
Oncology Research is committed to publishing high-quality, innovative research that is focused on the entire range of basic, translational, and clinical cancer research, with a particular interest in cancer therapeutics, providing a new platform for the understanding, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer.
Science Citation Index Expanded (Clarivate Analytics): 2024 Impact Factor: 4.1; Scopus CiteScore (Impact per Publication 2024): 3.6; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.673; Embase; PubMed Central; MEDLINE; EBSCO; Google Scholar; Proquest; Portico, etc.
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.075012 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Metabolic Heterogeneity in Cancer: Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Implications)
Abstract Tumor metabolic reprogramming is a core hallmark of cancer, characterized by pathways such as aerobic glycolysis, aberrant lipid metabolism, and glutaminolysis that support rapid proliferation and immunosuppressive microenvironments. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are highly stable, evolutionarily conserved non-coding RNAs that have emerged as critical modulators of these metabolic shifts. This review aims to systematically elucidate the roles and mechanisms of circRNAs in reprogramming tumor metabolism, and to discuss their clinical potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Through mechanisms including miRNA sponging, protein interactions, regulation of mitochondrial dynamics, and modulation of metabolic enzymes, circRNAs influence key metabolic… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073383 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Shaping the Future: The Next Evolution of Cancer Immunotherapy)
Abstract Skin cancer remains the most commonly diagnosed malignancy worldwide, with basal cell carcinoma (BCC), cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC), and melanoma representing the most clinically significant types. While traditional treatments are effective for early-stage disease, advanced or metastatic cases often pose significant therapeutic challenges. Patients with high-risk or recurrent disease face limited options and poor prognoses. The emergence of immunotherapy has dramatically transformed the treatment landscape across multiple cancer types, including cutaneous malignancies. This review highlights recent advancements in immunotherapeutic strategies for BCC, cSCC, and melanoma, underscoring their growing importance in dermatologic oncology. We synthesize More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.070281 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances and Innovations in Colorectal Cancer Research and Treatment)
Abstract Background: The Colorectal Cancer (CRC) pathogenesis and therapeutic efficacy are influenced by the gut microbiome, making it a promising biomarker for predicting treatment responses and adverse effects. This systematic review aims to outline the gut microbiome composition in individuals with CRC undergoing the same therapeutic regimen and evaluate interindividual microbiome profile variations to better understand how these differences may influence therapeutic outcomes. Methods: Key studies investigating the microbiome’s role in therapeutic approaches for CRC were searched in both PubMed and Cochrane databases on 12 and 22 March 2025, respectively. Eligible studies included free full-text English-language… More >
Graphic Abstract
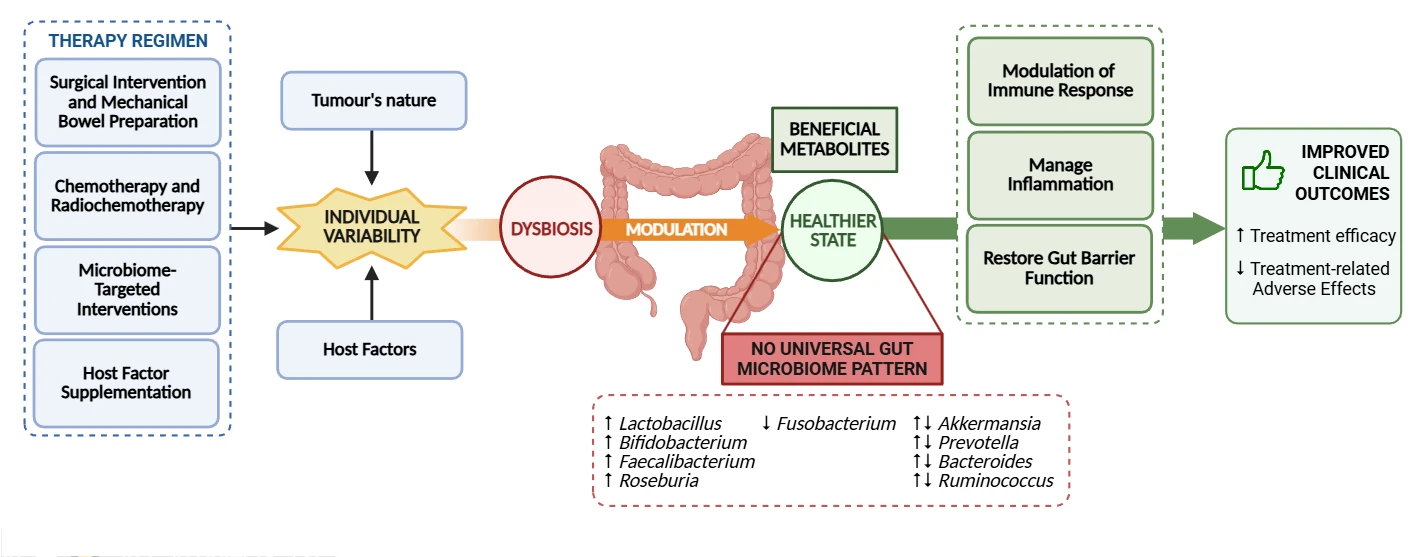
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072443 - 24 February 2026
Abstract Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains a biologically heterogeneous disease with historically limited targeted therapies and poor outcomes. The development of menin inhibitors represents a promising shift, particularly for patients harboring KMT2A rearrangements (KMT2Ar) and NPM1 mutations (NPM1m). This manuscript reviews the molecular rationale of menin inhibition for aberrant homeobox/myeloid ectopic insertion site 1 (HOX/MEIS1)-driven gene expression and leukemogenesis, clinical trial outcomes, and safety data for menin inhibitors, with a focus on recently FDA-approved revumenib and several other agents in development, ziftomenib (KO-539), bleximenib (JNJ-75276617), and icovamenib (BMF-219). We also focused our discussion on future directions to include More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071632 - 24 February 2026
Abstract Tumor survival, genomic stability, and therapy resistance are dictated by the DNA damage response (DDR). Although poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have established the DDR as a therapeutic target, many tumors evade first-generation drugs by rewiring their adaptive repair pathways and imposing microenvironmental constraints. This review synthesizes recent discoveries in key DDR pathways, such as PARP, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related kinase (ATR), ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase (ATM), checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1), WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase (WEE1), and DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), and describes the next-generation inhibitors designed to increase selectivity and circumvent resistance. We also… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072133 - 24 February 2026
Abstract This literature review explores the complex interaction between p53 and microRNAs (miRNAs) in the occurrence and progression of breast cancer (BC), the most common and lethal tumor type among women. BC is a multifactorial disease resulting from a combination of genetic and epigenetic alterations in cell DNA, influencing proliferation, differentiation, and migration. TP53 gene, which codifies p53 protein, is a known tumor suppressor, and it plays an important role in cell maintenance as DNA repair, cell proliferation control, and apoptosis activation. TP53 expression can be modulated by several miRNAs, as miR-30c, miR-34a, and the miR-200 family, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.072620 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Strategies in the Diagnosis, Prediction, Monitoring, and Treatment of Brain Tumors)
Abstract Metastatic brain tumors undergo profound metabolic–epigenetic reprogramming driven by the unique constraints of the brain microenvironment. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF1α) enhances glycolytic flux, lactate accumulation, and histone lactylation, collectively supporting metastatic colonization and immune evasion. Key metabolites including acetyl-CoA, S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), α-ketoglutarate (α-KG), fumarate, and 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG)—directly modify chromatin states by regulating histone acetyltransferases, DNA/histone methyltransferases, and α-KG dependent dioxygenases such as Ten-Eleven Translocation (TET) enzymes and lysine demethylases (KDMs). These metabolic shifts result in aberrant DNA methylation, histone lysine residue at position 27 on Histone H3 (H3K27) trimethylation, and depletion of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), all of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073008 - 24 February 2026
Abstract Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is characterized by rare Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg (HRS) tumor cells that uniformly express cluster of differentiation (CD)30 molecules and orchestrate an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, making CD30 an attractive and selective therapeutic target. We summarize the biological rationale for CD30 as a therapeutic target and the preclinical and clinical evidence across major platforms: antibody-drug conjugates (brentuximab vedotin), monoclonal antibodies (including acimtamig and its combinations with Natural Killer cells), second- and third-generation chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells, and alternative modalities. Particular attention is given to standardized response assessment (IWG, Lugano, RECIL criteria), which enables appropriate… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.069317 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy)
Abstract A clear goal in cold tumor research is to identify strategies for converting them into immunologically ‘hot’ tumors with enhanced immune cell infiltration and activity, thereby improving their responsiveness to immunotherapy. The genesis of cold tumors is exceedingly intricate. In recent times, as the analysis of this phenomenon has been pursued with greater depth, a suite of advanced diagnostic and therapeutic technologies has surfaced. These novel approaches and tactics are anticipated to modulate the tumor immune microenvironment across various dimensions, thereby facilitating the advancement of personalized and precise treatment modalities for cold tumors. The present… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.074893 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Transcriptome Analysis in Tumor Microenvironment and Tumor Heterogeneity)
Abstract Accumulating evidence indicates that the neuro-immune axis is central to gastric cancer pathogenesis. Dynamic, bidirectional signaling between neural circuits and immune cells promotes tumor progression, shapes an immunosuppressive microenvironment, and contributes to therapeutic resistance. We synthesize current knowledge on how autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) and sensory innervation regulate gastric cancer biology. These circuits act through neurotransmitters (catecholamines, acetylcholine) and neuropeptides (substance P [SP], calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]) to foster tumor growth and angiogenesis, facilitate perineural invasion, and enable immune evasion by recruiting suppressive myeloid and lymphoid populations and by inducing checkpoint molecule expression. We also… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072222 - 24 February 2026
Abstract This article has no abstract. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072141 - 24 February 2026
Abstract Objectives: The five-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer is notably low, posing a significant challenge to patient health. The primary treatments are radiotherapy and chemotherapy, sometimes combined with targeted therapy; however, their clinical benefits are limited. Therefore, developing new models to evaluate the therapeutic potential of novel molecules is essential. Fingolimod and Dimethyl Fumarate (DMF), currently used to treat multiple sclerosis, have recently been shown to have anti-cancer effects in several preclinical tumor models. This study aims to evaluate the therapeutic potential of Fingolimod and DMF in pancreatic cancer by investigating their respective in vitro cytotoxicity… More >
Graphic Abstract
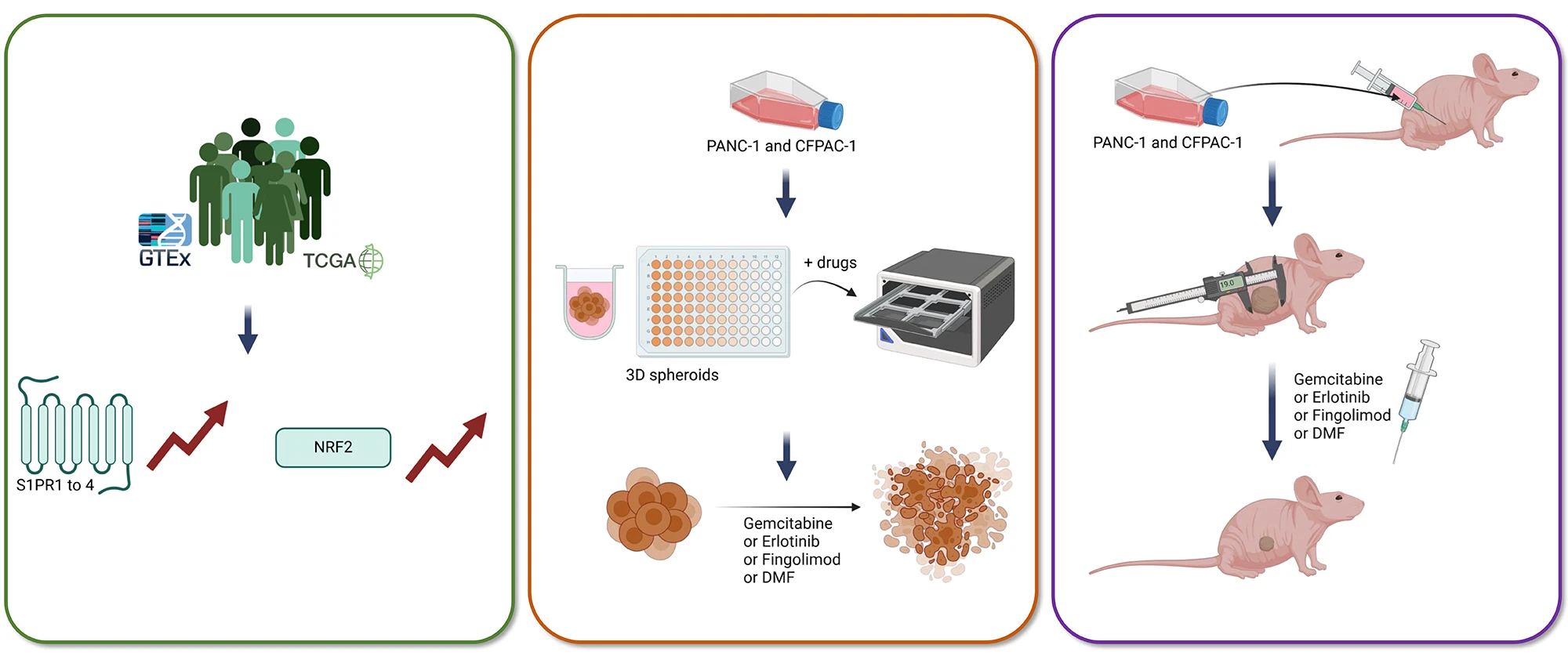
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072793 - 24 February 2026
Abstract Objectives: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) regulates tumor vascularization in response to hypoxia and inflammatory signals. The polyphenol curcumin is supposed to interfere with inflammation-induced VEGF secretion and might therefore support anti-VEGF-based treatments. We aimed to investigate the interaction between curcumin and the inflammatory cytokine Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) for VEGF secretion in breast cancer cell lines representing major breast cancer subtypes. Methods: VEGF in cell cultures was detected by Western blot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Kinase phosphorylation was investigated by Western blotting. Gene expressions were analyzed by correlation tests. VEGF was evaluated in a retrospective… More >
Graphic Abstract
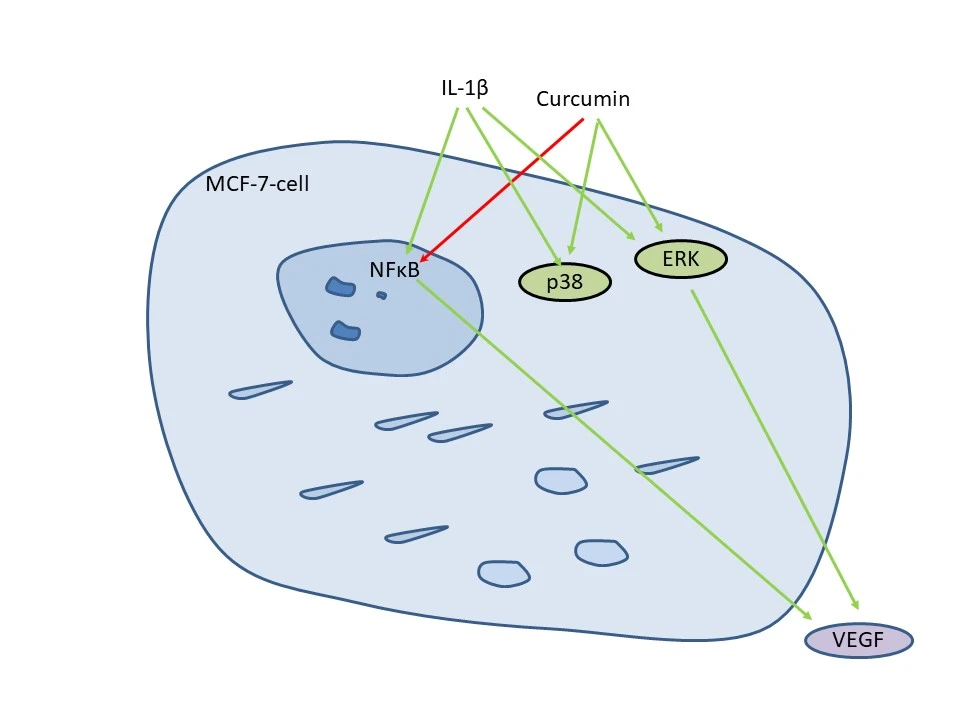
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072053 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy)
Abstract Objectives: The PACIFIC trial established the benefit of durvalumab following chemo-radiotherapy for stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the concurrent use of radiotherapy (RT) and durvalumab (PACIFIC-2 trial) showed no additional advantage. The PD-RAD study was set up to understand the immunological effects of RT on the tumor microenvironment (TME) to aid in optimizing sequencing of combination therapies. Methods: The PD-RAD trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03258788) aimed to enroll thirty NSCLC patients receiving radical-intent RT. Tumor biopsies and blood samples were collected pre-RT and at week 2 during RT and analyzed using multiplex… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.071919 - 24 February 2026
Abstract Objectives: Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a minimally invasive method used in the treatment of various cancers and skin diseases, but it is not widely used in bone cancer, where the current therapy is often not effective and accompanied by side effects. Alternative and more effective therapies like PDT are needed. In this in-vitro study, the effect of the photosensitizer (PS) chlorin e6 (Ce6) on cancerous bone tumor cells using PDT was examined. Methods: A total of 27 tissue specimens from patients with primary bone cancers or bone metastases of different origins were genetically characterized and treated… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072105 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Biomarkers and Treatment Strategies in Solid Tumor Diagnosis, Progression, and Prognosis (Ⅱ))
Abstract Objectives: Phosphodiesterase 1A (PDE1A) regulates intracellular cyclic nucleotide signaling and has been implicated in tumor progression, but its clinical relevance and functional role in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), particularly in relation to the response to platinum remain unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical significance of PDE1A in EOG and to clarify its functional role in tumor progression and response to platinum-based chemotherapy. Methods: PDE1A mRNA and protein levels were analyzed using public databases, RNA sequencing, and immunohistochemistry. Correlations between PDE1A expression, clinicopathological features, and prognosis were assessed. Functional roles were investigated in ovarian… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.069397 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances and Innovations in Colorectal Cancer Research and Treatment)
Abstract Background: The long-term outcomes of robotic-assisted surgery and the prognostic significance of the pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) remain uncertain. This study aimed to assess the long-term outcomes of patients with LARC undergoing robotic-assisted surgery and to determine the prognostic value of pretreatment NLR. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 252 patients with LARC who were treated at a single medical center in Taiwan between January 2012 and January 2023. All patients underwent neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) followed by robotic-assisted surgery with total mesorectal excision (TME). Patients were stratified into four groups… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.071034 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Biomarker Discovery for Personalized Medicine in Oncology)
Abstract Objectives: The eukaryotic initiation factor 4F (eIF4F) translation initiation complex inhibitors (eIF4Fi) were recently found to hyperactivate extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) signals, which contribute to acquired resistance to BRAF (B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase) inhibitors in melanoma. This present study aims to elucidate how to overcome the resistance of the eIF4Fi in BRAFV600E mutant melanoma cells and explore the underlying mechanisms. Methods: Melanoma A375 (vemurafenib [VEM]-sensitive) and A375R (VEM-resistant) cells were exposed to eIF4Fi RocA at varying doses and durations in vitro. We investigated the impact of RocA on the activity of ERK1/2, AKT serine/threonine kinase 1… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.074202 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Molecular Therapeutics for Prostate Cancer)
Abstract Background: Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most prevalent malignancy in men and often correlates with distant metastasis in its advanced stages. The study aimed to investigate the effects of Ugonin J, a natural compound isolated from Helminthostachys zeylanica, on PCa metastasis. Methods: The effects of Ugonin J on cell motility were assessed using migration and invasion assays. Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and Western blotting were used to evaluate the impact of Ugonin J on mRNA and protein expression. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis was performed to investigate candidate mechanisms. Differential gene expression analysis in PCa patients… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072592 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Discover Biomarkers for Personalized Oncology)
Abstract Objectives: Tamoxifen is a key drug that provides endocrine therapy for estrogen receptor (ER)
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073051 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Biomarkers and Treatment Strategies in Solid Tumor Diagnosis, Progression, and Prognosis (Ⅱ))
Abstract Background: Locally advanced laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LA-LSCC) presents clinical challenges due to the lack of reliable non-invasive biomarkers. This study aimed to evaluate miR-449a as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in LA-LSCC. Methods: miR-449a expression was analyzed in tumor tissues, adjacent normal tissues, and serum from 81 LA-LSCC patients and 50 controls using quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). We assessed the diagnostic accuracy by Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (ROC curves), clinicopathological associations, survival outcomes (Kaplan-Meier), and treatment response dynamics. Results: miR-449a was significantly downregulated in LA-LSCC tissues (p < 0.0001) and serum (p <… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.068508 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Microenvironment, Microbiota and Immune System in Digestive Cancers)
Abstract Background: Gastric cancer (GC) remains highly lethal, with metabolic reprogramming as a key hallmark. This study explores Centromere Protein F (CENPF)’s role in GC pathogenesis, specifically its regulation of glutamine metabolism. Methods: The Cancer Genome Atlas–Stomach Adenocarcinoma (TCGA-STAD), GSE19826, and GSE27342 datasets were analyzed by bioinformatics to identify key candidate genes in GC. The function of CENPF was assessed by flow cytometry, colony formation assays, and Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). RNA sequencing, metabolic profiling, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), western blot (WB), and luciferase reporter assay were employed to investigate the fundamental mechanisms. Results: CENPF was upregulated in GC… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.068695 - 24 February 2026
Abstract Objectives: B-cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) is a transcriptional repressor whose overexpression is closely linked to the progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), making it a promising therapeutic target. This study aims to identify a novel small molecule, synthesized via proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs), capable of degrading BCL6, thereby inhibiting DLBCL growth and providing a foundation for future preclinical studies. Methods: The expression of BCL6 in DLBCL was analyzed using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and the Human Protein Atlas. Western blotting assays confirmed BCL6 expression in tumor cell lines, leading to the identification of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.070207 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Therapeutics)
Abstract Objectives: Pancreatic cancer (PC) is characterized by poor prognosis due to its limited treatment choices and delayed detection. S100A14 has been implicated in tumor progression, yet its regulatory hierarchy and functional interplay in PC remain unclear. This study aimed to define the role of S100A14 in PC progression. Methods: Integrated bioinformatic analyses of TCGA-PAAD and GSE22780 datasets identified candidate hub genes. Prognostic relevance was assessed via Kaplan-Meier and ROC analyses. Functional experiments were performed in PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells, including qRT-PCR, CCK-8 assay, Western blotting, Transwell assay, and apoptosis assay. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) was used to verify… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.070333 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Identification of potential targets and biomarkers for cancers and the exploration of novel molecular mechanisms of tumorigenesis and metastasis)
Abstract Objectives: Gastric cancer (GC) is among the most prevalent malignancies worldwide, ranking as the fifth most common cancer and the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality. This study intends to investigate how Inhibin subunit beta A (INHBA) promotes the progression of GC by activating the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway via targeting Integrin alpha-6 (ITGA6). Methods: Quantitative reverse transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) were utilised to validate the expression levels of INHBA in GC, which were subsequently correlated with the clinicopathological factors and outcomes. Cellular and animal studies were conducted to ascertain… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071122 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning for Disease Subtyping, from Molecular to Clinical Features)
Abstract Background: Tertiary lymphoid structures (TLSs) promote antitumor immunity and predict favorable immunotherapy outcomes in breast cancer. The study aimed to investigate how Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO2)-associated tryptophan metabolism influences TLS maturation and B cell class switching in breast cancer. Methods: Bulk transcriptomic data from The Cancer Genome Atlas-Breast Invasive Carcinoma (TCGA-BRCA, n = 1055) were analyzed using Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA)–based metabolic scoring, immune deconvolution, and TLS quantification. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq, n = 26) and spatial transcriptomics (n = 1) were applied to map TDO2 expression and TLS spatial organization. Validation was performed by immunohistochemistry (n… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.071739 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Therapeutics)
Abstract Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly lethal malignancy driven by both intrinsic oncogenic pathways and immune microenvironmental regulation. Emerging evidence suggests that DNASE1L3 may influence tumor biology and immune responses; however, its specific roles in HCC progression and macrophage-mediated regulation remain unclear. This study aimed to elucidate the biological functions of DNASE1L3 in HCC and to determine how it modulates tumor behavior and immune interactions. Methods: Bioinformatics analyses of the GSE41804 and Cancer Genome Atlas-Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (TCGA-LIHC) datasets were used to identify hub genes. Functional assays assessed the impact of DNASE1L3 on HCC cell proliferation,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
COMMENTARY
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.069227 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics of Liver Cancer)
Abstract Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a global challenge, with limited effective treatment options for advanced-stage disease. The HIMALAYA trial (phase III randomized study that evaluated the STRIDE regimen) introduced the Single Tremelimumab Regular Interval Durvalumab (STRIDE) regimen, an immunotherapy-based approach that achieved a median overall survival (OS) of 16.43 months compared to 13.77 months with sorafenib. While statistically significant, this ~2.7 months OS gain warrants scrutiny in light of STRIDE’s increased immune-related toxicity and cost. This commentary evaluates STRIDE’s impact within the broader landscape of first-line systemic therapy for unresectable HCC, alongside other regimens such… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
VIEWPOINT
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.071847 - 24 February 2026
Abstract Hepatitis C virus (HCV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are increasingly recognized as significant etiological factors in the pathogenesis of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (B-NHLs). Epidemiological and molecular studies have demonstrated a consistent association between chronic viral infection and B-NHLs. Multiple pathogenic mechanisms have been implicated in lymphomagenesis, both direct and indirect, including chronic antigenic stimulation, direct infection of B cells, and viral protein–mediated oncogenic signaling, It is likely that a combination of several pathogenic conditions is required to eventually lead to the development of lymphoma. The prevalence of B-cell lymphomas among individuals with chronic… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072100 - 24 February 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances and Innovations in Head and Neck Cancer: Cutting-Edge Treatments and Future Directions)
Abstract Background: Collision medullary and papillary thyroid carcinoma (MTC/PTC) is a rare entity, constituting less than 1% of all thyroid malignancies. The concurrent presence of these malignancies in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease, such as Graves’ disease, is even more uncommon. Calcitonin (Ctn) is considered one of the key MTC biomarkers. Mixed tumors may alter this relationship. Case Description: We report the case of a 55-year-old female with a history of Graves’ disease, who underwent total thyroidectomy for persistent dysthyroid orbitopathy. Histopathological analysis revealed a 9-mm collision MTC/PTC tumor in the left thyroid lobe, confirmed through More >
 Open Access
Open Access
RETRACTION
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.080053 - 24 February 2026
Abstract This article has no abstract. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
RETRACTION
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.080055 - 24 February 2026
Abstract This article has no abstract. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
RETRACTION
Oncology Research, Vol.34, No.3, 2026, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.080056 - 24 February 2026
Abstract This article has no abstract. More >