Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Evangelos Manousakis1, Cristina Moreta-Moraleda1, Clàudia Martinez Miralles1, Anna Tomàs Pujolà1, Houda Baccara2, Laia Liñán Franquet1, Montserrat Montañés Albó1, Roberto Ferrari2, Roni H. G. Wright1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074965
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Pathology, Early Diagnosis and Therapeutic Strategies for Breast Cancer)
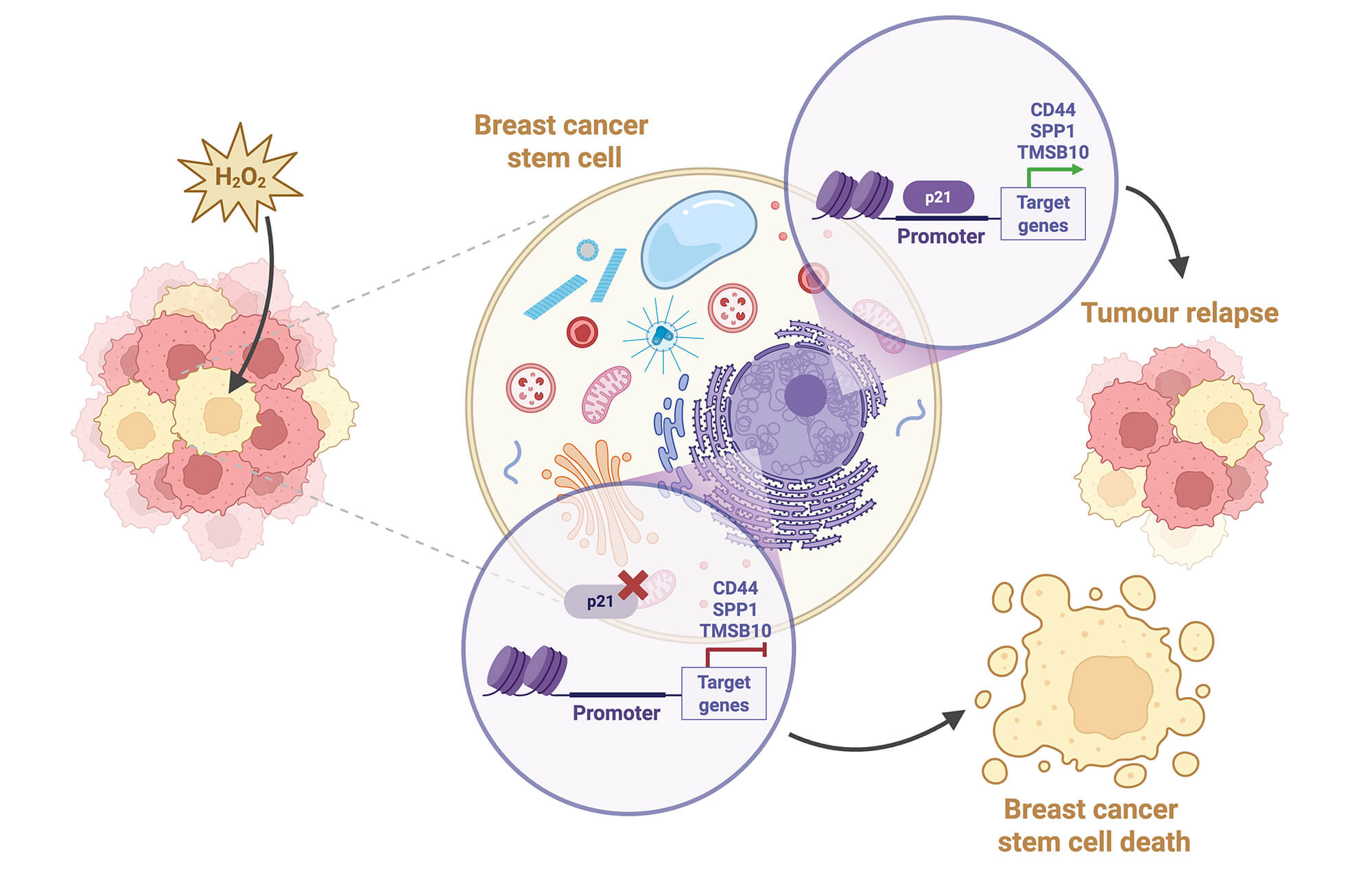
Abstract Objective: Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent malignancies among women worldwide, and despite advances in therapy and treatment options, tumour relapse and metastasis remain major clinical challenges, largely driven by the breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) niche that resists conventional treatments and regenerates tumours. In breast cancer, where approximately 30% of patients who initially respond to treatment ultimately relapse and die of metastatic disease, targeting BCSCs is critical for improving patient outcomes. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A/p21 (CDKN1A/p21) is a multifunctional protein that is known primarily for its role in regulating the cell cycle… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Kuan-Hao Lin1, Yu-Ju Lin1, Yu-Bin Hong1, Meng-Huai Hsu1, Zhen-Xiang Liao1, Shuo-Yu Chang1, Chiou-Hwa Yuh1,2,3,4,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074144
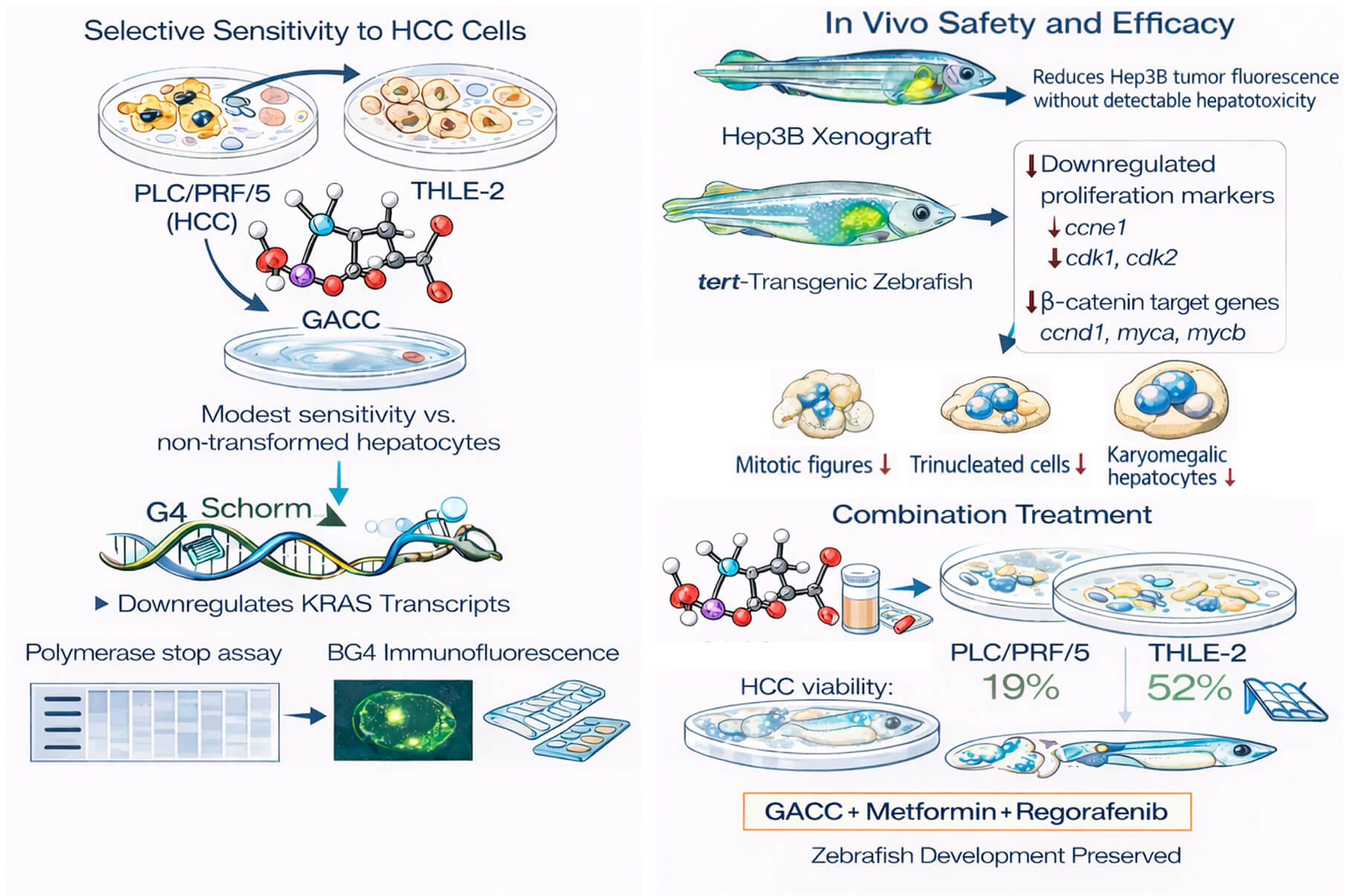
Abstract Objectives: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has limited systemic options with substantial toxicity. G-quadruplex (G4) structures in oncogene promoters are attractive but challenging drug targets. This study aimed to determine whether glutamic acid–chelated cobalt (GACC) is a G4-active scaffold with anti-HCC efficacy and favorable in vivo safety, and whether an AI-guided phenotypic response surface (PRS) can optimize less toxic combinations. Methods: Anticancer activity was tested in HCC cell lines (PLC/PRF/5, Hep3B, HepG2) and non-transformed THLE-2 hepatocytes (CCK-8, IC50). In vivo safety/efficacy were assessed in zebrafish embryo toxicity assays, a Hep3B xenograft model, and a tert-overexpressing transgenic zebrafish model, with hepatotoxicity… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Wubin Zhao#, Qi Wang#, Jun Zhang*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.076406
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Therapeutic Challenges in Targeting Cell Death)
Abstract Disulfidptosis is a newly identified form of regulated cell death (RCD) first described in 2023, representing a significant advance in understanding programmed cell death pathways. This unique cell death modality is characterized by abnormal intracellular accumulation of disulfide bonds and disruption of redox homeostasis, leading to cytoskeletal collapse without caspase activation. Disulfidptosis is primarily triggered by glucose deprivation in cells with high expression of solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11). Under these conditions, insufficient NADPH supply prevents the effective reduction of accumulated cystine to cysteine, thereby inducing disulfide stress. Distinct from apoptosis, ferroptosis, cuproptosis,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Carlo Ronsini1,*, Giuseppe Cucinella1, Maria Cristina Solazzo1, Mariano Catello Di Donna1, Cono Scaffa1, Stefano Cianci2, Manuela Ludovisi3, Sandro Pignata4, Vito Chiantera1
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074934
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Drug Targets and Combination Strategies in Gynecologic Cancers)
Abstract Background: The optimal sequencing of surgery and chemotherapy in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer remains debated. While primary debulking surgery (PDS) has been considered the standard approach, recent randomized trials have questioned its survival advantage over neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) followed by interval debulking surgery (IDS). The study aimed to systematically evaluate phase III randomized controlled trials comparing PDS and NACT. Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines (PROSPERO ID 1169057), PubMed and Scopus were systematically searched in October 2025 for phase III randomized clinical trials evaluating cytoreductive strategies in ovarian carcinoma. Only full-text English studies reporting overall survival (OS)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chang He#, An Wang#, Youbo Wang#, Qinyun Ma*, Xiaofeng Chen*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074880
Abstract Objectives: Combined chemotherapy and photothermal therapy (PTT) represents a promising approach for enhancing cancer treatment efficacy. This study aimed to develop arsenic trioxide (ATO) and poly(cyclopentadithiophene-alt-benzothiadiazole) (PCPDTBT)-loaded nanoparticles (ATO/PCPDTBT@NPs) to evaluate their synergistic efficacy in inhibiting lung cancer growth and metastasis. Methods: Nanovesicles were synthesized via a streamlined protocol and subjected to 808 nm NIR irradiation to assess their photothermal conversion capabilities. The therapeutic efficacy was evaluated in vitro using A549 lung carcinoma cells to assess apoptosis, invasion, and migration, and in vivo to monitor tumor volume reduction. Results: The nanoparticles exhibited excellent hemocompatibility and low cytotoxicity while More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chun-Shiang Lin1,2,#, Ta-Wen Hsu3,4,#, Hsiang-Lin Lee5,6,*, Shao-Hsuan Kao1,7,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074231
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Signaling Pathway Crosstalk in Malignant Tumors: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics)
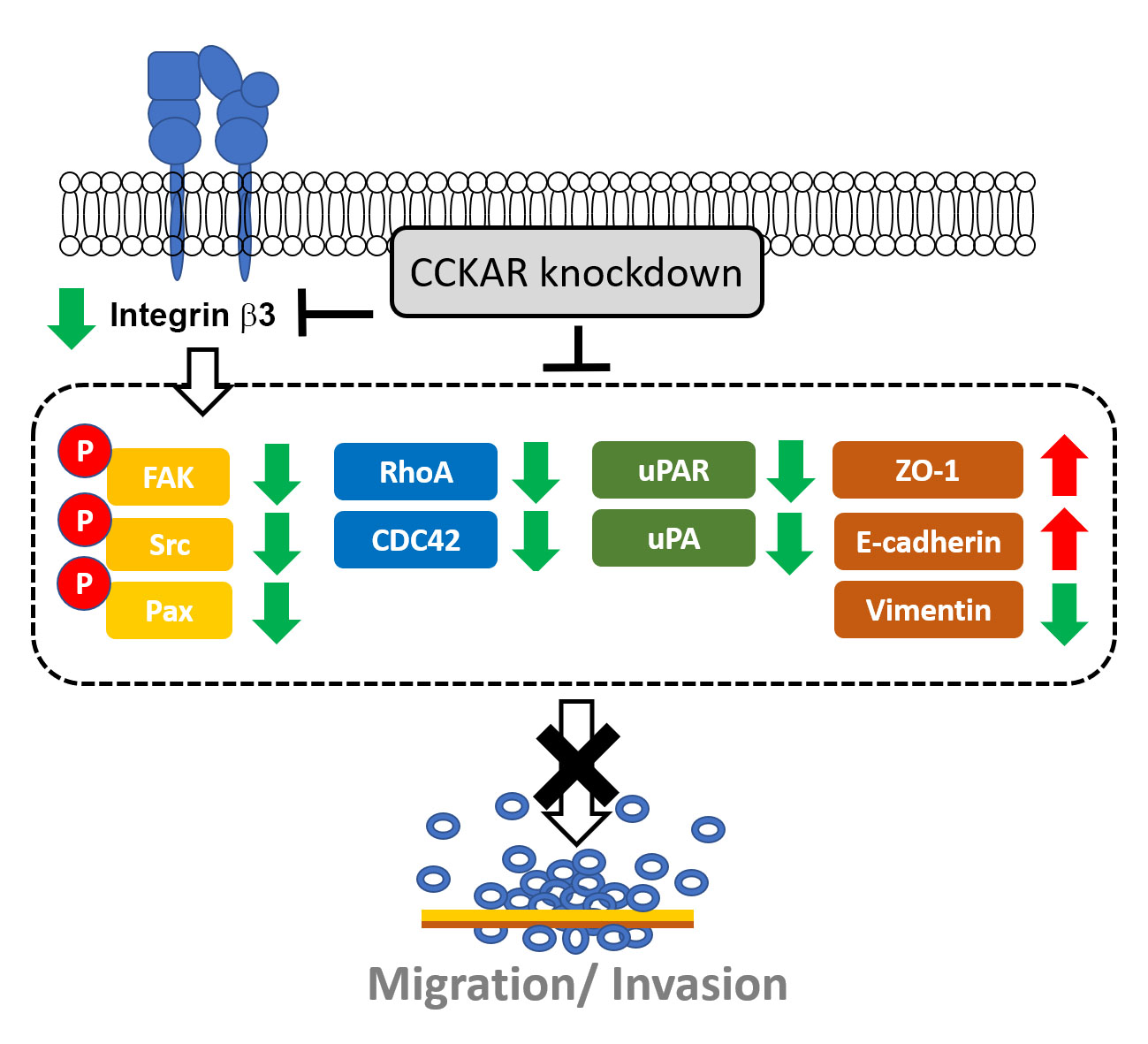
Abstract Objectives: Cholecystokinin A receptor (CCKAR) has been linked to poor prognosis in colon cancer patients, but the role of CCKAR in colon cancer cell invasiveness and the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. This study aimed to explore the effect of CCKAR on the invasive potential of colon cancer cells. Methods: Different human colon cancer cell lines were used. Gene expression was evaluated by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qPCR), while protein expression and phosphorylation were assessed by Western blotting. Cell motility and invasiveness were examined through wound healing and invasion assays,… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Benjamin Heckelmann#, Jannis Duhn#, Rüdiger Braun*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.075028
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Gastroenteropancreatic Tumors: From Basic Research to Therapeutic Approach)
Abstract Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is currently the third leading cancer-related cause of death worldwide and is forecasted to become the second leading cause in the United States by 2030. Despite the development of multimodal treatment regimens, 5-year overall survival remained as low as 12%. Several efforts have been made to account for different aspects of heterogeneous tumor biology in PDAC, aiming to enable treatment stratification of defined subtypes. Besides targeting specific mutations, the definition of molecular (transcriptional) subtypes has gained substantial interest regarding response prediction and treatment stratification. Despite numerous advances in the field of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Denisse A. Gutierrez*, Elisa Robles-Escajeda, Jose A. Lopez-Saenz, Robert A. Kirken, Edgar A. Borrego, Ana P. Betancourt, Soumya Nair, Sourav Roy, Armando Varela-Ramirez, Renato J. Aguilera*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074945
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Discovery of a Potent Antitumor Agent: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential)
Abstract Objectives: Drug resistance is the major determinant of chemotherapy failure, leading to relapse and tumor progression, demonstrating the urgent need for novel antineoplastic drugs. This study aimed to evaluate the anticancer potential of two novel pyrazole derivatives, P3C.1 and P3C.2, and to elucidate their mechanism of action in cancer cells. Methods: The cytotoxicity of the compounds was evaluated across 27 different cancer cell lines via a nuclear staining assay. Subsequent flow cytometric and biochemical analyses were performed to assess reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, apoptosis induction, mitochondrial integrity, and cell cycle progression. Additional studies included… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chanwoong Yoon1,#, Euihyeon Na2,#, Min Joo Choi1, Sang-Pil Yoon1,3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074140
Abstract Objective: Increased Src kinase activity is known to correlate with cancer progression and poor prognosis, indicating that Src plays a central role in cell migration and invasion. In this study, we investigated the effects of saracatinib, a Src kinase inhibitor, under anoikis-resistant conditions in colorectal cancer cells. Methods: Wild-type and 5-fluorouracil-resistance acquired SNU-C5 colorectal cancer cells were cultured in both monolayer and spheroid systems under fetal bovine serum (FBS) or growth factor (GF) supplemented conditions. Cell viability assay, flow cytometry, wound healing assay, spheroid formation and morphometric analysis, and Western blotting were performed using both… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Farzana Yasmeen1,#, Abdul Manan1,#,*, Wook Kim1, Sangdun Choi1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.076072
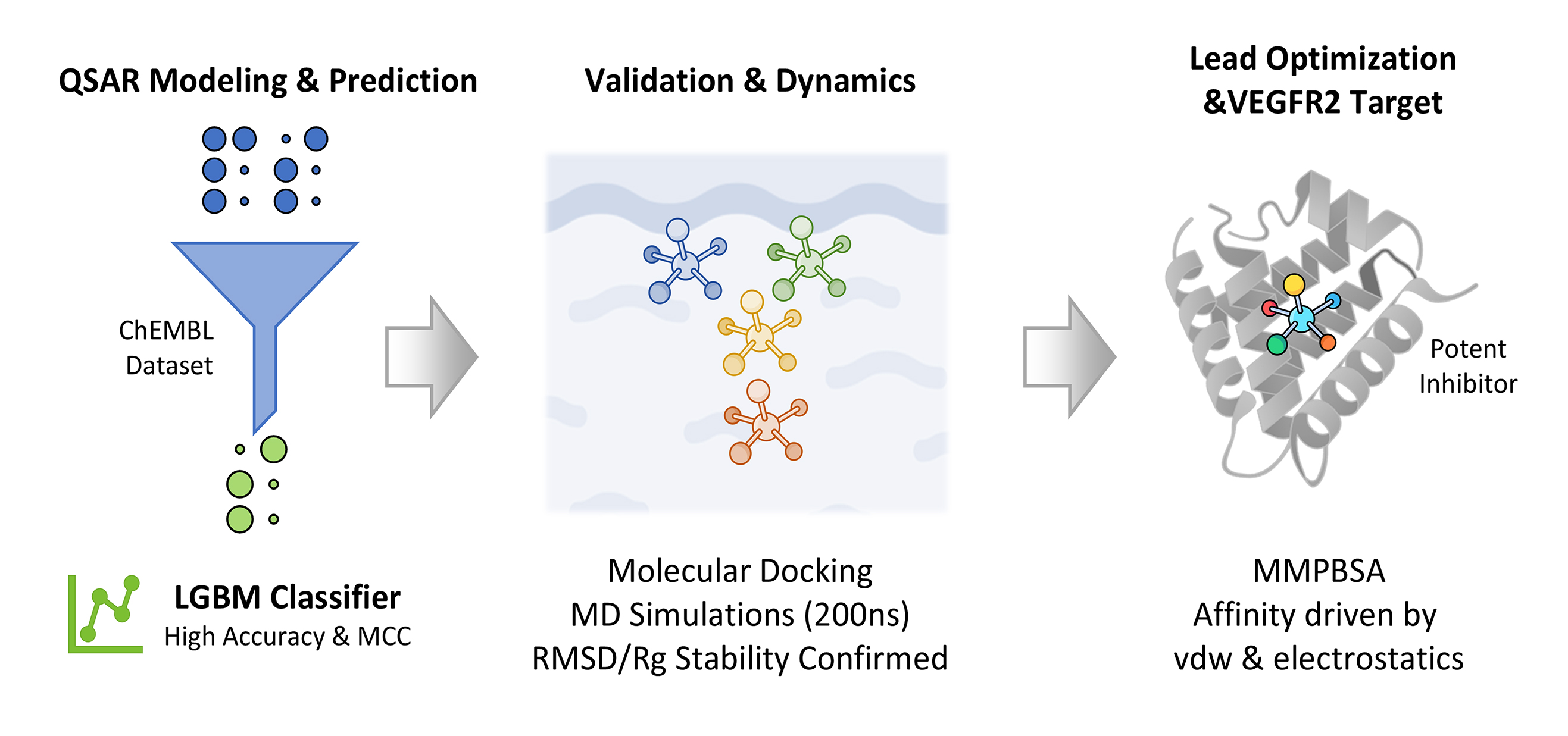
Abstract Objectives: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) is a critical therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) due to its role in angiogenesis and tumor progression. While several inhibitors are currently used, clinical utility is often limited by resistance and adverse effects, necessitating the discovery of novel therapeutic agents. The aim of this study was to identify and characterize novel, highly effective VEGFR2 inhibitors using an integrated computational pipeline to advance the development of new HCC treatments. Methods: A comprehensive dataset from the ChEMBL database was curated and standardized for Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) modeling.… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nicola Marrano1,#, Mariangela Caporusso2,#, Cosimo Matino1,#, Irene Caruso3,#, Carlo Ganini4, Mimma Rizzo5, Ludovico Di Gioia2, Angelo Cignarelli1, Sebastio Perrini1,6, Luigi Laviola1, Camillo Porta4, Francesco Giorgino1,*, Annalisa Natalicchio1
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074672
Abstract Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are a cornerstone of systemic therapy for renal cell carcinoma (RCC), used both in the adjuvant and metastatic settings across various lines of treatment, often in combination with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (VEGFR-TKIs). These therapies are associated with endocrine immune-related adverse events (irAEs), which can be irreversible and life-threatening if not promptly managed. Using data from the Food and Drug Administration Adverse Reporting System (FAERS), this study aimed to evaluate the real-world occurrence of endocrine irAEs in all approved VEGFR-TKI + ICI combinations for RCC, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yen-Pin Chen1,2,3, Rathinasamy Baskaran4, Hema Sri Devi4, Chaouhan Hitesh Singh4, Yu-Jung Lin4,5, Marthandam Asokan Shibu6, Wei-Wen Kuo7, Shih-Chieh Liao8, Ming-Cheng Chen9, Tso-Fu Wang10, Chi-Cheng Li11, Tsung-Jung Ho12, Tzu-Ching Shih13, Shinn-Zong Lin14,15,16,*, Chih-Yang Huang4,17,18,19,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073080
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Overcoming Drug Resistance in Cancer: Strategies and Natural Compound-Based Therapeutics)
Abstract Objective: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNAs that play a key role in the development of chemoresistance in various cancer types, including colorectal cancer (CRC). In this study, we aimed to study the underlying mechanisms of miRNA in chemotherapy-resistant CRC. Methods: LoVo CRC cell line was exposed to oxaliplatin at an increased dose, and cells were cultured in the presence of oxaliplatin to develop LoVoOXR cells. Microarray and Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR), western blot, and transwell assay were used to evaluate the chemoresistance in LoVoOXR CRC cells. Results: Microarray and qRT-PCR analysis showed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Kassiani Lalechou, Despoina Pantazi*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074452
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Cancer Pharmacology)
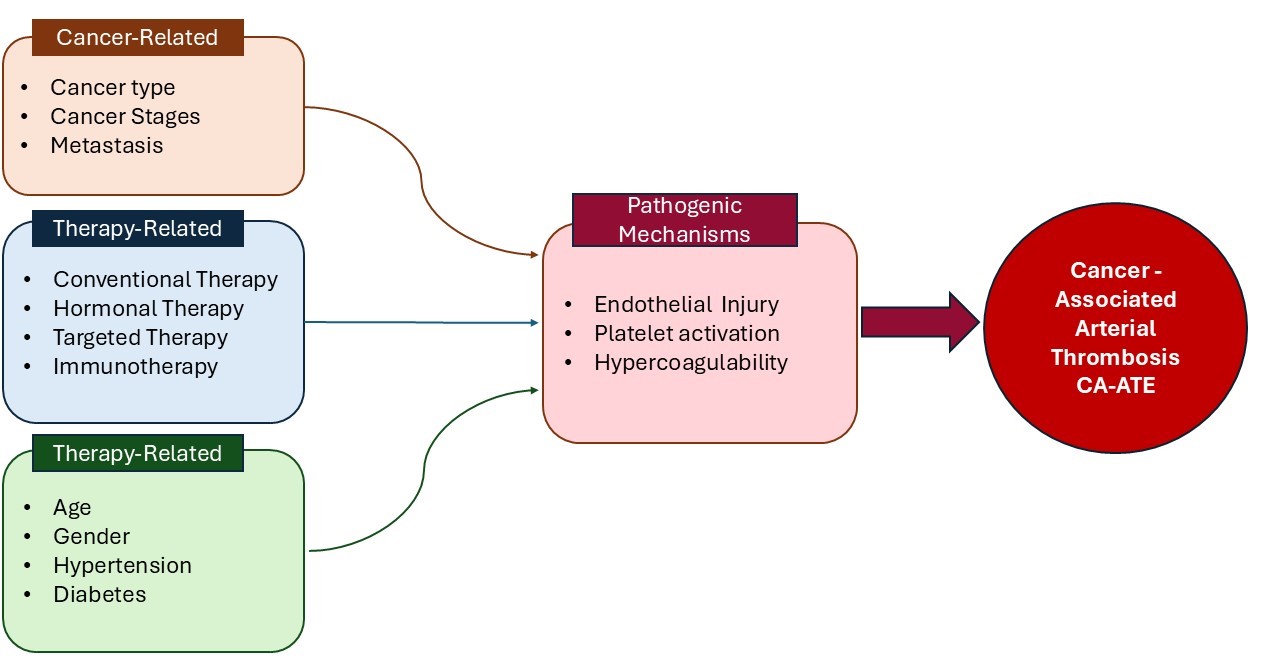
Abstract Cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among cancer patients. While venous thromboembolic events have been extensively studied due to their higher incidence, arterial thrombosis in cancer patients—referred to as cancer-associated arterial thromboembolism (CA-ATE)—is less well understood but may pose a greater danger. The pathophysiology of CA-ATE involves complex interactions between the tumor microenvironment, cancer cells, patient-related factors, and cancer therapies. Some chemotherapeutic agents, particularly platinum-based compounds (cisplatin, oxaliplatin), gemcitabine, taxanes, and targeted therapies such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), have been associated with an increased risk of arterial thrombosis. In… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Andrea Dalbeni1,2, Marco Vicardi1,2,*, Leonardo A. Natola1,2, Alessandra Auriemma3, Bernardo Stefanini4, Caterina Vivaldi5, Piera Federico6, Andrea Polloni7, Caterina Soldà8, Lorenzo Lani4, Ingrid Garajová9, Stefano Tamberi10, Stefania De Lorenzo11, Fabio Piscaglia4,12, Vincenzo Di Maria1, Gianluca Masi5, Sara Lonardi8, Giovanni Brandi4,7, Bruno Daniele6, Franco Trevisani4,13, Gianluca Svegliati-Baroni14, Laura Schiada14, Fabio Marra15, Claudia Campani15, Ciro Celsa16, Giuseppe Cabibbo16, Mariangela Bruccoleri17, Massimo Iavarone17,18, Leonardo Stella19, Francesca R. Ponziani19, Tiziana Pressiani20, Lorenza Rimassa20,21, Francesco Tovoli
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics of Liver Cancer)
Abstract Objectives: The combination of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (A+B) represents one of the standards first-line treatments for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Metformin has garnered attention for its potential antitumour and immunomodulatory properties beyond glycaemic control. This study aimed to assess metformin’s impact in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) receiving A+B therapy. Methods: This retrospective analysis of a prospectively-maintained multicentre database included 523 patients with HCC treated with A+B from the ARTE (Atezolizumab-bevacizumab Real-life Experience for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma) dataset across 18 Italian centres (May 2020–January 2024). We evaluated objective response rate (ORR), disease… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yin-Lun Chang1,2, Hao-Lun Luo1, Jei-Ming Peng3,*, Chang-Chun Hsiao2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.070837
Abstract Background: Upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) is an aggressive malignancy with high recurrence rates. Lymphovascular invasion (LVI) predicts a poor prognosis, yet its molecular drivers remain unclear. BOC cell adhesion-associated, oncogene-regulated (BOC, also known as Brother of CDO [Cell adhesion molecule-Related/Down-regulated by Oncogenes]), a hedgehog-related cell surface receptor, may serve as a biomarker for tumor progression and chemotherapy response. The study aimed to investigate the role of BOC in UTUC and its potential to predict LVI and chemotherapy response. Methods: Sequencing (RNA-seq) of 10 stage III UTUC, treatment-naïve, fresh tissue samples identified BOC as a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hui Zha1,#, Chao Li2,#, Jia Chen3, Hao Bo2, Zhaolan Hu4, Zailong Qin5,6,*, Jie Guo7,8,*, Junbin Yuan1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.067601
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Breast Cancer Biomarkers and Drug Targets Discoveries Towards a More Personalized Treatment Setting)
Abstract Objective: Long non-coding RNAs have been found to play a pivotal role in breast cancer, yet the majority of these lncRNAs remain to be thoroughly investigated. This study aimed to explore the role of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in breast cancer stemness and drug sensitivity. Methods: Database mining was performed to evaluate the expression of LINC00467 in different types of breast cancer and its association with clinical features. The function of LINC00467 was examined through colony formation assays, quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR), and western blotting following LINC00467 silencing in breast cancer cell lines. Results: LINC00467… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Lu Hao1,#, Jiao Lu2,#, Jisu Xue2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.076420
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancing Cellular Therapeutics in Oncology: Innovations, Challenges, and Clinical Translation)
Abstract In vivo Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy reprograms a patient’s own T cells directly inside the body, bypassing the complex and costly traditional manufacturing process. This is achieved by systemically delivering viral or non-viral vectors that genetically modify endogenous T lymphocytes to produce functional CAR-T cells de novo. By eliminating ex vivo cell processing, this strategy can simplify workflows, reduce costs, improve accessibility, and allow faster treatment. Key delivery platforms include engineered lentiviral and adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors for lasting CAR expression and targeted lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for transient mRNA delivery. Emerging technologies like biomaterial scaffolds and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yan Zhu1,#, Bin Guan1,#, Wencai Guan1, Jihong Zhang1, Shiyu Wang1, Jimin Shi1, Wei Fan1, Qi Lu2,3, Lingyun Zhang4,5,*, Guoxiong Xu1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.075241
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: New Advance in Gynecologic Oncology)
Abstract Background: Ovarian cancer poses the greatest threat to survival among gynecologic cancers in women. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as critical regulators in oncogenesis. The current study aimed to elucidate the function and regulatory mechanism of lncRNA KRT7-AS in ovarian cancer. Methods: The clinical significance of KRT7-AS was evaluated through bioinformatics analysis of data from public repositories. KRT7-AS expression was examined by RT-qPCR and fluorescence in situ hybridization. The function analyses were conducted using assays for cell proliferation, migration, invasion, wound healing, and colony formation. Assessment of cell cycle and apoptosis was performed using flow… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Luigi Coltelli1,2,#, Paola Orlandi3,#, Chiara Finale1,4,#, Gianna Musettini1,4,#, Luna Chiara Masini1,4, Marco Scalese5, Giulia Soria1,4, Elena Sartori1,4, Ylenia Nodari1,4, Giada Arrighi1,2, Arianna Bandini3, Marta Banchi3, Costanza Tacchi3, Donghao Tang3, Barbara Salvadori6, Lucia Tanganelli1,7, Simona Giovannelli1,8, Mirco Pistelli9, Samanta Cupini1,4, Maurizio Lucchesi1,10, Alessandro Cosimi11, Giulia Lorenzini1,7, Elisa Biasco1,4, Chiara Caparello1,4, Giulia Acconci1,4,6, Eloise Fontana1,4, Eleonora Bona1,4, Azzurra Farnesi1,4, Antonio Pellino1,4, Andrea Marini1,4, Ermelinda De Maio1,4, Irene Stasi1,4, Cecilia Barbara1,4, En
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073799
Abstract Background: The treatment of advanced hormone receptor-positive (HR+) breast cancer has seen relevant changes in last years. However, bevacizumab remains an option when combined with paclitaxel, but no certified pharmacogenetic profiles are now usable for the prediction of its response in breast cancer patients. This study aimed to explore the pharmacogenetic interactions among single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of genes involved in the angiogenic process and their impact on progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in hormone receptor-positive (HR+) metastatic breast cancer subjects administered with bevacizumab plus paclitaxel, or with paclitaxel alone (clinicaltrial.gov… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Shuo Wang, Miao Wang, Wei Yao*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073554
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancing Cellular Therapeutics in Oncology: Innovations, Challenges, and Clinical Translation)
Abstract Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the most lethal malignancies, characterized by a highly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME), dense stromal architecture, and limited response to conventional therapies. This review comprehensively examines the emerging role of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered immune cells, including chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T), CAR-macrophages (CAR-M), and CAR-natural killer (CAR-NK) cells, as innovative immunotherapeutic strategies for PDAC. We delve into the mechanistic foundations of these platforms, highlighting their unique abilities to target tumor-associated antigens, overcome stromal barriers, and remodel the immunosuppressive TME. Recent preclinical and clinical advances demonstrate promising antitumor activity, particularly More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Antonio Ruggiero1,2,*, Fernando Fuccillo1, Valerio Di Paola3, Alberto Romano1, Palma Maurizi1,2, Dario Talloa1, Nazario Foschi4, Pierluigi Russo4, Marco Racioppi4, Stefano Mastrangelo1,2, Giorgio Attinà1
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.072807
Abstract Background: The management of renal neoplasms in adolescent patients poses unique clinical challenges due to their transitional position between paediatric and adult populations. This age group exhibits marked heterogeneity in tumour histology, ranging from entities commonly observed in paediatric oncology to tumours typical of adult age, as well as rare histological subtypes that exceptionally affect the kidney. Given the substantial differences in clinical protocols between paediatric and adult populations, rigorous multidisciplinary evaluation is essential to determine optimal diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for adolescent patients. Case Description: We present four cases from our tertiary referral centre that… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Roberta Giorgione1,#, Daniela Grasso2,#, Elisabetta Gambale1, Federico Scolari3, Virginia Rossi1, Fabrizio Di Maida4, Marinella Micol Mela1, Barbara Marzocchi2, Laura Doni1, Adriano Pasqui1, Andrea Minervini4, Enrico Caliman1, Sergio Serni4,5,6, Andrea Bernini2, Serena Pillozzi3, Lorenzo Antonuzzo1,5,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.068896
Abstract Objectives: To date, predictive and prognostic biomarkers for Bladder Cancer (BC) remain lacking. Existing literature underscores the potential of metabolomics as a valuable tool for biomarker identification. The primary objective of this study is to characterize the serum metabolic profile of BC patients undergoing platinum-based chemotherapy (Pt-CT) to identify potential biomarkers. Methods: In this pilot study, we investigated the metabolomic profiles of 14 BC patients undergoing Pt-CT in different settings. We compared their baseline profiles with those of healthy controls and tracked key metabolites throughout chemotherapy cycles. Metabolomics profiling was conducted using nuclear magnetic resonance… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Francisco Raúl Borzone1,2,*, María Belén Giorello1, Agustina Freire3, Leandro Marcelo Martinez4, Leonardo Feldman5, Federico Dimase6, Pablo Evelson3, Irene Larripa7, Emilio Batagelj8, Marcela Beatriz González Cid9, Norma Alejandra Chasseing1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074321
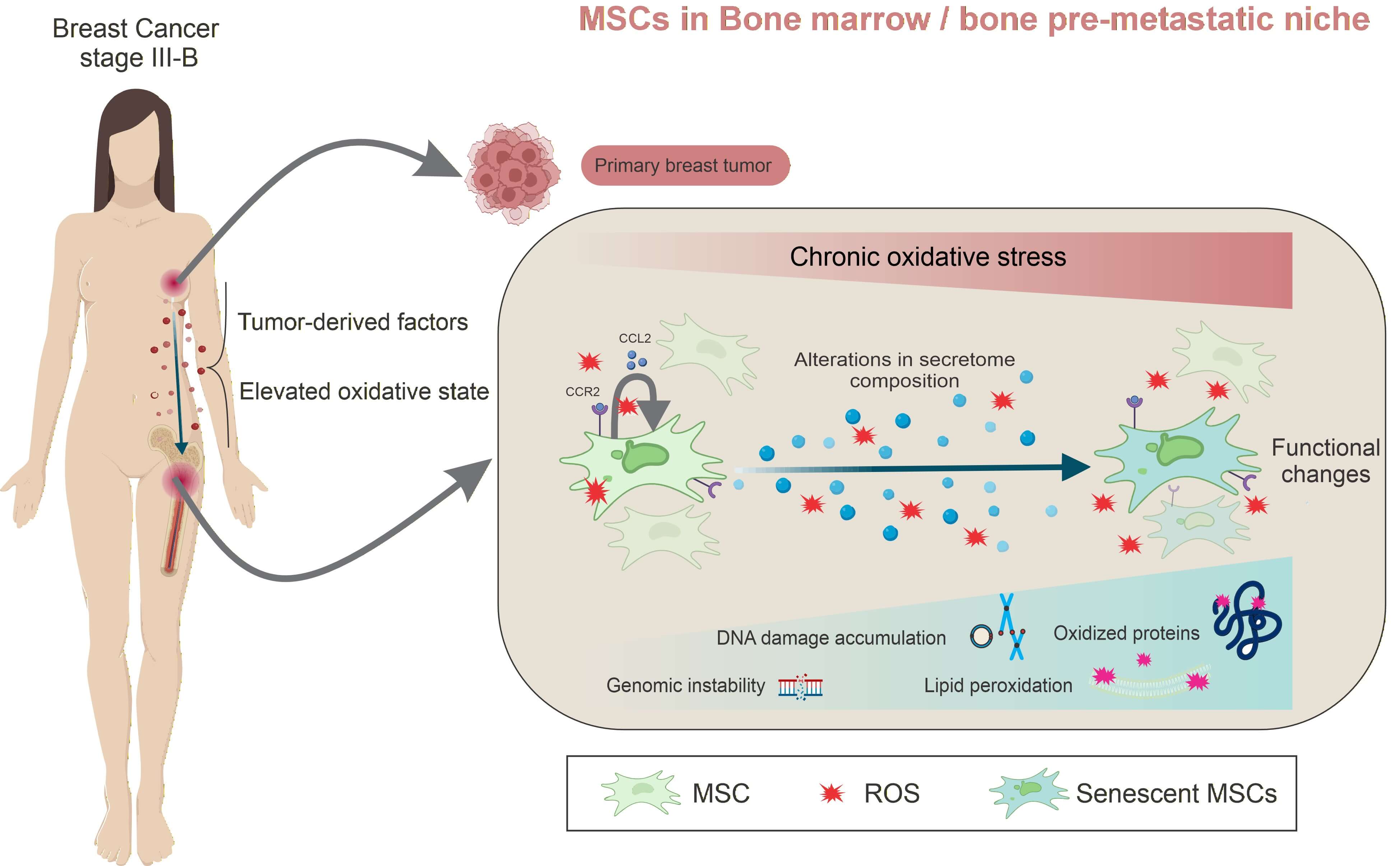
Abstract Backgrounds: Breast cancer metastasis remains the leading cause of mortality and frequently targets the bone. Breast cancer cells release soluble factors and extracellular vesicles that disrupt bone marrow (BM)/bone homeostasis, promoting osteoclastogenesis and the accumulation of senescent cells. In line with updated cancer hallmarks, senescent mesenchymal stem/ stromal cells (MSCs), osteoblasts, and osteocytes contribute to remodeling of the BM microenvironment, thereby favoring pre-metastatic niche (PMN) formation and subsequent bone metastasis. We previously demonstrated that untreated stage III-B breast cancer patients (BCPs) exhibit increased oxidative stress and elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, accompanied by senescent… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Awatif Rashed Z. Almotairy1,2, Eman Fayad3, Fatimah Hadadi4, Ahmad F. Alhomodi5, Dalal Nasser Binjawhar6, Hanadi A. Katouah7, Bassma H. Elwakil8,*, Keshav Raj Paudel9,10,*, Mostafa El-Khatib11
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.070645
Abstract Objectives: Prostate cancer cells often develop mechanisms to evade conventional therapies. Nanomedicine offers the potential for targeted drug delivery, improved tumor accumulation, and reduced systemic toxicity. This study biosynthesizes silver nanoparticles (NPP/AgONPs) functionalized with propolis, evaluates their antibacterial efficacy against uropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli), and assesses their cytotoxic effect on cancer cell proliferation using the PC-3, human prostate epithelial cell line. Methods: The synthesized NPP/AgONPs physiochemical parameters were characterized, followed by in vitro assays to evaluate their antibacterial activity against multiple uropathogenic E. coli strains; determining the cytotoxicity against HPrEC and PC-3 cells by measuring cytotoxicity (CC50)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Abdul Manan1,2, Sidra Ilyas2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074185
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics of Liver Cancer)
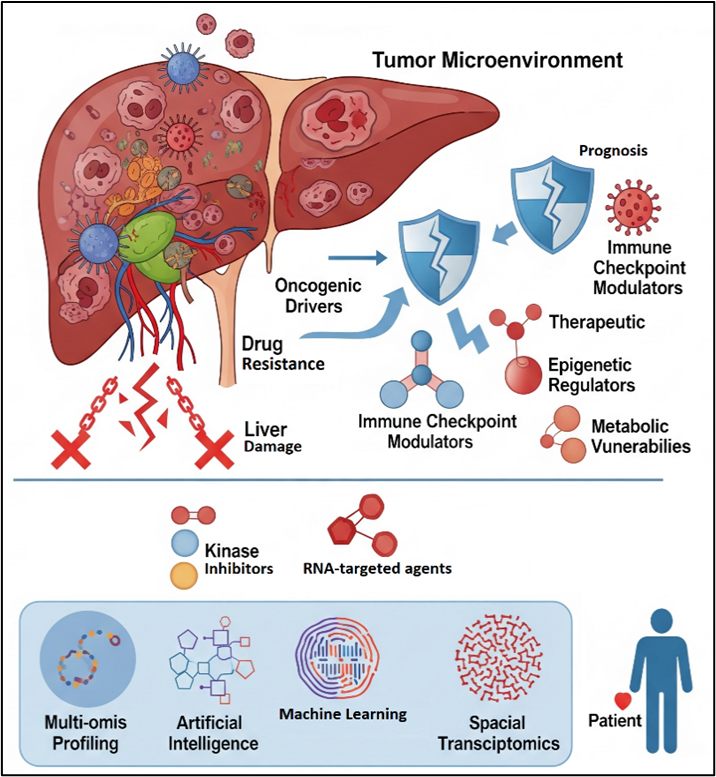
Abstract Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a significant global health challenge, with therapeutic efficacy in advanced stages often limited by underlying liver dysfunction and adaptive resistance. In this review, the evolving landscape of molecular targets and combinatorial strategies is critically examined, with a particular focus on the transition from preclinical discovery to clinical application. While traditional molecular heterogeneity is acknowledged, the aim is to elucidate how emerging computational paradigms are redefining target discovery and therapeutic stratification in HCC. The primary purpose is to evaluate the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) as integrative tools… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yingzheng Tan1,#, Jiao Xiao2,#, Liyun Tang3,4,#, Jian Wan3,#, Tian Zeng3, Wenchao Zhou3, Xueru Liu3, Xun Chen3,5,*, Yukun Li3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071536
Abstract Background: Lactate, as a critical byproduct of tumor metabolic reprogramming, plays an important role in DNA damage repair and tumor immune infiltration. This work aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which lactate promotes tumor DNA damage repair (DDR) and subsequent immune evasion. Methods: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), and ovarian cancer (OC) cells with cisplatin-induced DNA damage were treated with lactate at a concentration gradient, Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM1) shRNA, ESM1 overexpression plasmid, or the Protein Kinase B (AKT) Serine/Threonine Kinase 1 (Akt1) inhibitor LY294002. Proliferation, apoptosis, and DNA damage levels were… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Daniel Burg1, Aryeh Babkoff1, Omer Or2, Noam Olshinka2, Jonathan Abraham Demma3, Mohamad Adila1,3, Marc Wygoda4, Philip Blumenfeld4, Judith Diment5, Masha Galiner6, Yusef Azraq6, Daniela Katz1,7, Petachia Reissman8, Sadie Ostrowicki9, Gabriella Sebbag10, Narmine Elkhateeb1,11, Anat Hershko Moshe1,11, Dania Jaber1,11, Adi Hollander1,11, Limor Rubin1,11, Aviad Zick1,12,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.070233
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Combined Therapy for Soft Tissue Sarcomas)
Abstract Background: —Synovial sarcoma is a rare soft tissue sarcoma. Treatment of synovial sarcoma includes surgery, radiation, pazopanib, and chemotherapy. Targeted therapies, such as B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (BRAF) inhibitors, are emerging as a potential treatment option. We describe the sixth case of a BRAFV600E synovial sarcoma, the first extra-thoracic case. This case is the first to show a complete pathological response to BRAF & mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors. Case description: —We treated a 22-year-old male with a left groin BRAFV600E synovial sarcoma with doxorubicin, Ifosphamide & Sodium 2-Mercaptoethanesulfonate. When we identified BRAFV600E in the tumor,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Adam Khorasanchi, Merve Hasanov, Richard Wu, Hisham Alsharif, Kari Kendra, Claire Verschraegen*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.069012
Abstract Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) is the second most common type of skin cancer and typically involves the head and neck. Systemic therapy is often required for patients with advanced CSCC to achieve optimal disease control. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are now the standard of care for these patients, with a 50%–60% response rate and sustainable remission for at least 30% of patients. Given the activity of ICIs in advanced head and neck CSCC, ICIs are being studied in early-stage disease or neoadjuvant situations. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yiran Dong1, Jingyue Wang1, Jiayang Chen2, Liang Mo2, Yong You1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.075191
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Identification of potential targets and biomarkers for cancers and the exploration of novel molecular mechanisms of tumorigenesis and metastasis)
Abstract Background: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), the most prevalent histological subtype of lung cancer, remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality due to late diagnosis, metastasis, and therapy resistance. The aim of the study is to investigate the role of Kinetochore Scaffold 1 (KNL1) in promoting LUAD progression and its underlying molecular regulatory mechanisms. Methods: KNL1 mRNA expression levels across 33 cancer types were analyzed using bioinformatics analysis based on the TCGA database. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to assess KNL1 expression in LUAD and normal tissues. Stable KNL1-knockdown and KNL1-overexpressing LUAD cell lines were established using lentiviral… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yingying Zhao1,2, Jiakang Ma1,3, Rujin Huang1,2, Shuxian Pan1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.070208
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning for Disease Subtyping, from Molecular to Clinical Features)
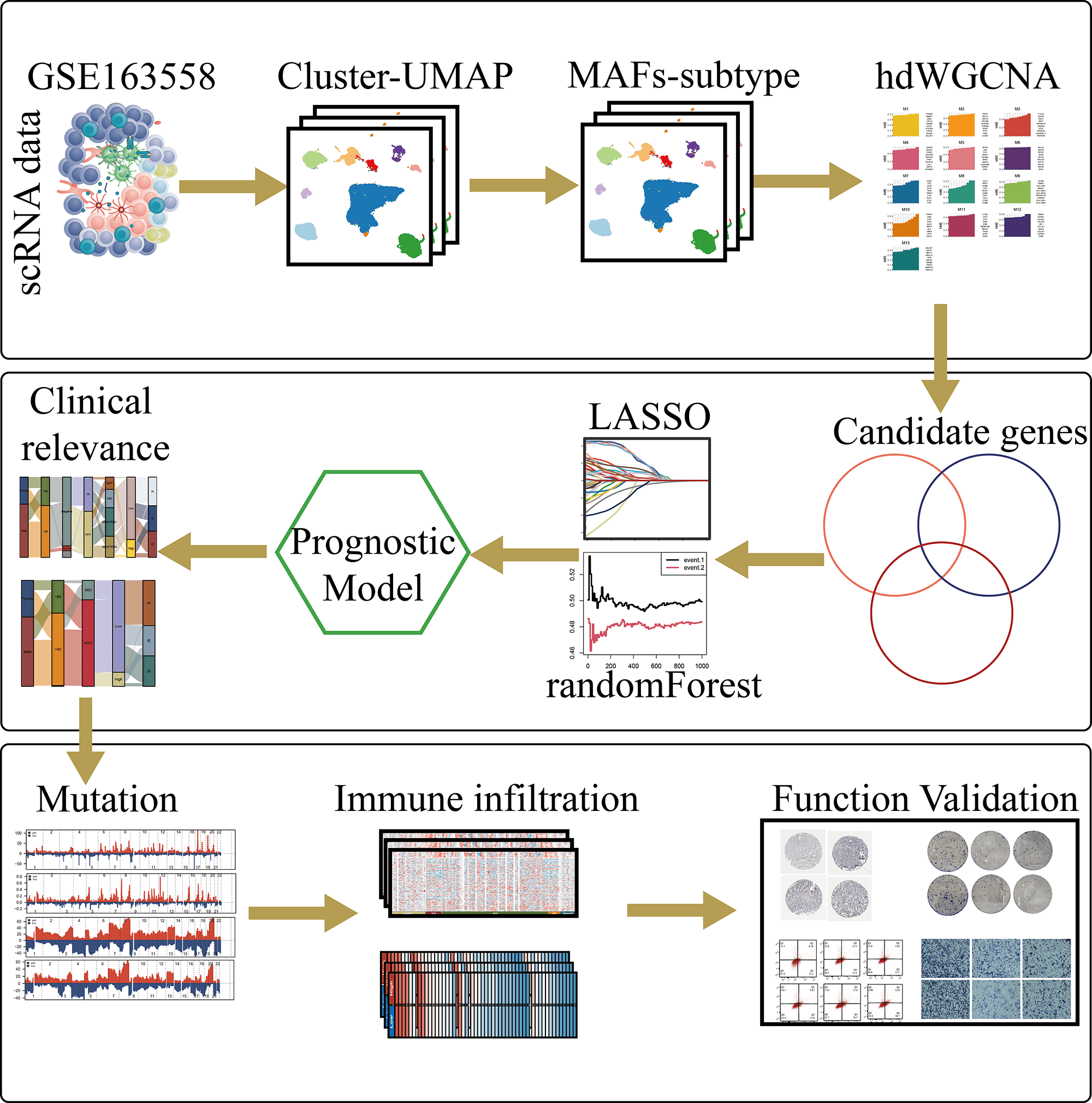
Abstract Background: Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) play critical roles in tumor progression and immunosuppression; however, their contribution to the functional classification and personalized treatment of gastric cancer remains poorly defined. This study aimed to identify effective therapeutic targets to facilitate individualized treatment strategies for patients with gastric cancer. Methods: Single-cell and bulk transcriptomic analyses were integrated to characterize gastric cancer fibroblasts. “Seurat”, “Slingshot”, and “CellChat” were used for dimensionality reduction, trajectory inference, and cell–cell communication analyses, respectively. Key metastasis-associated fibroblast modules were identified using High-dimensional weighted gene co-expression network analysis (hdWGCNA) to construct a prognostic model, which was further… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Aktham Mestareehi1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073745
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Liver Cancer: Novel Therapeutics and Biomarkers for HCC and CCA)
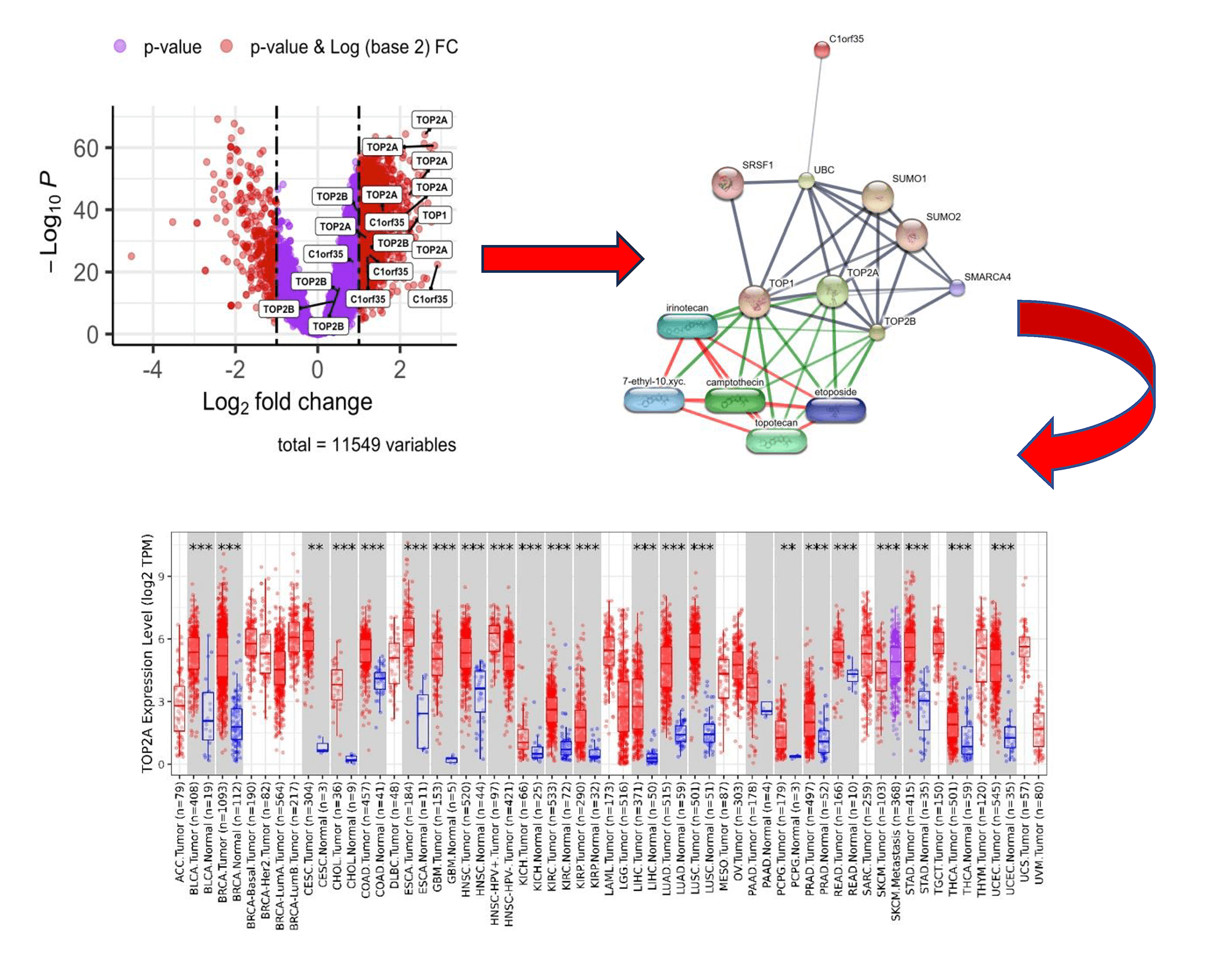
Abstract Objective: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, largely due to late diagnosis, molecular heterogeneity, and limited prognostic biomarkers. Aberrant protein phosphorylation plays a critical role in cancer progression by regulating DNA damage response, cell cycle control, and signaling pathways; however, the prognostic relevance of phosphorylation events in key DNA topology–related proteins remains incompletely understood. This study aimed to investigate the prognostic significance of phosphorylation of TOP1, TOP2A, TOP2B, and C1orf35 in HCC and to characterize their associated molecular features to identify potential diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers. Methods: Publicly available HCC… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shanbao Ke, Junya Yan, Xiao Feng, Baiyu Li*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071617
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning for Disease Subtyping, from Molecular to Clinical Features)
Abstract Objectives: Tumor recurrence is a major determinant of poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), yet its cellular and molecular basis remains incompletely understood. This study aimed to identify recurrence-associated genes at single-cell resolution and to develop a prognostic model for predicting survival outcomes and immunotherapy responsiveness in HCC. Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing data from 12 primary and 6 recurrent HCC samples were integrated and analyzed to identify genes characteristic of recurrence. After quality control, principal component analysis, and t-SNE-based clustering were used to identify highly variable genes for cell clustering and annotation. Based on macrophage… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Ye Ri Han1,*, Sang Bong Lee2,3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.075923
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Therapeutics)
Abstract Radiopharmaceuticals deliver diagnostic or therapeutic radionuclides to disease sites with molecular precision. Over the past five years, clinical adoption has accelerated, led by U.S. Food and Drug Administration approvals of 177Lu-DOTA-TATE and 177Lu-PSMA-617 and their complementary Positron Emission Tomography agents (68Ga-DOTA-TATE, 68Ga-PSMA-11), which have established radiotheranostics as a pillar of oncology care. The new generation of agents couples optimized radionuclides (β−, α, and Auger emitters) to antibodies, peptides, and small-molecule vectors that improve tumor uptake, residence time, and clearance profiles, thereby enhancing efficacy and safety. Beyond neuroendocrine tumors and prostate cancer, radiotheranostic strategies are advancing for diverse malignancies… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Maureen Veilleux1,2,#, Anh Nguyen3,#, Charles Cao4,#, Yihui Shi2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.072194
Abstract ADP-ribosyltransferases (ARTs) regulate key processes in cancer, including DNA repair, transcription, immune responses, and treatment resistance. The clostridial toxin-like ADP-ribosyltransferase (ARTC) family and the diphtheria toxin-like ADP-ribosyltransferase (ARTD) family play a crucial role in genomic stability by modification of proteins either with mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation (MARylation) or poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation (PARylation). These ARTs are promising therapeutic targets and could serve as biomarkers in cancer management. This review explores the roles of these enzymes and current knowledge on specific inhibitors. A literature search was conducted in PubMed and Google Scholar to identify studies published between 1992 and 2025 on ADP-ribosyltransferases… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Francesco Chiari1,*, Giovanni Motta2, Daria Maria Filippini3, Claudio Donadio Caporale1, Pierre Guarino1
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073086
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Challenges and Controversies in Laryngeal Cancer)
Abstract Objective: Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) of the larynx is an extremely rare malignancy, accounting for less than 1% of primary laryngeal tumors. The optimal role of adjuvant therapy, particularly radiotherapy (RT), remains unclear due to limited evidence. This systematic review aimed to evaluate oncologic outcomes and the impact of adjuvant treatment in patients with early- and advanced-stage laryngeal MEC. Methods: A systematic literature search was performed according to PRISMA 2020 guidelines in PubMed/Embase, Scopus, and Cochrane for studies published up to 31 July 2025. Results: Twenty-two studies, encompassing 55 patients, were included. Early-stage (T1–T2) patients (n =… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
So-Ye Jeon1,#, Zeeshan Ahmad Bhutta1,#, Hong Kyu Lee2, Kyung-Chul Choi1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071328
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Breast Cancer Biomarkers and Drug Targets Discoveries Towards a More Personalized Treatment Setting)
Abstract Objectives: Progesterone (P4) is believed to inhibit breast cancer growth, but its role in counteracting estrogen (E2)-driven progression remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the inhibitory effect of P4 on E2-induced cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in Estrogen receptor (ER)+/progesterone receptor (PR)+ breast cancer cells by examining its regulatory role in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Methods: ER and PR-positive MCF-7 clonal variant (MCF-7 CV) breast cancer cells were treated with E2 and co-treated with various concentrations of P4. The effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were assessed. The expression of key EMT markers… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Mohsina Patwekar1,2, Faheem Patwekar3, Zulhisyam Abdul Kari1,4,*, Muhammad Rajaei Ahmad Mohd Zain5,*, Arifullah Mohammed6, Rohit Sharma7,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073601
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: The Evolving Landscape of Cancer Treatment: Molecular Insights and Immunotherapeutic Breakthroughs)
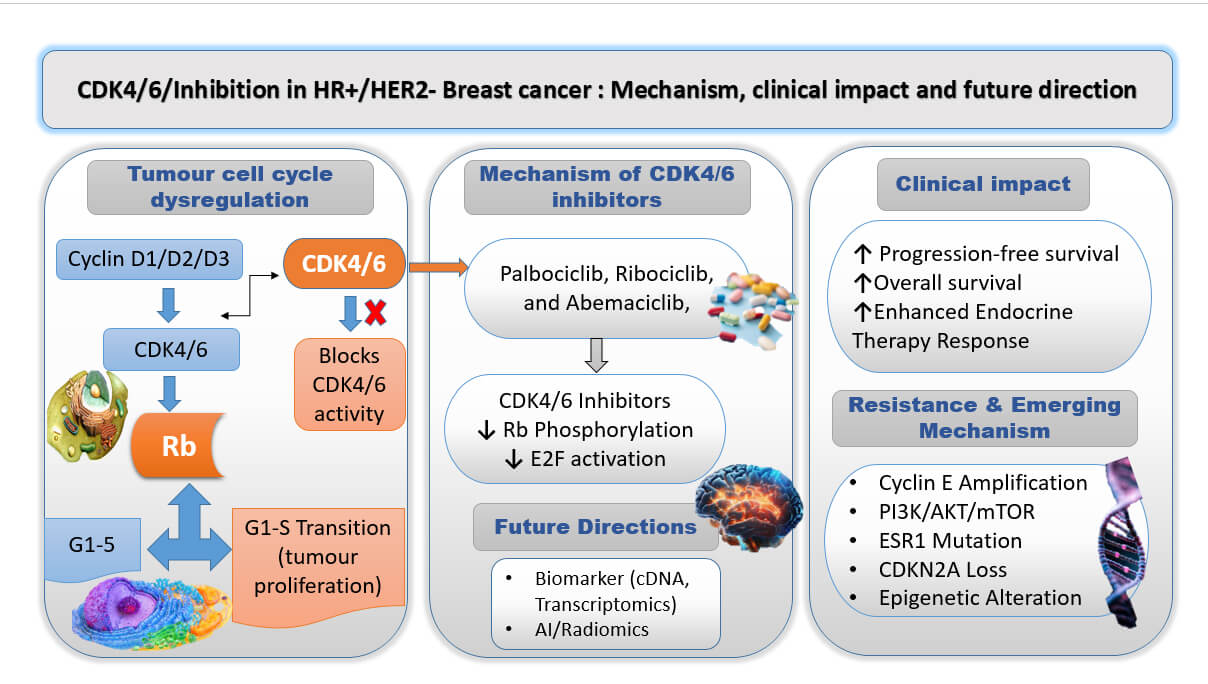
Abstract Breast cancer remains the primary cause of cancer-related mortality for women globally; therefore, further breakthroughs in treatment approaches are crucial. Palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib are among the Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors that have become an innovative family of targeted therapy for hormone receptor-positive, Human Epidermal Growth factor receptor 2 (HR+/HER2−) breast cancer. These inhibitors work by preventing the action of CDK4/6, which are crucial in the regulation of the cell cycle. Leading cancer cells to cell cycle arrest and undergo apoptosis. When these inhibitors are used with endocrine medicines like letrozole and… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ya-Ling Yang1,#, Ying-Hsien Huang2,#, Hung-Yu Lin3,4,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.075284
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy)
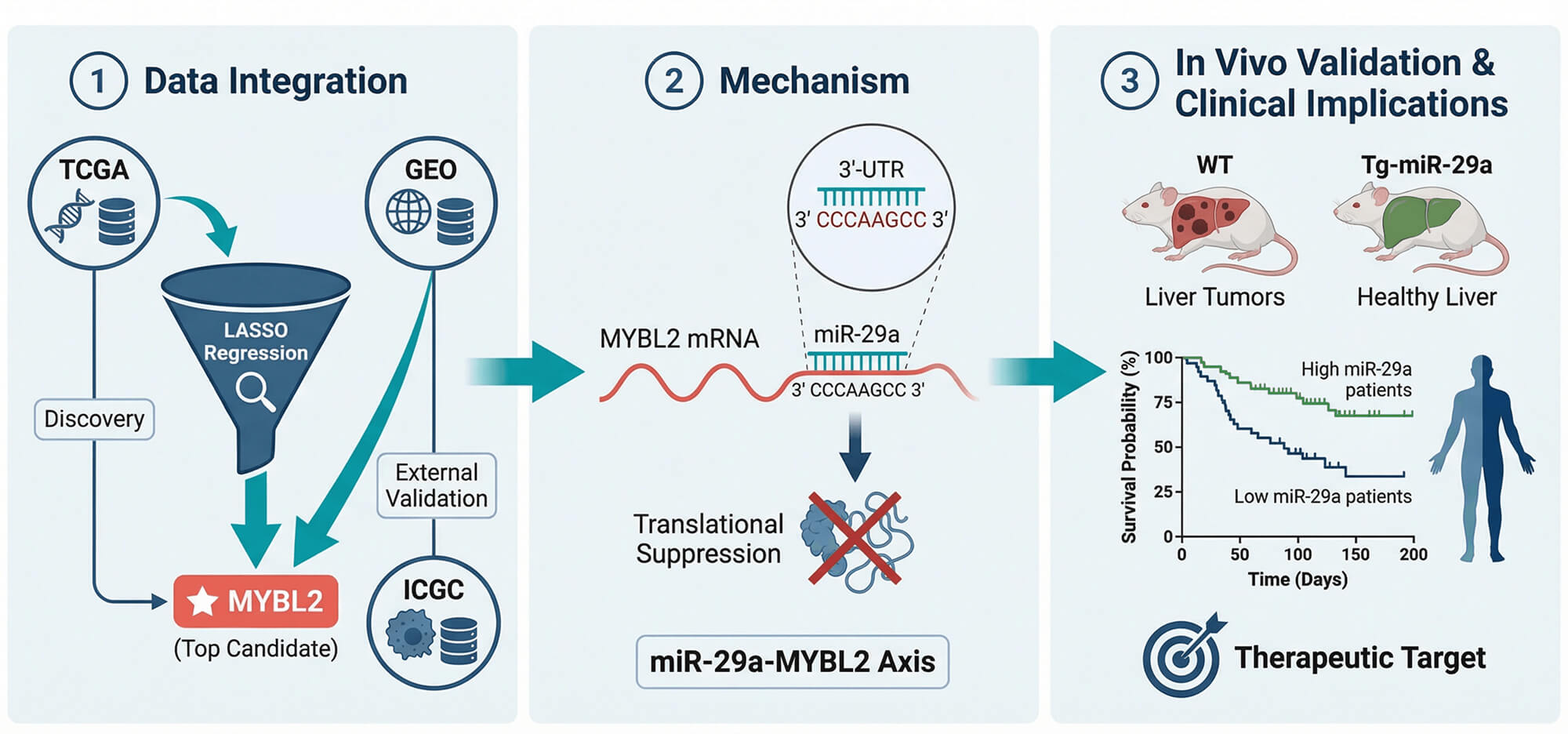
Abstract Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presents with poor treatment outcomes, creating an urgent need for novel biomarkers to improve diagnosis, prognosis, and precision medicine. While the MYB family of oncogenes is implicated in cancer, the role and regulatory mechanisms of its member, particularly MYB proto-oncogene like 2 (MYBL2), remain underexplored in HCC. Therefore, this study aimed to systematically validate the clinical significance of MYBL2, elucidate its functional role in tumor progression and drug sensitivity, and identify its upstream regulatory mechanisms using an integrative machine learning and experimental framework. Methods: We applied an integrative pipeline combining LASSO-based… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jiaxi Li#, Deepak Iyer#, Siming Sui, Zheng Huang, Ryan Wai-Yan Sin, Abraham Tak-Ka Man, Wai-Lun Law, Chi-Chung Foo*, Lui Ng*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074981
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy)
Abstract Objectives: Piwi-associated RNAs are small non-coding RNAs implicated in cancer, yet few have been characterized in colorectal cancer (CRC). This study aimed to identify a CRC-related piRNA and investigate its clinical relevance, biological function, and biomarker potential. Methods: Candidates were identified by reanalysis of small-RNA sequencing. piR-37524 was quantified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in colorectal cancer tissues, matched adjacent non-tumor tissues, colorectal adenomas, liver metastases, and serum samples from patients and healthy controls. Clinicopathological correlations and diagnostic performance were evaluated. Functional assays included 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) proliferation, colony formation, and wound-healing migration… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Munro Matthew James1,*, López Vásquez Clara Elena1,2, Wickremesekera Agadha3, Chan Alex Ho Chuen1, Gray Clint Lee1,4,5,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074958
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Drug Targets in Oncology: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Innovations)
Abstract Objective: Meningioma is the most common primary brain tumour. Invasion into the brain is a diagnostic feature of grade II meningiomas and is associated with recurrence and poor prognosis. Mebendazole is a microtubule inhibitor typically prescribed as an anthelmintic. However, it has the potential to be repurposed for cancer treatment. Here, we aimed to assess the ability of mebendazole to inhibit meningioma cell invasion. Methods: Primary patient-derived meningioma cell lines were cultured as 3D spheroids and embedded in an extracellular matrix-like matrix as an in vitro model of invasion. Mebendazole-treated and untreated control spheroids were analysed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Crystal J. Byrd1, Monasia Evans1, Woojung Kim2, Quintera Knight3, Geou-Yarh Liou1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073532
Abstract Objective: The progression of prostate cancer cells to metastasis is supported by their tumor microenvironment. Within this microenvironment, infiltrating immune cells, such as B cells, can be either anti-tumorigenic or pro-tumorigenic. Our preliminary data showed that a higher density of the infiltrating B cells was found near prostate cancer cells in human cancer tissues, as compared to the benign prostate tissue regions, thus suggesting that infiltrating B cells would promote the progression of prostate cancer cells. In this study, we aim to investigate the role of infiltrating B cells in enhancing the migratory ability of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
VIEWPOINT
Paolo Maione1,*, Valentina Palma1,2, Cesare Gridelli1
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.072992
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Therapeutics)
Abstract After about 20 years of exciting improvements in treatment efficacy outcomes of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), also combined with a progressively better safety profile, from chemotherapy to new generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) (osimertinib, alectinib, brigatinib), the recent MARIPOSA and CROWN trials have changed this trend. For the first time in the history of EGFR and ALK treatments, we must face the issue of being a step behind in terms of toxicity profile. The combination of amivantamab plus lazertinib in EGFR mutant NSCLC, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Masanobu Tsubaki*, Taira Matsuo, Rie Komori
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.075217
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Targeting Therapy for Anticancer Treatment)
Abstract Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a hematopoietic malignancy originating from hematopoietic stem cells. It is characterized by the Philadelphia chromosome, which arises from a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22. The breakpoint cluster region::Abelson murine leukemia 1 (BCR::ABL1) fusion protein produced from this chromosome is the main factor responsible for disease onset. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have led to significant advances in CML treatment and contributed to improved patient survival rates. Nonetheless, a substantial number of patients develop resistance to TKIs, which remains a major challenge in CML therapy. Currently, two mechanisms are considered More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Eshita Dhar1,2, Muhammad Ashad Kabir3, Divyabharathy Ramesh Nadar4, Li-Jen Kuo5, Jitendra Jonnagaddala6,7, Yaoru Huang1, Mohy Uddin8,*, Shabbir Syed-Abdul1,2,9,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074385
Abstract Objectives: Decisions regarding CT after nCCRT for locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) are challenging due to limited evidence guiding treatment. This study aimed to (i) evaluate the predictive performance of machine learning (ML) models in patients treated with neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy (nCCRT) alone vs. those receiving nCCRT plus chemotherapy (CT), (ii) identify features associated with treatment improvement, and (iii) derive ML-based thresholds for treatment response. Methods: This retrospective study included 409 patients with LARC treated at three affiliated hospitals of Taipei Medical University. Patients were categorised into two groups: nCCRT alone followed by surgery (n =… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Sophiette G. Hong1,2, George F. Murphy2, Christine G. Lian2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073894
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Skin Cancer Management: From Molecular Targets to Innovative Treatments)
Abstract Malignant melanoma (MM) is a highly aggressive skin cancer known for its rapid progression, potential for metastasis, and resistance to treatment. Despite advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapy, the prognosis for metastatic melanoma remains unfavorable. Recent research has shed light on the significance of epigenetic modifications in the pathogenesis of melanoma, revealing critical mechanisms of melanoma development and progression. Epigenetic modifications, including DNA and RNA modifications, histone modifications, chromatin remodeling, and non-coding RNA regulation, disrupt normal gene expression without modifying the DNA sequence, leading to cellular transformation, invasion, immune evasion, and therapeutic resistance. The reversible… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Vincenzo Montanarella1, Marcelo Guerrero2,3, David Filho2,3, Júlia German-Cortés1, Giacomoluciano Vitelli1, Magalí Sureda1, Carlos Pavón Regaña1, Roser Ferrer1,4, Simó Schwartz1,4, Esteban Durán-Lara2,3, Fernanda Andrade1,5,*, Diana Rafael1,6,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074061
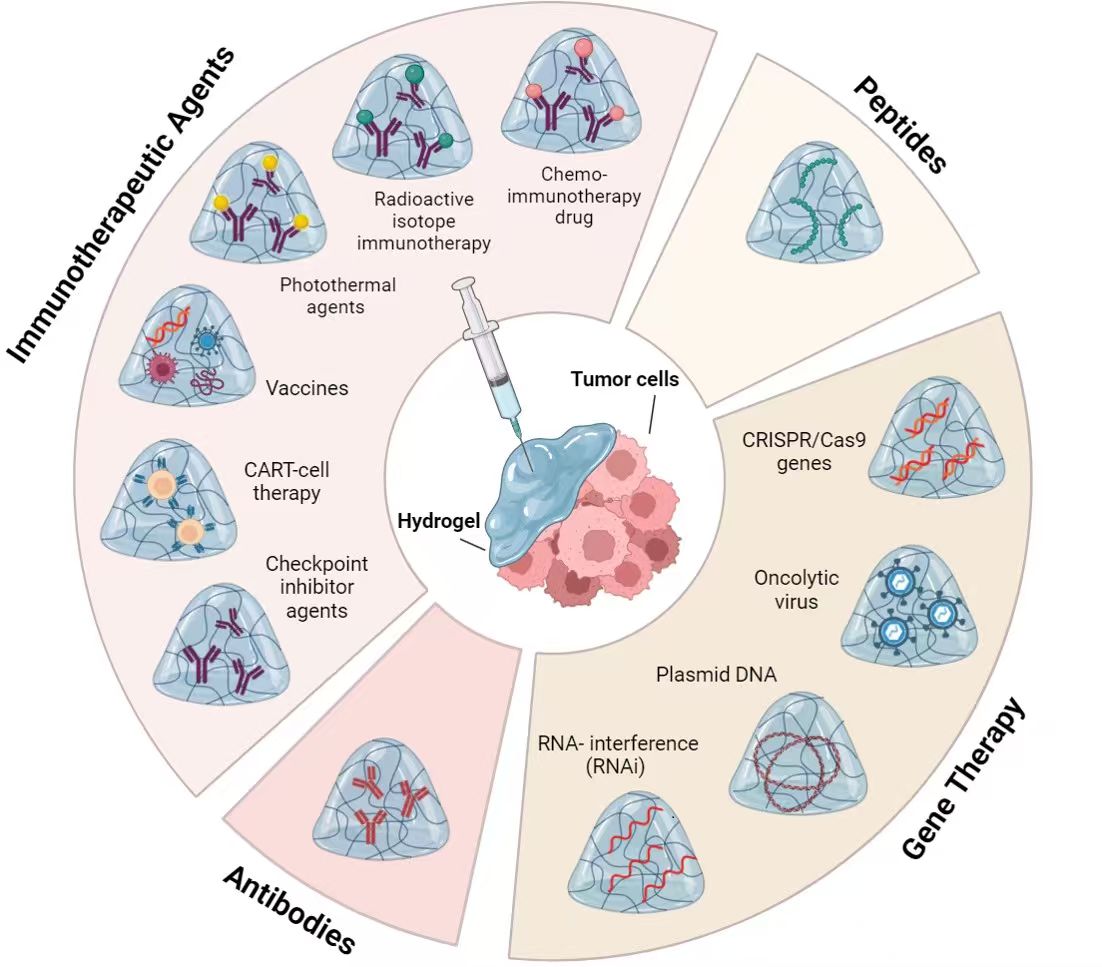
Abstract Despite remarkable advances in nanomedicine, localized delivery of advanced cancer therapeutics remains underexploited. Advanced therapies based on biopharmaceuticals, immunotherapy, or gene therapy have revolutionized oncology. Yet, their systemic administration is often associated with limitations such as poor site-specific accumulation, instability, and systemic toxicity. Hydrogels/macrogels offer the ability to encapsulate, protect, and release biomolecules in situ with sustained and stimulus-responsive profiles, addressing key translational gaps. This review provides a focused synthesis of the last five years of hydrogel-based research for cancer therapy, with emphasis on peptides, antibodies, immunotherapeutic agents, and gene delivery systems. We discuss design principles,… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zheng Qin1,2,#, Yueyao Zhang3,#, Dongze Liu4,#, Xiaokang Zheng5, Kaibin Wang1,2, Xiao Zhu1,2, Yuanhao Zhang1,2, Kexin Xu1,2, Changying Li1,2, Lijuan Kang1,2, Lili Wang1,2, Haitao Wang1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073455
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Biomarkers and Treatment Strategies in Solid Tumor Diagnosis, Progression, and Prognosis (Ⅱ))
Abstract Objective: Prostate cancer is the second most common fatal cancer in men. Identifying new biological therapeutic targets is crucial to effectively improve the prognosis of prostate cancer patients. Ovarian tumor family deubiquitinase 4 (OTUD4) is a member of the ovarian tumor-associated protease domain (OTUDs) family. Although previous studies have shown that the expression and function of OTUD4 vary across different tumors, its role in prostate cancer remains unknown. The aim of this study is to explore new therapeutic targets and diagnostic markers for prostate cancer and investigate their mechanisms of action. Methods: Cell culture, Cell… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shuwen Sun1,2,3,4,#, Jingcheng Zhang1,2,3,#, Zongtai Zheng5,#, Yajuan Hao1,3, Tianyuan Xu1,2,3, Ji Liu1,3, Liang Sun2, Aimin Wang2, Yadong Guo1,3, Shiyu Mao1,3, Xu Zhang6, Yunfei Xu1,3,*, Yifan Chen1,2,3,*, Yang Yan1,2,3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072373
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment: Emerging Insights into Cancer Progression and Therapeutics)
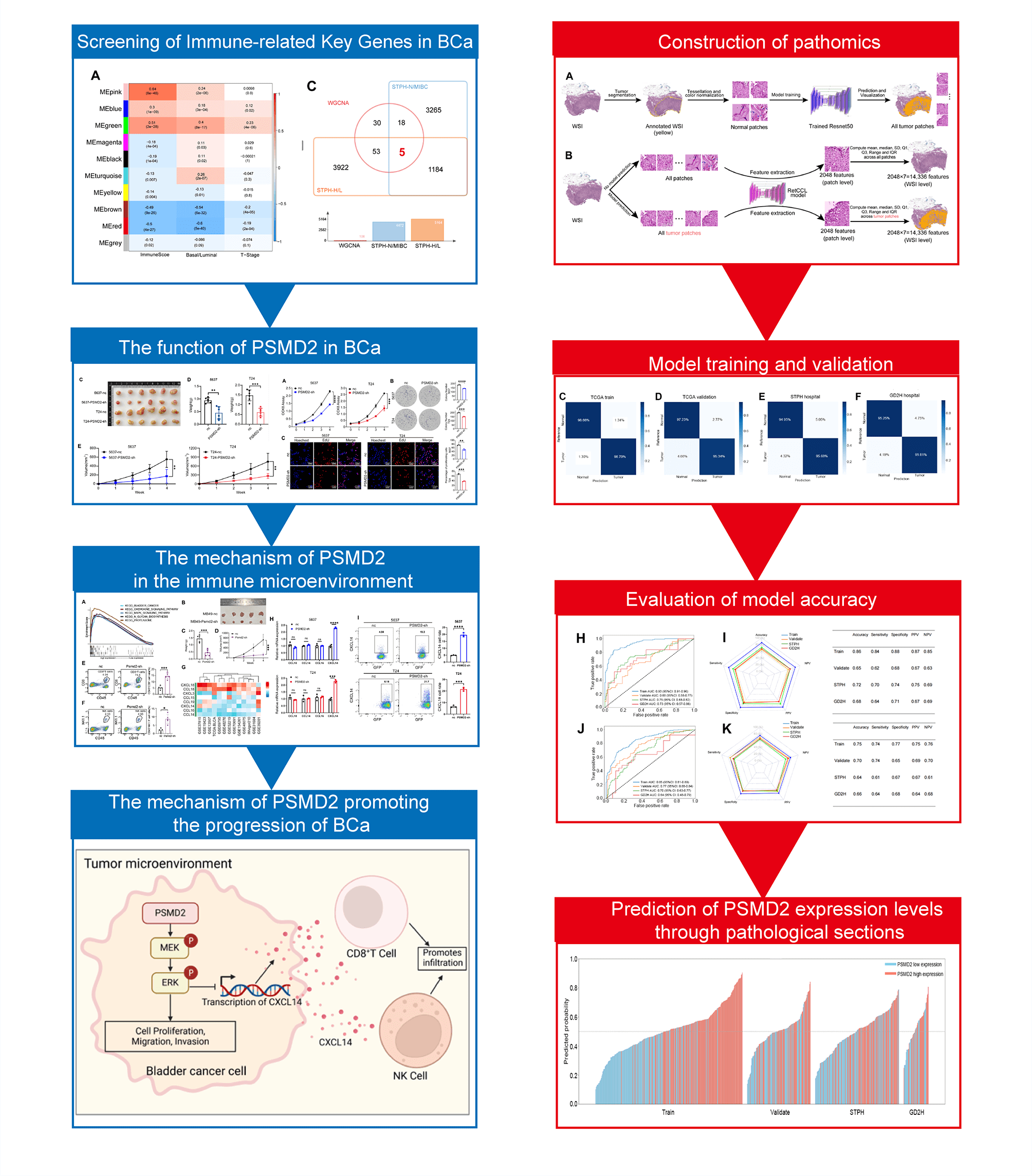
Abstract Objectives: Bladder cancer (BCa) progression is closely linked to the immune microenvironment. However, the key molecules that regulate this microenvironment and their specific mechanisms remain poorly understood. This study aims to identify a key molecule and elucidate its mechanisms, providing a theoretical basis for identifying novel therapeutic targets. Methods: Immune microenvironment-related genes in BCa were identified using The Cancer Genome Atlas and Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital datasets. Proteasome 26S subunit non-ATPase 2 (PSMD2) expression was validated via quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), Western blot (WB) analysis, and immunofluorescence (IF). In vitro and in vivo experiments confirmed the… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Candela Cives-Losada1,2, Cristiana Soldani2, Michela Anna Polidoro2, Barbara Franceschini2, Ana Lleo3,4, Marcello Di Martino1,5, Matteo Donadon1,5,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.074093
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment: Emerging Insights into Cancer Progression and Therapeutics)
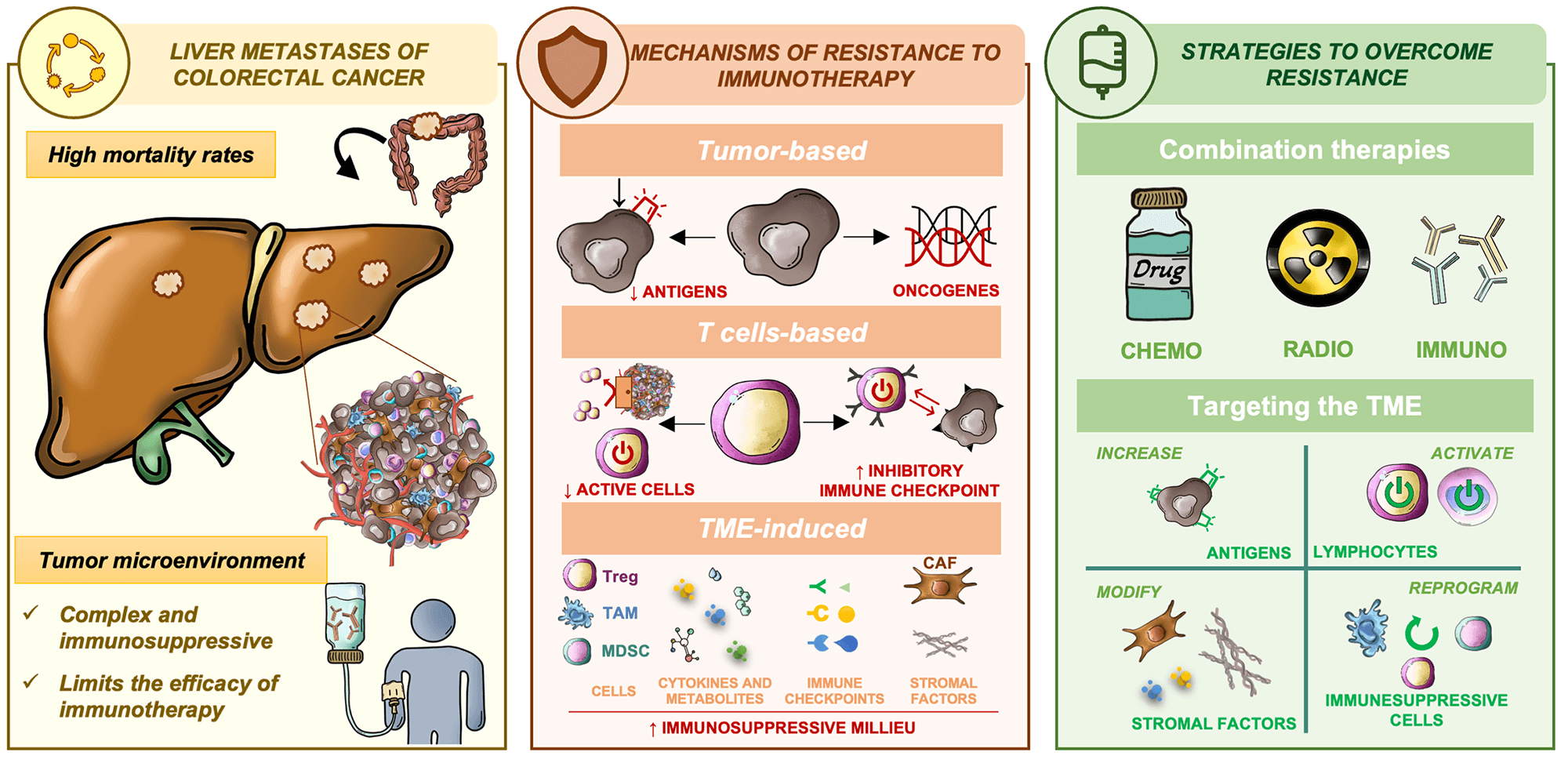
Abstract Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second deadliest cancer worldwide, being the presence of metastasis, mainly in the liver, a major contributor to high mortality rates in affected patients. The tumor microenvironment (TME)—comprised of interacting endothelial, stromal, and immune cells—plays a critical role in creating a supportive niche for tumor cell colonization and immune evasion and, thus, the establishment of metastases. The liver’s intrinsic nature further facilitates the development of immune tolerance, mediated by regulatory T cells, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and soluble factors such as anti-inflammatory cytokines, which together dampen antitumor immune responses. This immunosuppressive milieu More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Donatella Coradduzza1,#, Anna La Salvia2,#, Giuseppe Fanciulli3, Maria Rosaria De Miglio3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073045
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy)
Abstract Background: An increasing number of studies have shown that ferroptosis is related to the initiation and development of small cell lung cancer (SCLC). The systematic review aimed to summarize the characteristics of ferroptosis from its pathogenetic role to translational therapeutic implications in SCLC. Methods: This systematic review, registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251090058), followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines. Comprehensive research of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science was performed for studies published between January 2010 and July 2025 investigating ferroptosis mechanisms, genetic or pharmacological modulation, or molecular profiling in SCLC. Two reviewers independently performed data extraction and quality… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Saad Alobid1,#, Hussam Albassam1,#, Tebyan O. Mirgany2, Faris Almutairi1, Mohammed Mufadhe Alanazi1, Ahmed H. Bakheit2, Hanadi H. Asiri2, Eram Eltahir3, Gamaleldin I. Harisa3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073371
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Pharmacological Bases of Anticancer Drug Therapies in Precision Oncology)
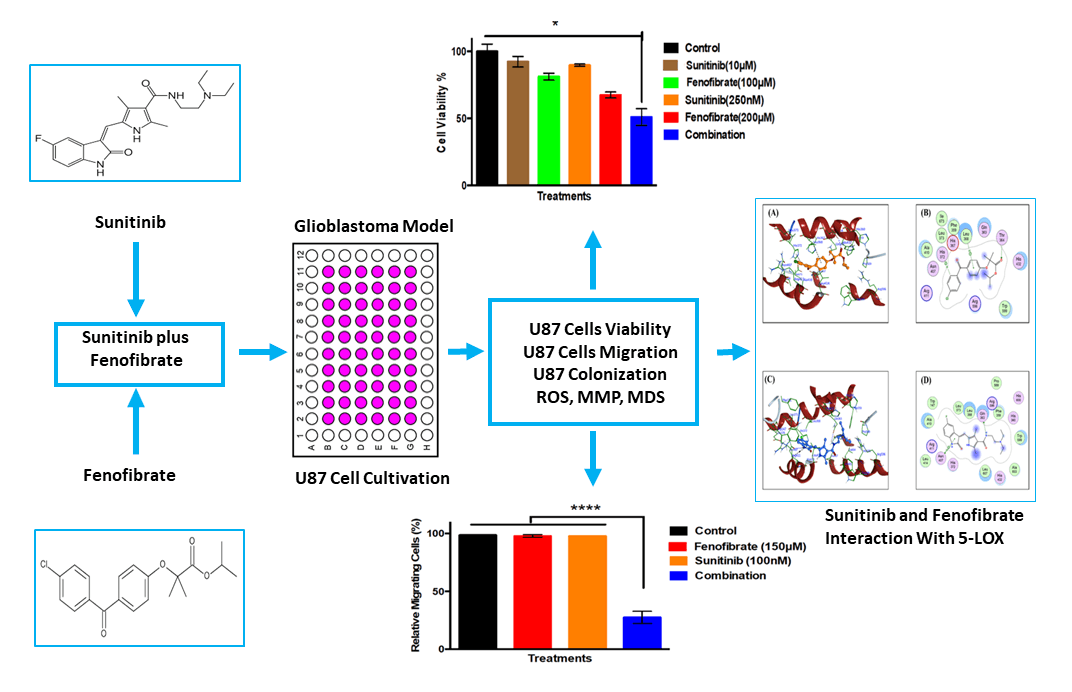
Abstract Objective: Glioblastoma (GB) therapy is challenged by tumor heterogeneity and multidrug resistance (MDR), highlighting the need for effective therapies. This study aimed to explore the combined anticancer effects of Sunitinib (SNB) and Fenofibrate (FEN) on U87 cells. Methods: U87 cells were exposed to SNB, FEN, or their combination for 24 h, followed by evaluations of cell viability, migration, and clonogenic survival using MTT, scratch, and colony formation assays. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) were quantified via the 2′, 7′-dichlorofluorescein assay, while mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) was assessed using JC-1 red/green fluorescence. Molecular docking was performed to… More >
Graphic Abstract