 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
An Sn-Lignosulfonate Catalyst for the Dehydration of Xylose into Furfural in a Biphasic System
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Papermaking and Paper-Based Materials, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, 510640, China
2 Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion, Chinese Academy of Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Renewable Energy, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of New and Renewable Energy Research and Development, Guangzhou, 510640, China
* Corresponding Author: Junli Ren. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(11), 2091-2107. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0060
Received 17 March 2025; Accepted 28 April 2025; Issue published 24 November 2025
Abstract
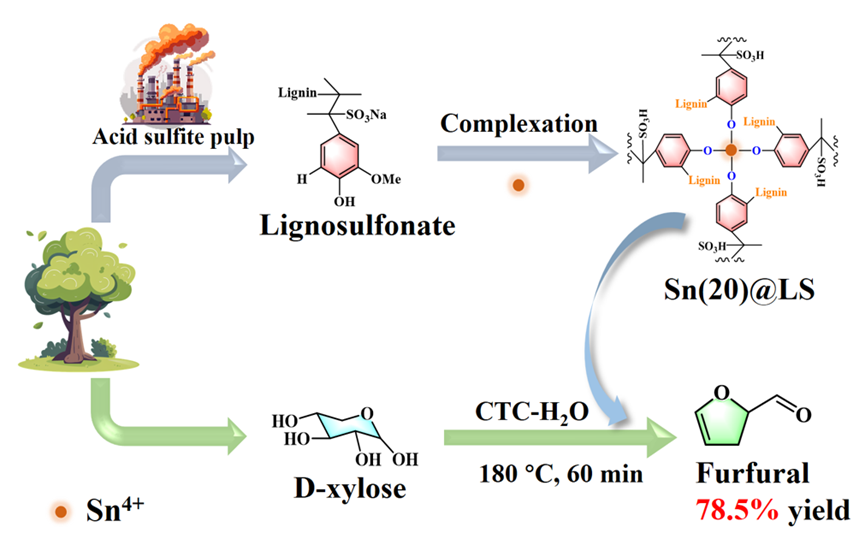
It is highly attractive for the catalysts prepared from renewable materials and/or industrial by-products. Herein, lignosulfonate (LS) as the by-product in the papermaking industry was utilized to fabricate Sn-containing organic-inorganic complexing catalysts (Sn(x)@LS) by a simple hydrothermal self-assembly process. The fabricated Sn(x)@LS played an excellent performance in the dehydration of xylose into furfural in the carbon tetrachloride (CTC)-water biphasic system, yielding 78.5% furfural at 180°C for 60 min. It was revealed that strong coordination between Sn4+ and the phenolic hydroxyl groups of LS created a robust organic-inorganic skeleton (-Ar-O-Sn-O-Ar-), simultaneously generating potent Lewis acidic sites, and sulfonic acid groups of LS acted as Brønsted acidic sites. Gromacs simulations verified that CTC did not form hydrogen bonds with xylose, which may reduce xylose consumption. The CTC phase effectively extracted furfural, thereby preventing its side reactions throughout the entire process. In addition, Sn(x)@LS exhibited excellent cyclic stability in at least five reaction cycles with only a 5.0% decrease in furfural yield. Thus, this work will give a new window for the catalysts prepared from LS as the industrial by-products in the production of platform chemicals, which is a sustainable chemical conversion process.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools