 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Performance Evaluation of Hierarchically Structured Superhydrophobic PVDF Membranes for Heavy Metals Removal via Membrane Distillation
1 Centre for Rural Development and Technology, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi, 110016, India
2 Department of Chemical Engineering and Applied Chemistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON M5S 3E5, Canada
* Corresponding Authors: Pooja Yadav. Email: ; Vivek Kumar. Email:
Journal of Polymer Materials 2025, 42(4), 1181-1197. https://doi.org/10.32604/jpm.2025.072564
Received 29 August 2025; Accepted 26 November 2025; Issue published 26 December 2025
Abstract
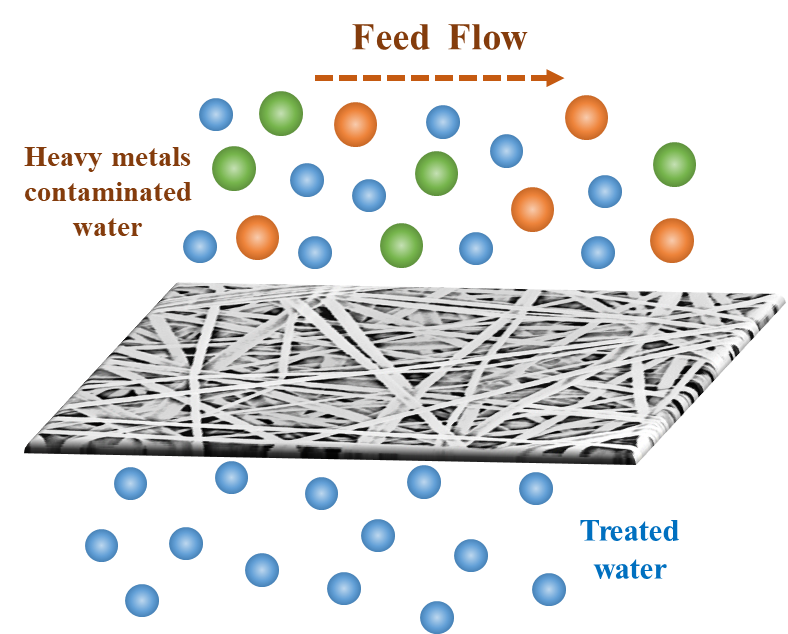
Heavy metal contamination in water sources is a widespread global concern, particularly in developing nations, with various treatment approaches under extensive scientific investigation. In the present study, we fabricated electrospun composite polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofibrous membranes exhibiting hierarchical surface roughness and superhydrophobicity for the removal of heavy metal ions via vacuum membrane distillation (VMD) process. The membranes were prepared by incorporating optimized dosing of silica nanoparticles, followed by a two-step membrane modification approach. These membranes exhibited notable characteristics, including elevated water contact angle (152.8 ± 3.2°), increased liquid entry pressure (127 ± 6 kPa), and reduced average pore size (0.28 ± 0.03 μm). The study demonstrated the efficacy of fabricated membranes in VMD process, specifically for the removal of heavy metals such as arsenic and iron from aqueous solutions. The membrane produced stable permeate flux of 12.7 kg·m−2·h−1 for arsenic-containing feed and 13.2 kg·m−2·h−1 for iron-containing feed, and excellent rejection of >99.9% over a 12-h testing period without any observed wetting of membrane pores. These performance results were compared with those of typical commercial PVDF and pristine electrospun PVDF membranes. Consequently, the developed membrane demonstrated high efficiency and scalability as a water treatment option, showing significant potential for industrial heavy metal removal and the treatment of contaminated groundwater.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools