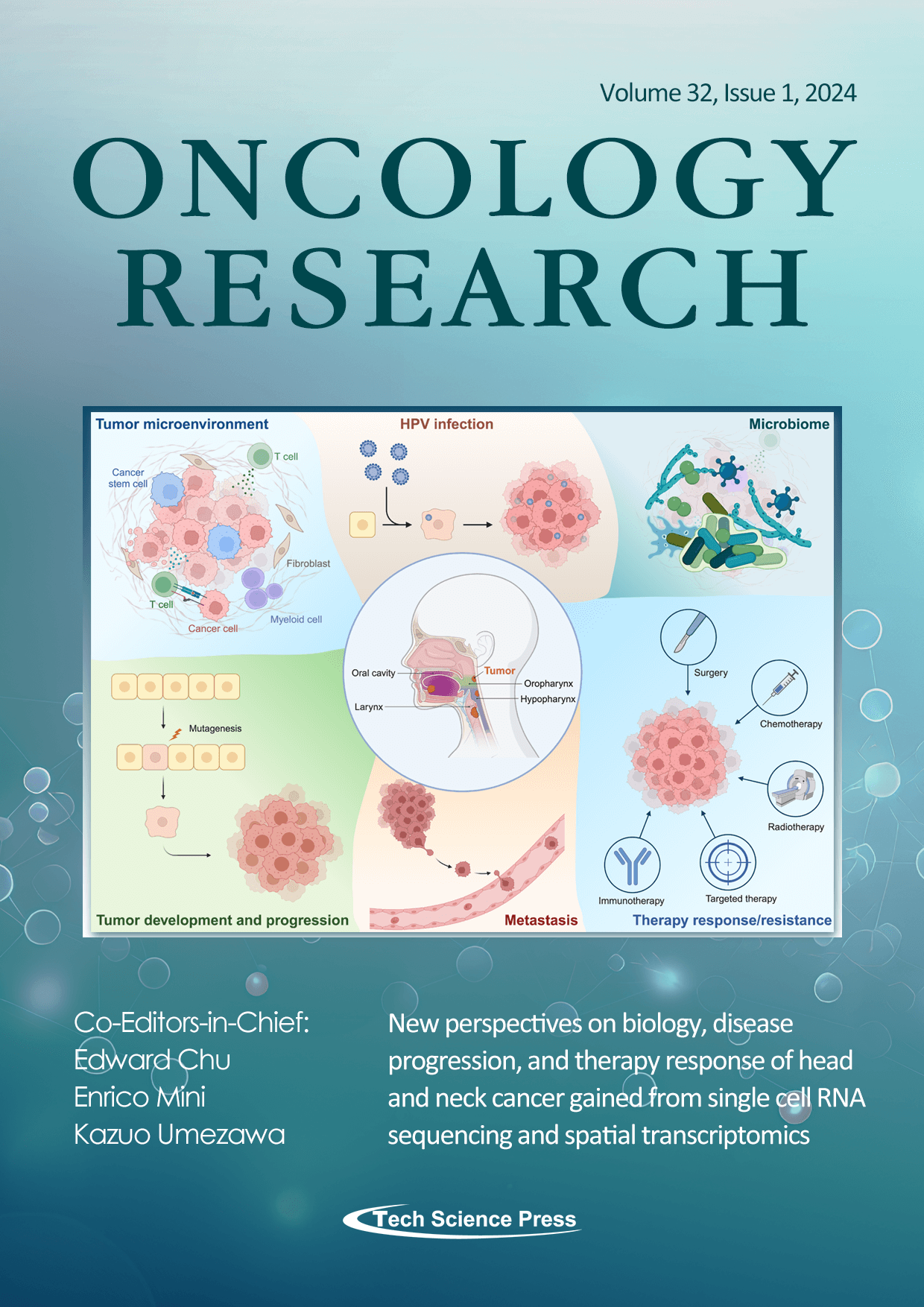
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the 7th-most frequent cancer worldwide, with alcohol, tobacco, and HPV infection as key risk factors. Progress regarding therapeutic options is limited, and outcome remains unsatisfactory. In the past two decades, omics methods have greatly advanced our understanding of the biology of malignant diseases, including HNSCC. Most recently, methodological advances have established single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics as novel and game-changing tools. A review in the current issue highlights the contributions of these methods to deciphering the complex nature of the emergence, progression, intra-tumoral heterogeneity and cell-cell communication, and therapeutic responses of HNSCC.
View this paper