 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Cancer 3D Models: Essential Tools for Understanding and Overcoming Drug Resistance
1 Institute for Biological Research “Siniša Stanković”-National Institute of the Republic of Serbia, University of Belgrade, Bulevar Despota Stefana 142, Belgrade, 11108, Serbia
2 Institute of Molecular Genetics and Genetic Engineering (IMGGE), University of Belgrade, Vojvode Stepe 444a, Belgrade, 11042, Serbia
* Corresponding Author: Jelena Dinić. Email:
Oncology Research 2025, 33(10), 2741-2785. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2025.067126
Received 25 April 2025; Accepted 12 August 2025; Issue published 26 September 2025
Abstract
Anticancer drug resistance remains a major challenge in cancer treatment hindering the efficacy of chemotherapy and targeted therapies. Conventional two-dimensional (2D) cell cultures cannot replicate the complexity of the in vivo tumor microenvironment (TME), limiting their utility for drug resistance research. Therefore, three-dimensional (3D) tumor models have proven to be a promising alternative for investigating chemoresistance mechanisms. In this review, various cancer 3D models, including spheroids, organoids, scaffold-based models, and bioprinted models, are comprehensively evaluated with a focus on their application in drug resistance studies. We discuss the materials, properties, and advantages of each model, highlighting their ability to better mimic the TME and represent complex mechanisms of drug resistance such as epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), drug efflux, and tumor-stroma interactions. Furthermore, we investigate the limitations of these models, including scalability, reproducibility and technical challenges, as well as their potential therapeutic impact on personalized medicine. Through a thorough comparison of model performance, we provide insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each approach and offer guidance for model selection based on specific research needs.Graphic Abstract
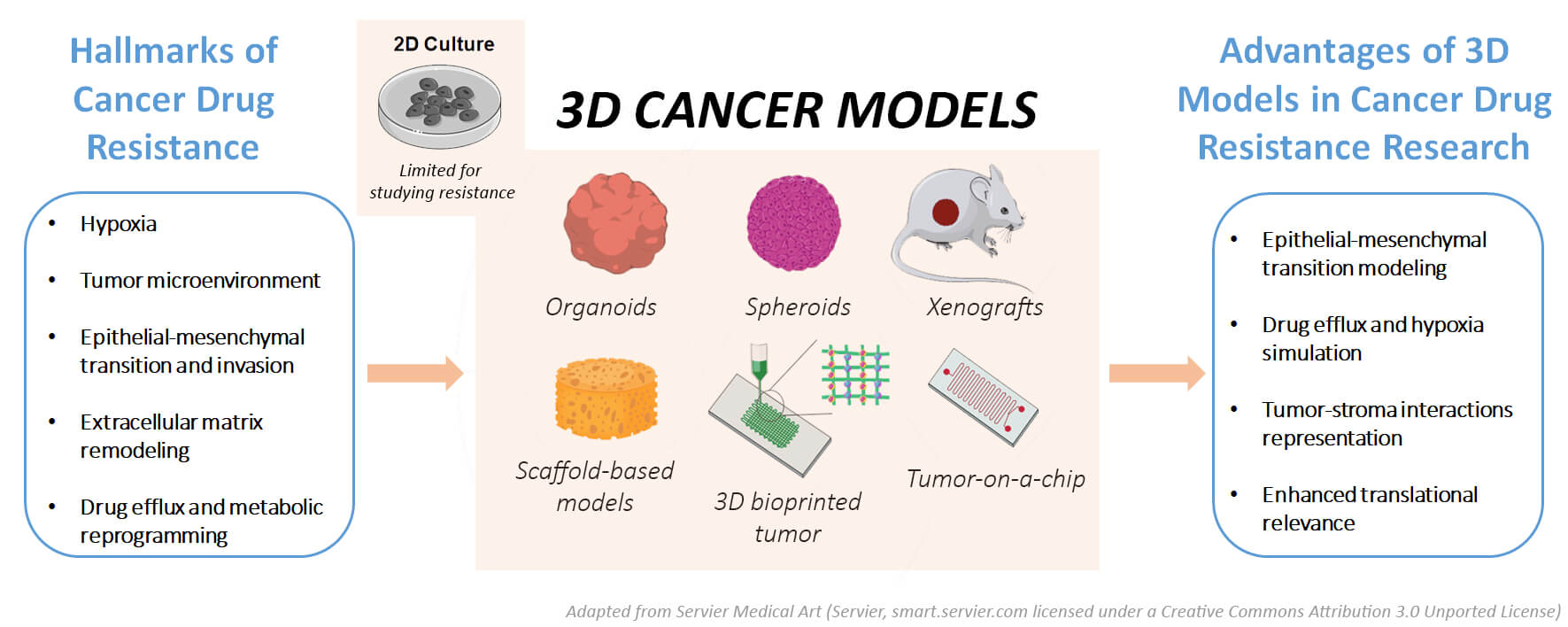
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools