 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
An Implementation of Multiscale Line Detection and Mathematical Morphology for Efficient and Precise Blood Vessel Segmentation in Fundus Images
1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, COMSATS University Islamabad, Abbottabad Campus, Abbottabad, 22060, Pakistan
2 Department of Computer Engineering, College of Computer and Information Sciences, King Saud University, P. O. Box 51178, Riyadh, 11543, Saudi Arabia
3 Faculty of Information and Communication Technology, University Tunku Abdul Rehman, Kampar Campus, Kampar, 31900, Malaysia
4 Centre for Intelligent Signal and Imaging Research, University Teknologi PETRONAS, Bandar Seri Iskandar, Perak, 32610, Malaysia
5 School of Computing Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, NR47TJ, UK
* Corresponding Authors: Syed Ayaz Ali Shah. Email: ; Aamir Shahzad. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Ophthalmic Diseases Diagnosis using AI)
Computers, Materials & Continua 2024, 79(2), 2565-2583. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2024.047597
Received 10 November 2023; Accepted 15 March 2024; Issue published 15 May 2024
Abstract
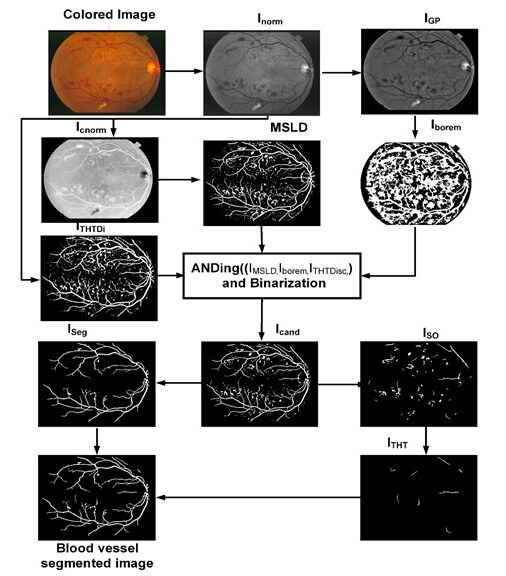
Diagnosing various diseases such as glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, cardiovascular conditions, and diabetic retinopathy involves segmenting retinal blood vessels. The task is particularly challenging when dealing with color fundus images due to issues like non-uniform illumination, low contrast, and variations in vessel appearance, especially in the presence of different pathologies. Furthermore, the speed of the retinal vessel segmentation system is of utmost importance. With the surge of now available big data, the speed of the algorithm becomes increasingly important, carrying almost equivalent weightage to the accuracy of the algorithm. To address these challenges, we present a novel approach for retinal vessel segmentation, leveraging efficient and robust techniques based on multiscale line detection and mathematical morphology. Our algorithm’s performance is evaluated on two publicly available datasets, namely the Digital Retinal Images for Vessel Extraction dataset (DRIVE) and the Structure Analysis of Retina (STARE) dataset. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, with mean accuracy values of 0.9467 for DRIVE and 0.9535 for STARE datasets, as well as sensitivity values of 0.6952 for DRIVE and 0.6809 for STARE datasets. Notably, our algorithm exhibits competitive performance with state-of-the-art methods. Importantly, it operates at an average speed of 3.73 s per image for DRIVE and 3.75 s for STARE datasets. It is worth noting that these results were achieved using Matlab scripts containing multiple loops. This suggests that the processing time can be further reduced by replacing loops with vectorization. Thus the proposed algorithm can be deployed in real time applications. In summary, our proposed system strikes a fine balance between swift computation and accuracy that is on par with the best available methods in the field.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools