 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Numerical Simulation of Contamination Accumulation Characteristics of Composite Insulators in Salt Fog Environment
Department of Energy, Power and Mechanical Engineering, North China Electric Power University, Baoding, 071003, China
* Corresponding Author: Zeze Chen. Email:
Energy Engineering 2023, 120(2), 483-499. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2023.023649
Received 07 May 2022; Accepted 11 July 2022; Issue published 29 November 2022
Abstract
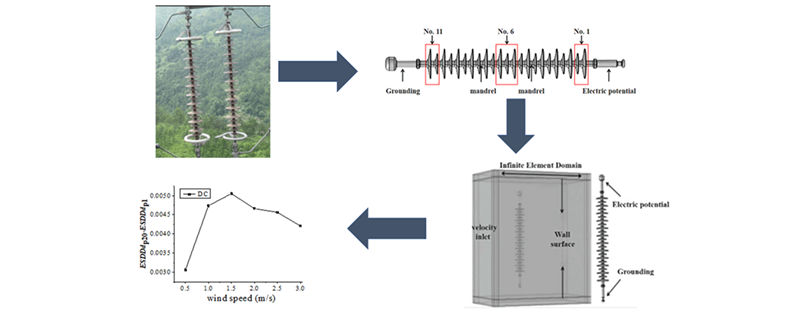
To investigate the fouling characteristics of the composite insulator surface under the salt fog environment, the FXBW-110/120-2 composite insulator was taken as the research object. Based on the field-induced charge mechanism, the multi-physical field coupling software COMSOL was used to numerically simulate the fouling characteristics, explored the calculation method of ESDD, and demonstrated its rationality. Based on this method, the pollution characteristics of the composite insulator under the pollution fog environment were studied, and the influence of wind speed, droplet size, and voltage type on the pollution characteristics of the composite insulator was analyzed. The results showed that: with the increase in wind speed, the amount of accumulated pollution of insulator increases in the range of droplet size, and the relationship between wind speed and accumulated pollution is approximately linear; at the same wind speed, the amount of accumulated pollution increases with the increase of droplet size under the action of DC voltage; when there is no voltage, the amount of dirt on the upper surface of the insulator is more than that on the lower surface, while it is the opposite under DC voltage.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools