 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
The Potential of Wacapou (Vouacapoua americana) Extracts to Develop New Biobased Protective Solutions for Low-Durability Wood Species
1 CIRAD, Ecologie de Forêts de Guyane (EcoFoG), AgroparisTech, CNRS, INRAE, Université de Guyane, Kourou, 97379, France
2 CIRAD, UPR BioWooEB, Montpellier, F-34398, France
3 BioWooEB, Université de Montpellier, CIRAD, Montpellier, F-34398, France
4 CNRS, Ecologie de Forêts de Guyane (EcoFoG), AgroparisTech, CIRAD, INRAE, Université de Guyane, Kourou, Guyane Française, 97379, France
5 Sorbonne Université, CNRS, Laboratoire de Biodiversité et Biotechnologies Microbiennes, LBBM, Observatoire Océanologique, Banyuls-sur-Mer, 66650, France
* Corresponding Author: Kévin Candelier. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(1), 79-100. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.056731
Received 29 July 2024; Accepted 27 September 2024; Issue published 20 January 2025
Abstract
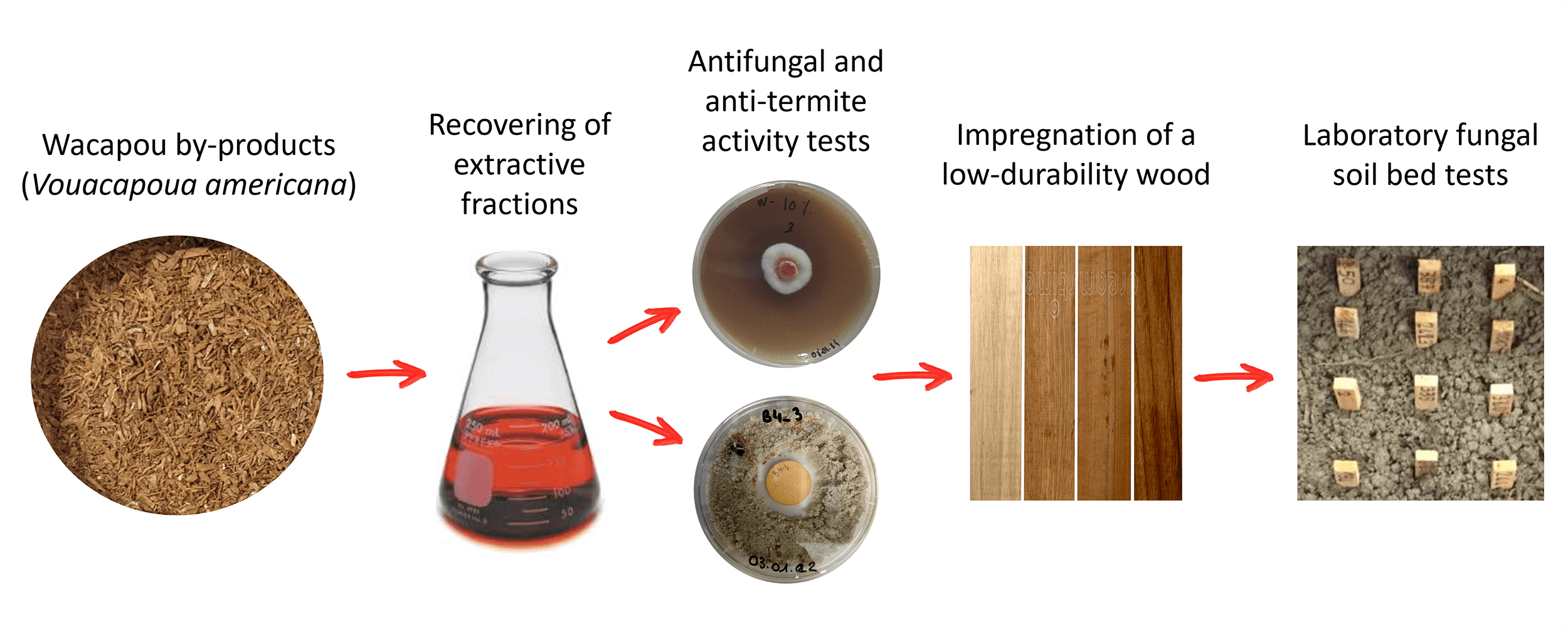
The valorization of Amazonian wood residues into active chemical compounds could be an eco-friendly, cost-effective and valuable way to develop wood preservative formulations to enhance the decay and termite resistance of low-durable wood species. Wacapou (Vouacapoua americana., Fabaceae) is a well-known Guianese wood species commonly used in local wood construction due to its outstanding natural durability, which results from the presence of a large panel of extractives compounds. In addition, its industrial processing generates large amounts of residues. Wacapou residues were extracted by maceration using four different solvents (water/ethanol, ethyl acetate, hexane and dichloromethane/methanol), separately and successively. The yield of each extractive fraction was determined, and their chemical compositions were analyzed by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS). Ethyl acetate led to the highest extraction yield, and the active compounds were identified in the obtained extractive fraction. In this sense, the fungicidal and termite-repellent properties of these extractives were then tested using a screening laboratory (with temperate and tropical microorganisms), according to the solution concentration (1%, 2.5%, 5%, 8% and 10%). Finally, Virola michelii Heckel wood samples (low durable species) were impregnated with the 8% concentration solution. The impregnated wood samples were then exposed to a soil bed test. The results highlighted that the nature of the solvent used during wood maceration affects the content of the obtained extractive fractions. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS) analyses showed the influence of extraction parameters on the nature of the extracted molecules. Wacapou extracts (from ethyl acetate maceration) showed good anti-fungal and anti-termite activities. Additionally, the concentration in extractives had an impact on the anti-termite activity level for Reticulitermes flavipes and Cryptotermes sp. Formulations based on Wacapou extractives showed a good potential for valorization in eco-friendly preservatives, aiming to confer better durability to local low-durability wood species.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools