 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hole Cleaning and Critical Transport Rate in Ultra-Deep, Oversized Wellbores
1 China National Petroleum Corporation, Chuanqing Drilling Engineering Company Limited, Chengdu, 610051, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu, 610500, China
* Corresponding Author: Shiqian Xu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Fluid and Thermal Dynamics in the Development of Unconventional Resources II)
Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2025, 21(4), 799-817. https://doi.org/10.32604/fdmp.2025.062862
Received 29 December 2024; Accepted 14 March 2025; Issue published 06 May 2025
Abstract
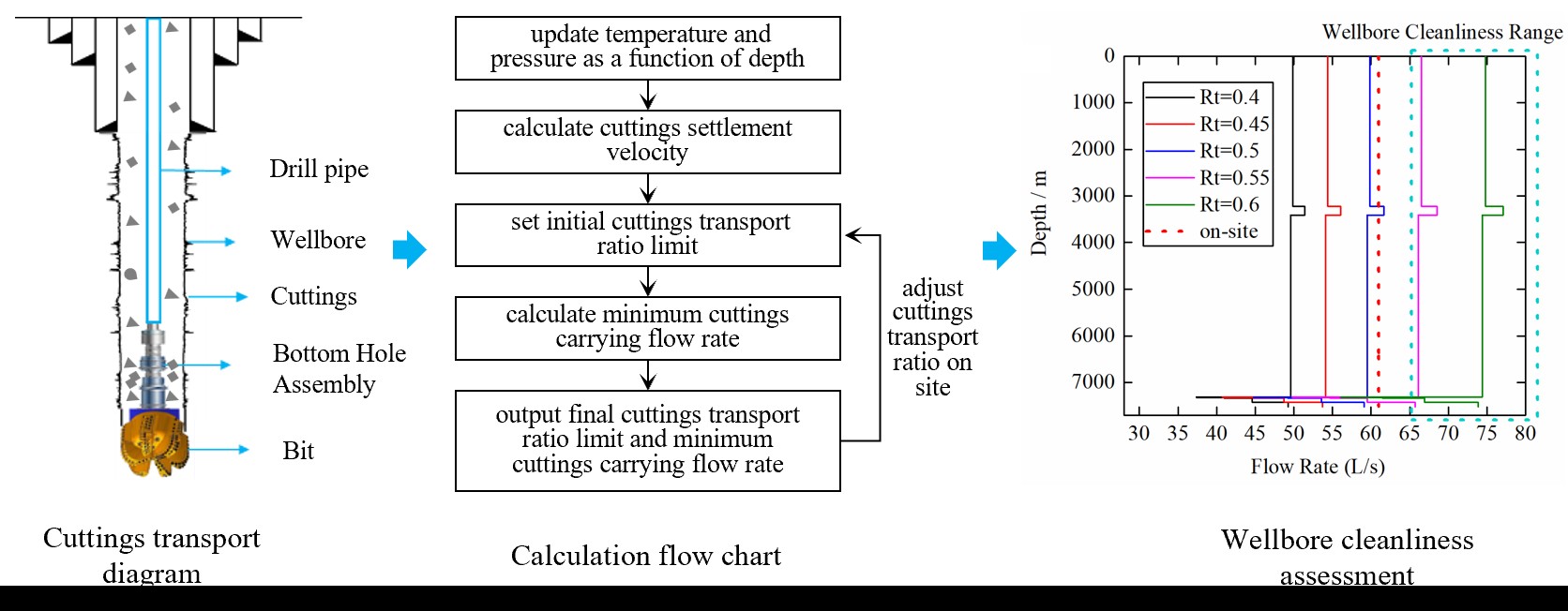
In ultra-deep and large well sections, high collapse stresses and diminished annular return velocity present significant challenges to wellbore cleaning. With increasing depth, rising temperature and pressure constrain the regulation of displacement and drilling fluid rheology, impairing the fluid’s capacity to transport cuttings effectively. A precise understanding of cuttings settlement behavior and terminal velocity is therefore essential for optimizing their removal. This study accounts for variations in wellbore temperature and pressure, incorporates non-spherical cuttings and wellbore diameter parameters, and develops accordingly a simplified model to predict terminal settlement velocity. The cuttings carrying ratio is introduced as a metric for evaluating wellbore cleanliness. Findings reveal that temperature and pressure fluctuations can alter terminal velocity by up to 3.4%. Cuttings shape plays a crucial role, with block-shaped cuttings requiring higher annular return velocity than flake-shaped ones at the same carrying ratio. As wellbore size increases, the minimum required carrying flow rate rises nonlinearly, though the rate of increase gradually declines. For a Φ444.5 mm wellbore, a carrying ratio of at least 0.6 is recommended. Terminal velocity decreases with increasing consistency coefficient, particularly in high-viscosity regimes. The proposed carrying ratio offers a more accurate and practical assessment of wellbore cleanliness.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools