 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Retrofitting Design of a Deep Drilling Rig Mud Pump Load Balancing System
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, HR-10000, Croatia
* Corresponding Author: Danijel Pavković. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Selected Papers from the SDEWES 2024 Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems)
Energy Engineering 2025, 122(5), 1669-1696. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2025.061916
Received 06 December 2024; Accepted 17 March 2025; Issue published 25 April 2025
Abstract
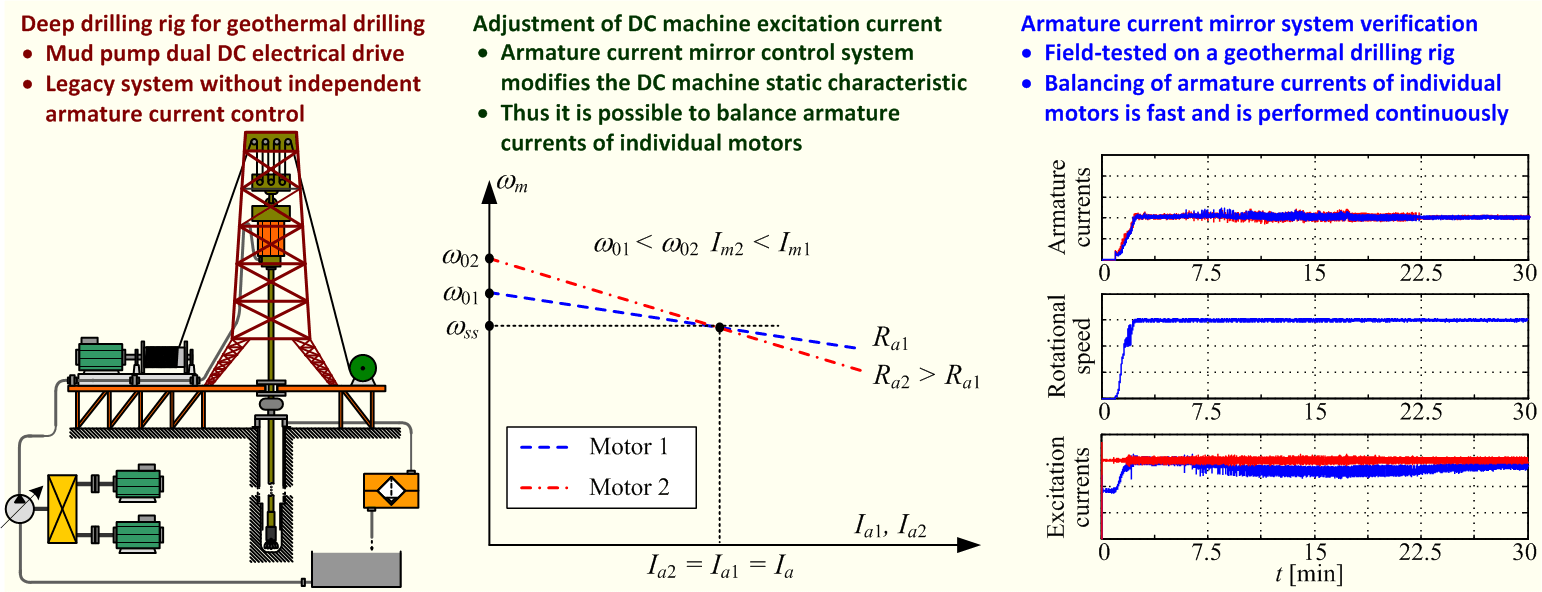
In deep drilling applications, such as those for geothermal energy, there are many challenges, such as those related to efficient operation of the drilling fluid (mud) pumping system. Legacy drilling rigs often use paired, parallel-connected independent-excitation direct-current (DC) motors for mud pumps, that are supplied by a single power converter. This configuration results in electrical power imbalance, thus reducing its efficiency. This paper investigates this power imbalance issue in such legacy DC mud pump drive systems and offers an innovative solution in the form of a closed-loop control system for electrical load balancing. The paper first analyzes the drilling fluid circulation and electrical drive layout to develop an analytical model that can be used for electrical load balancing and related energy efficiency improvements. Based on this analysis, a feedback control system (so-called “current mirror” control system) is designed to balance the electrical load (i.e., armature currents) of parallel-connected DC machines by adjusting the excitation current of one of the DC machines, thus mitigating the power imbalance of the electrical drive. The proposed control system effectiveness has been validated, first through simulations, followed by experimental testing on a deep drilling rig during commissioning and field tests. The results demonstrate the practical viability of the proposed “current mirror” control system that can effectively and rather quickly equalize the armature currents of both DC machines in a parallel-connected electrical drive, and thus balance both the electrical and mechanical load of individual DC machines under realistic operating conditions of the mud pump electrical drive.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools