 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Unraveling the Rheology of Nanocellulose Aqueous Suspensions: A Comprehensive Study on Biomass-Derived Nanofibrillated Cellulose
1 Key Laboratory of Bio-Based Material Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, 150040, China
2 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Rowan University, Glassboro, New Jersey, 08028, USA
* Corresponding Authors: Wenshuai Chen. Email: ; Ping Lu. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Nanocellulose and Nanocellulose-Derived Functional Materials-Ⅱ)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(3), 443-455. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.030412
Received 04 April 2023; Accepted 11 May 2023; Issue published 11 April 2024
Abstract
The rheological properties of nanocellulose aqueous suspensions play a critical role in the development of nanocellulose-based bulk materials. High-crystalline, high-aspect ratio, and slender nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) were extracted from four biomass resources. The cellulose nanofibrils and nanofibril bundles formed inter-connected networks in the NFC aqueous suspensions. The storage moduli of the suspensions with different concentrations were higher than their corresponding loss moduli. As the concentration increased, the storage and loss modulus of NFC dispersion increased. When the shear rate increased to a certain value, there were differences in the changing trend of the rheological behavior of NFC aqueous suspensions derived from different biomass resources and the suspensions with different solid concentrations. NFC dispersion’s storage and loss modulus increased when the temperature rose to nearly 80°C. We hope this study can deepen the understanding of the rheological properties of NFC colloids derived from different biomass resources.Graphic Abstract
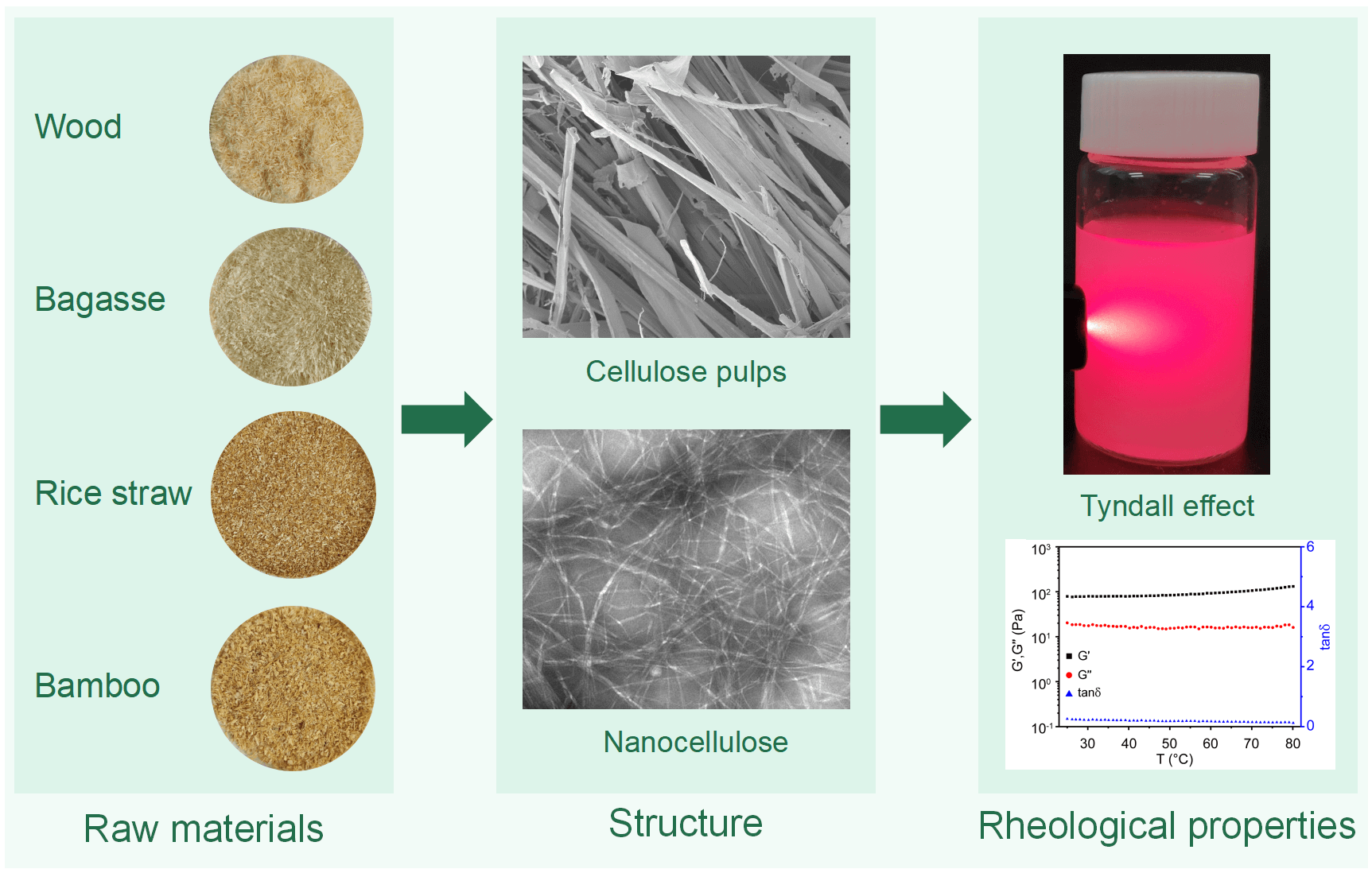
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools