided into three groups: control, MTX group (received MTX injections), and MTX + probiotics group (received MTX injections along with a diet containing probiotics). Morphological and histological changes, the level of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage, the level of lipid peroxidation products, and gene expression in the mice’s small intestine were assessed. Results: We demonstrated that intraperitoneal MTX injections significantly increased mtDNA damage in the liver (p < 0.001), small intestine (p < 0.001), and blood of mice (p < 0.01). MTX elevated the quantity of lipid peroxidation products in the liver and small intestine, indicating its strong prooxidative properties. MTX induced structural changes in the mice’s intestines, characterized by leukocytic infiltration of tissues. Probiotic therapy in mice partially mitigated the morphological and histological changes in the small intestine induced by MTX, reduced oxidative stress, and promoted increased expression of quinone oxidoreductase 1 (Nqo1), which participates in both cell protection against oxidative stress and drug/xenobiotic detoxification. Probiotics prevented the upregulation of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1b in the small intestine and induced increased expression of genes associated with the Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/Antioxidant response element (Nrf2/ARE) pathway, an important mechanism of cell protection. Conclusions: Probiotics can be considered an effective approach to reducing the toxicity of MTX during psoriasis or cancer treatment.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools