Journal of Polymer Materials is published quarterly (4 issues per year), which covers most of the fundamental areas of Polymer Science and Technology broadly. It reports reviews on current topics and original research results on the synthesis of monomers and polymers, polymer analysis, characterization and testing, properties of polymers, structure-property relation, polymer processing and fabrication, and polymer applications. Research and development activities on functional polymers, polymer blends and alloys, composites and nanocomposites, paints and surface coatings, rubbers and elastomeric materials, and adhesives are also published.
Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE): 2024 Impact Factor 1.2; EBSCO; J-GATE; Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS); National Academy of Agricultural Sciences (NAAS); Portico; etc.
Starting from 2024, Journal of Polymer Materials (JPM) will be published by Tech Science Press.
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 893-908, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.071240 - 26 December 2025
Abstract Anion exchange membrane (AEM) fuel cells require membranes with a balance of high conductivity and durability. In this work, a novel bi-crown-ether modified piperidine structure was designed and synthesized, which was then introduced into the side chain of poly(arylene piperidinium), making a unique bi-crown-ether modified bi-piperidinium side chain grafted polymer for AEM fabrication. The double crown ether units enhanced cation–water interactions and promoted microphase separation, thereby forming efficient hydroxide ion transport channels. The resulting membrane exhibited high water uptake, well-defined ion clusters, and a hydroxide conductivity of 123 mS cm−1 at 80°C with an ion exchange More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 909-927, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.071607 - 26 December 2025
Abstract MXene (Ti3C2Tx) is known for its excellent hydrophilicity, electrical conductivity, and dispersibility. It is a promising candidate for the fabrication of moisture-responsive actuators due to the strong interaction between MXene sheets and water molecules. Inspired by natural organisms, a variety of moisture-actuated soft robots have been successfully developed through the systematic integration of MXene-based actuators. This minireview summarizes recent advances in the preparation and applications of MXene-based moisture-responsive actuators. The hydrophilic properties of MXene, along with design principles, working mechanisms, current progress, and applications of MXene-based actuators, are discussed. The future prospects and developmental directions of More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 929-957, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.074529 - 26 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sustainable Development and Multifunctional Application of Cellulose Composites)
Abstract Global water pollution is becoming increasingly serious, and compound pollutants such as heavy metals and organic dyes pose multidimensional threats to ecology and human health. Metal-organic skeleton compounds (MOFs) have been proven to be highly efficient in capturing a variety of pollutants by virtue of their large specific surface area, adjustable pore channels, and abundant active sites. However, the easy agglomeration of powders, the difficulty of recycling, and the poor long-term stability have limited their practical applications. Cellulose, as the most abundant renewable polymer in nature, has the characteristics of a three-dimensional network, mechanical flexibility,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 959-992, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.072005 - 26 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Polymer Materials in Controlled Drug Delivery)
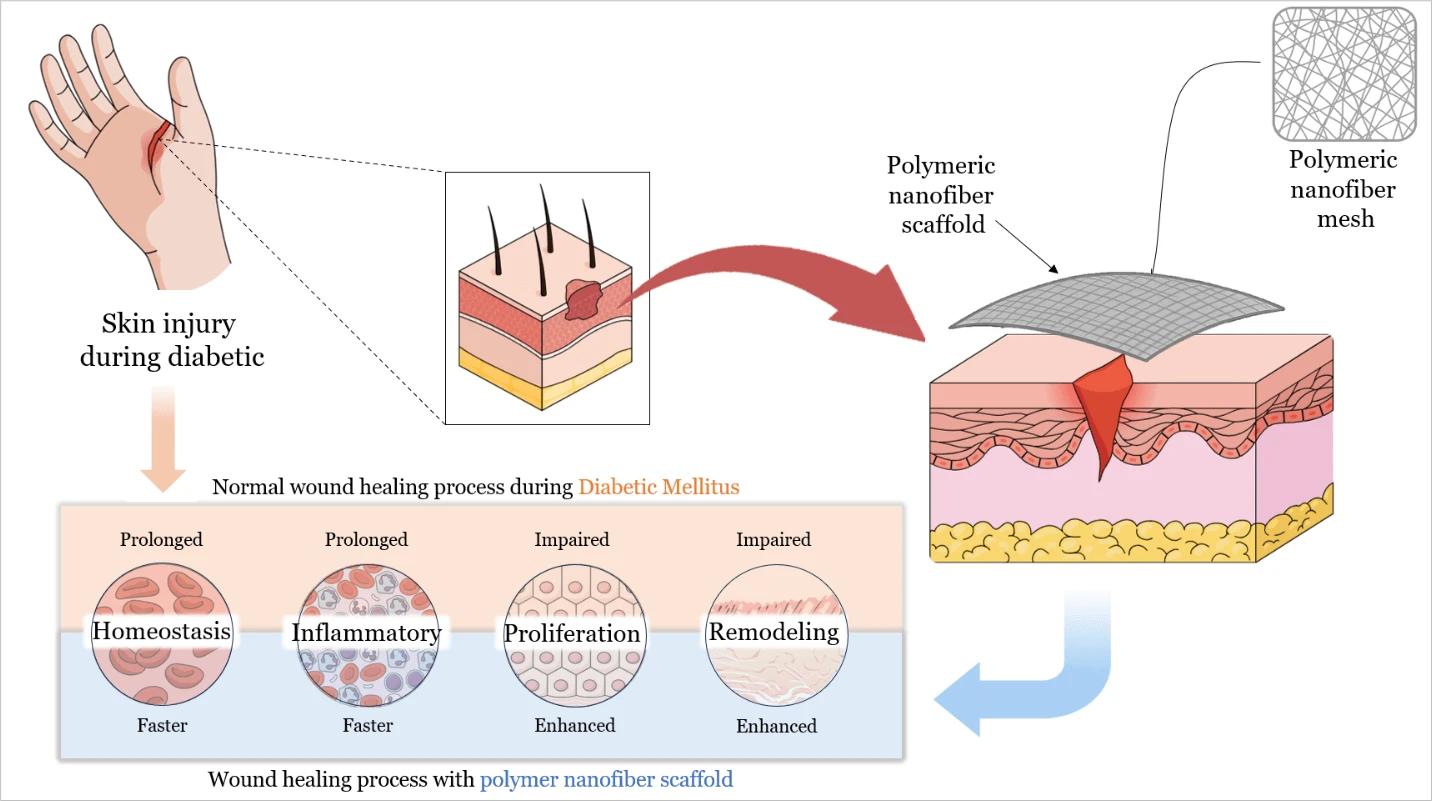
Abstract With the global diabetes epidemic, diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) have become a major health burden, affecting approximately 18 million people worldwide each year, and account for about 80% of diabetes-related amputations. Five-year mortality among DFU patients approaches 30%, which is comparable to that of many malignancies. Yet despite standard wound care, only about 30%–40% of chronic DFUs achieve complete healing within 12 weeks. This persistent failure shows that conventional dressings remain passive supports. They do not counteract underlying pathologies such as ischemia, prolonged inflammation, and infection. Recent advances in polymeric nanofiber scaffolds, particularly electrospun matrices,… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 993-1033, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.071740 - 26 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Polymer Materials in Controlled Drug Delivery)
Abstract Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has a long history and is widely used to prevent and treat various diseases. With the development of modern technology, an increasing number of active ingredients—such as curcumin, berberine, and baicalin—have been identified and validated within TCM. Concurrently, the emergence of nanotechnology has led to the discovery of numerous nanomedicines based on the self-assembly of active ingredients from TCM. Polymer materials can enhance the bioavailability of these active compounds and reduce their toxic side effects. Moreover, compared to synthetic polymers, natural polymer materials offer advantages such as non-toxicity and high biosafety… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1035-1049, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.073108 - 26 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Polymer-based Functional Composite Materials: Cutting-edge Advances and Innovative Applications)
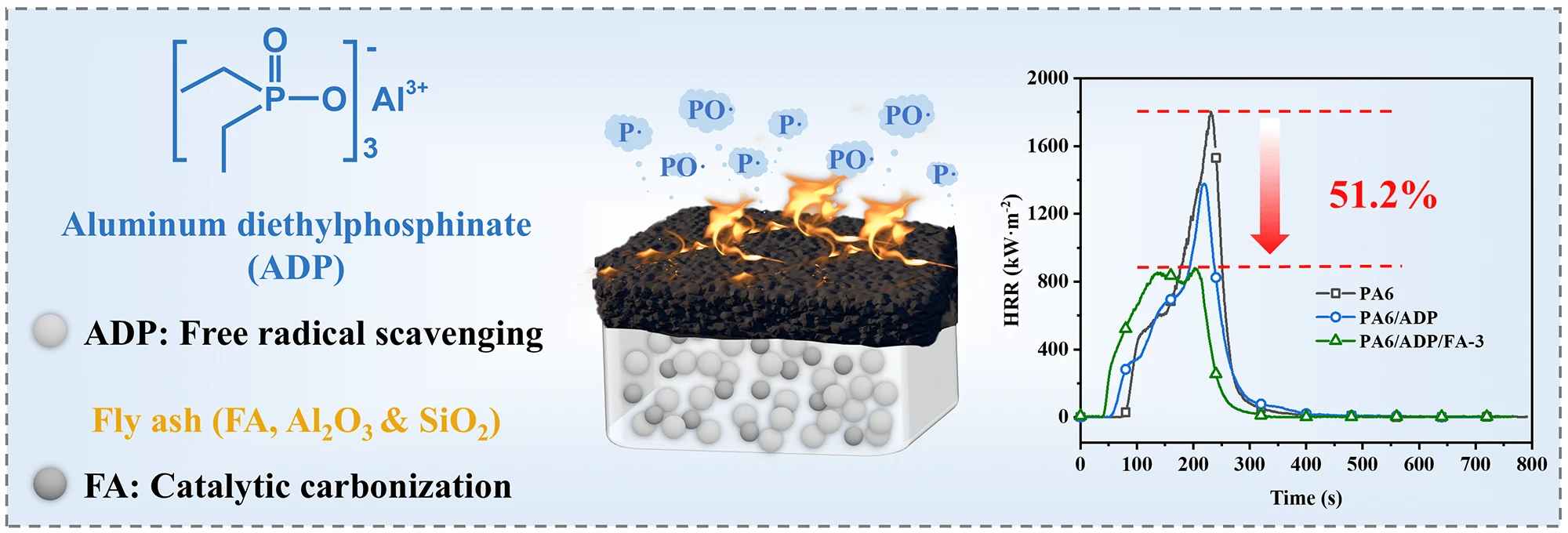
Abstract The fabrication of highly flame-retardant polyamide 6 (PA6) composites is of great significance for expanding their practical applications. Herein, a new flame-retardant system (ADP/FA) was developed by combining aluminum diethylphosphinate (ADP) with excellent flame retardancy and fly ash (FA), an economical and environmentally friendly industrial waste. Due to the synergistic flame-retardant effect of ADP/FA in the condensed phase and gas phase, the PA6 composite containing only 11 wt% of ADP/FA (mass ratio 93:7) obtained vertical burning (UL-94) tests V-0 rating with a limiting oxygen index (LOI) of 30.9%. To obtain the same flame-retardant level of… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1051-1073, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.070688 - 26 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Damage and Fracture of Polymer Composites)
Abstract Carbon fiber-reinforced composites (CFRCs) have a wide range of applications in the aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors. A higher specific strength-to-weight ratio is desired in high-performance applications. The failure mechanism of CFRCs involves multiscale phenomena, such as failure that can occur at the matrix, fibers, interface, layers, lamina, and laminates. When an impactor hits the CFRCs, the design involves analyzing each of these stages to prevent failure and optimize the properties of CFRCs under various loading conditions. A numerical model was employed to predict the fracture toughness of CFRCs with varying weight fractions and orientations.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1075-1095, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.072263 - 26 December 2025
Abstract Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is widely used in diverse applications such as protective components (e.g., automotive lamp covers and structural casings), optical devices, and biomedical products, owing to its lightweight nature and impact resistance. However, its surface hardness and wear resistance remain insufficient under prolonged exposure to abrasive environments. In this study, a multi-filler strategy with nano-silica (SiO2), brominated lignin (Br-Lignin), and cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) was employed to enhance PMMA tribological properties. SiO2 provided localized reinforcement, Br-Lignin established stable network structures, and CNCs improved compactness, enabling strong synergistic effects. As a result, the composites achieved up to More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1097-1109, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.071129 - 26 December 2025
Abstract To study the behavior of structural dynamics, ionic conductivity and ion transport properties, the gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs) was developed using polyvinyl alcohol in combination with potassium iodide, dimethyl sulfoxide, ethylene carbonate, propylene carbonate and tetra-N-propylammonium iodide (C12H28IN), The GPEs were synthesized via a solution mixing technique, systematically varying the tetra-N-propylammonium iodide concentration to optimize ionic transport properties. The gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs) preparation was initially dissolving the potassium iodide and tetra-N-propylammonium iodide in a measured combination of ethylene carbonate, propylene carbonate, and dimethyl sulfoxide within a glass container. Subsequently, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was introduced into… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1111-1123, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.070939 - 26 December 2025
Abstract This study investigates the effects of honey concentration on the crystallinity, morphology, and thermal behavior of zein-based polymer systems, aiming to assess honey’s role as a natural plasticizer. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis confirmed the presence of strong intermolecular interactions and hydrogen bonding between zein and honey, indicating good miscibility. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns revealed a significant reduction in crystallinity with increasing honey concentration up to 25 wt.%, with the ZH5 (75 wt.% zein-25 wt.% honey) sample exhibiting the smallest crystallite size (4.23 nm), suggesting enhanced amorphous character suitable for ionic mobility. Field emission… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1125-1141, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.073300 - 26 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Modification Methods for Polymers)
Abstract Polypropylene (PP) has low inherent susceptibility to common industrial lasers, which poses a significant challenge for laser-based marking. To improve the laser sensitivity of PP, molybdenum disulfide grafted with polystyrene (MoS2-g-PS) was synthesized via in-situ free radical polymerization and used as a laser-sensitive filler for PP composites prepared by melt blending. The composites were then marked with a 1064 nm semiconductor laser, producing clear and legible patterns. The marked surfaces were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), colorimetry, Raman spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The results demonstrate that the PP/MoS2-g-PS composites exhibit significantly More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1143-1157, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.073414 - 26 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Synthesis, Processing and Mechanical Properties of Hydrogel-Based Materials)
Abstract The pursuit of safer energy storage systems is driving the development of advanced electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. Traditional liquid electrolytes pose flammability risks, while solid-state alternatives often suffer from low ionic conductivity. Gel polymer electrolytes (GPEs) emerge as a promising compromise, combining the safety of solids with the ionic conductivity of liquids. Cellulose, an abundant and eco-friendly polymer, presents an ideal base material for sustainable GPEs due to its biocompatibility and mechanical strength. This study systematically investigates how drying methods affect cellulose-based GPEs. Cellulose hydrogels were synthesized through dissolution-crosslinking and processed using vacuum drying (VD),… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1159-1179, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.072450 - 26 December 2025
Abstract Addressing the persistent challenge of shale hydration and swelling in water-based drilling fluids (WBDFs), this study developed a smart thermo-responsive shale inhibitor, Hyperbranched Polyethyleneimine-Propylene Oxide-N-isopropylacrylamide (HPN). It was synthesized by grafting hyperbranched polyethyleneimine (HPEI) with propylene oxide (PO) and N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM), creating a synergistic hydration barrier through hydrophobic association and temperature-triggered pore plugging. Structural characterization by Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and gel permeation chromatography (GPC) confirmed the successful formation of the HPN terpolymer, revealing a unique “cationic–nonionic” amphiphilic architecture with temperature-responsive properties. Performance evaluation demonstrated that HPN significantly outperforms conventional inhibitors, including potassium chloride (KCl),… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1181-1197, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.072564 - 26 December 2025
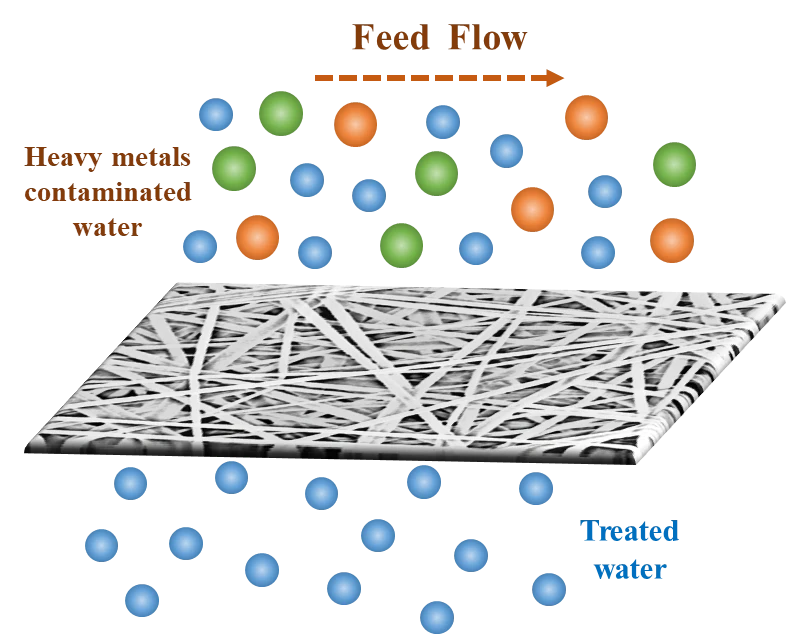
Abstract Heavy metal contamination in water sources is a widespread global concern, particularly in developing nations, with various treatment approaches under extensive scientific investigation. In the present study, we fabricated electrospun composite polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofibrous membranes exhibiting hierarchical surface roughness and superhydrophobicity for the removal of heavy metal ions via vacuum membrane distillation (VMD) process. The membranes were prepared by incorporating optimized dosing of silica nanoparticles, followed by a two-step membrane modification approach. These membranes exhibited notable characteristics, including elevated water contact angle (152.8 ± 3.2°), increased liquid entry pressure (127 ± 6 kPa), and… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Polymer Materials, Vol.42, No.4, pp. 1199-1229, 2025, DOI:10.32604/jpm.2025.072987 - 26 December 2025
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Polymer Materials in Controlled Drug Delivery)
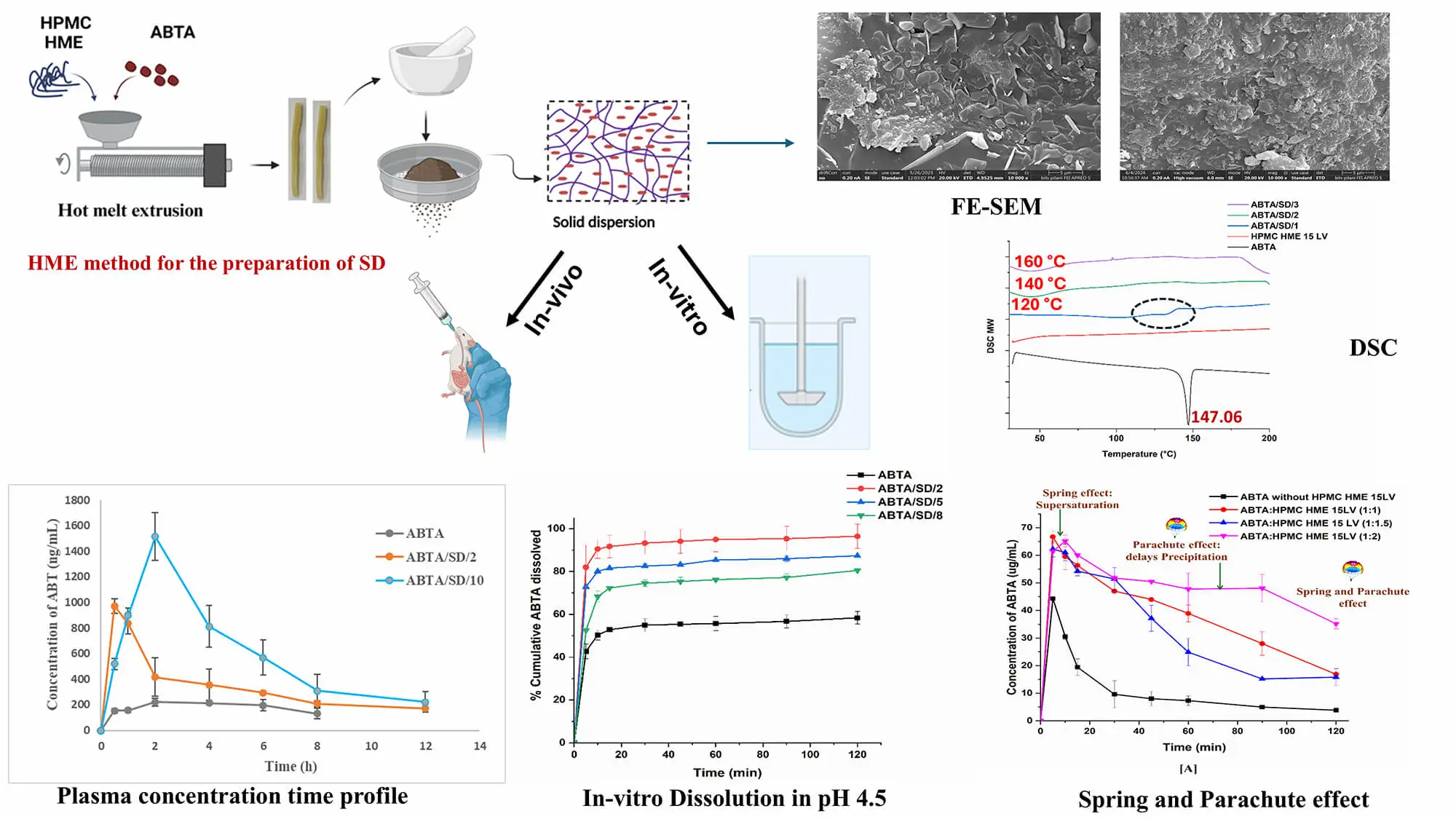
Abstract Abiraterone acetate (ABTA) was approved by the USFDA in 2011 for treating metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). ABTA exhibits poor aqueous solubility, inadequate dissolution, low oral bioavailability (<10%), and significant positive food effects. To overcome these limitations, in the present work, ABTA solid dispersions (SDs) were developed by using hot melt extrusion technology (HME) with various grades of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose HME (HPMC HME 15LV and 100LV) at different extrusion temperatures. HPMC HME demonstrated the ability to prevent drug precipitation for up to 120 min compared to the free drug (10 min), sustaining the supersaturation state… More >
Graphic Abstract